Bitlocker Encryption: The Guard of Your Data [All You Need to Know]
As remote work becomes increasingly popular, more devices are accessing confidential information from off-site locations. This poses a significant risk, as devices can be lost, stolen, or compromised, allowing an adversary to access sensitive information stored on them.
BitLocker is a built-in encryption feature in Windows that secures entire drives against data breaches by encrypting the entire drive. By enabling disk encryption, businesses can protect their data from unauthorized access, making it a crucial tool for securing volumes of sensitive information.

What is Bitlocker Encryption?
BitLocker is a Windows full-BitLocker is a full-disk encryption (FDE) solution that protects Windows data at rest by encrypting the entire hard drive. It's available in business-focused Windows editions, with a limited version in Home. Without BitLocker, data stored on a computer is unencrypted and accessible to attackers.
BitLocker encrypts data using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), with encryption and decryption keys stored in the trusted platform module (TPM), a computer chip that secures data with hardware-based protections. When the user authenticates, the disk encryption keys are unlocked, allowing Windows to decrypt the drive's files.
Windows 11/10/8/7 requires a BitLocker recovery key when it detects a possible unauthorized attempt to access data, using a unique 48-digit numerical password. This key is safely backed up during the encryption process, but if forgotten, you'll need to recover the BitLocker recovery key.
Importance and Practical Application of Bitlocker Encryption
Data security is best achieved by encryption, which makes modern algorithms unbreakable, and only accessible to the key holder. Full disk encryption is a must, protecting against theft or negligence that gives an attacker access to a business device.
Enterprises, schools, and public institutions should utilize BitLocker to safeguard their Windows computers, particularly those handling sensitive data. This is especially crucial for institutions that handle Protected Health Information (PHI), as HIPAA mandates the use of a data encryption solution for any device storing such information. By implementing BitLocker, these organizations can ensure the confidentiality and integrity of their data, meeting the necessary security standards.
- If your PC were lost or stolen, you'd wince at the replacement cost. Encrypting the device ensures that only you or someone with the recovery key may access its contents. This means that even if someone finds your device, they won't be able to access your personal files, keeping your sensitive information safe.
- Encrypting devices is a way for organizations to protect their private data from employees, allowing only those with the encryption key to access and decrypt the information.
If you need to format a hard drive or USB that's been encrypted with Windows BitLocker, it can be a bit more complicated than usual. However, there are steps you can take to format the drive or system, and resources available to guide you through the process.
System Requirements of Bitlocker Encryption
BitLocker uses a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) to store its recovery key, which is a smartcard-like gadget on the motherboard of many modern computers.
Enabling BitLocker requires creating a PIN to enter at startup, and it generates a recovery key in case the password is forgotten. After generating the recovery key, the computer is restarted, and encryption begins. To use BitLocker, the device must meet specific criteria.
Operating systems that are supported:
- Windows 11: Pro, Enterprise, and Education versions.
- Windows 10: Education, Professional, or Business.
- Windows 8: Professional or Enterprise version.
- Windows 7: Enterprise or Ultimate version.
For Windows 7, you must install Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 1.2 or later, have it turned on and enabled.
Additional requirements:
- You need to be logged in as an admin.
- To print the recovery key, you need to be able to use a printer.
To resize the BitLocker partition or clone an encrypted BitLocker drive without disabling protection, you can use Partition BitLocker Drive.
How do I Manage BitLocker Encryption?
BitLocker is mostly a set-After encrypting your disk, it requires no upkeep, allowing you to manage your computer using built-in OS utilities.
Step 1. To manage BitLocker, right-click any drive icon in File Explorer and select "Manage BitLocker".
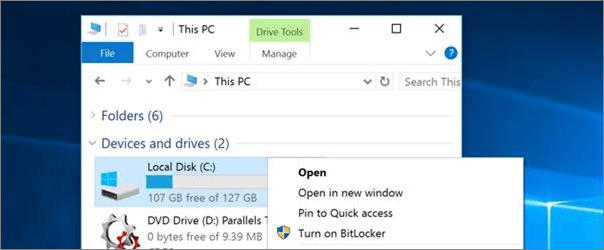
Step 2. This page allows you to turn BitLocker on or off, and if it's already enabled for the system drive, you can either suspend the encryption process or back up your recovery key.
Step 3. You can encrypt removable and internal secondary disks, with Windows Home settings having an on/off button.
Step 4. Select "Update & Recovery" > "Device Encryption in Windows 10".
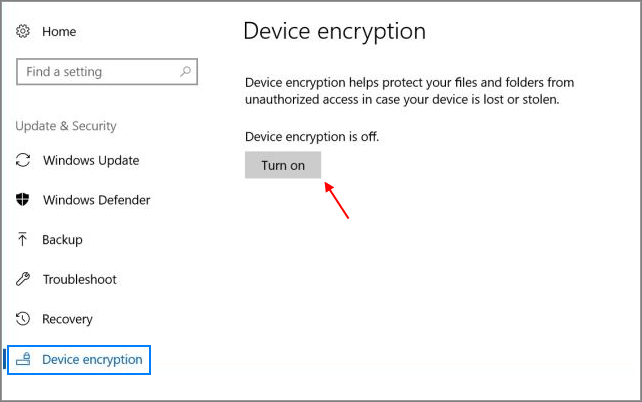
- Notice:
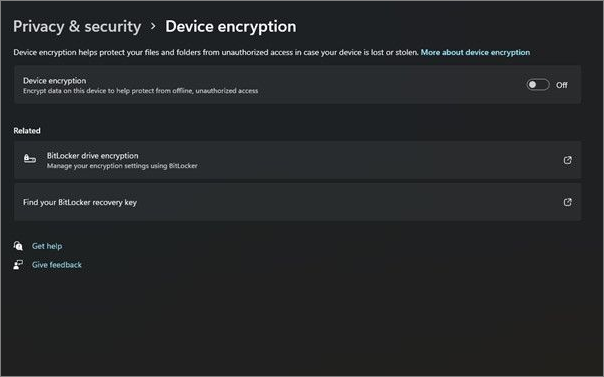
- If you have Windows 11, go to Settings > Privacy & Security > Device Encryption to enable it.
Step 5. To administer or repair BitLocker, you can use the `manage-bde` or `repair-bde` command in the command line. These tools allow you to perform various tasks such as unlocking a BitLocker-protected drive, enabling or disabling BitLocker, or repairing a BitLocker-protected drive.
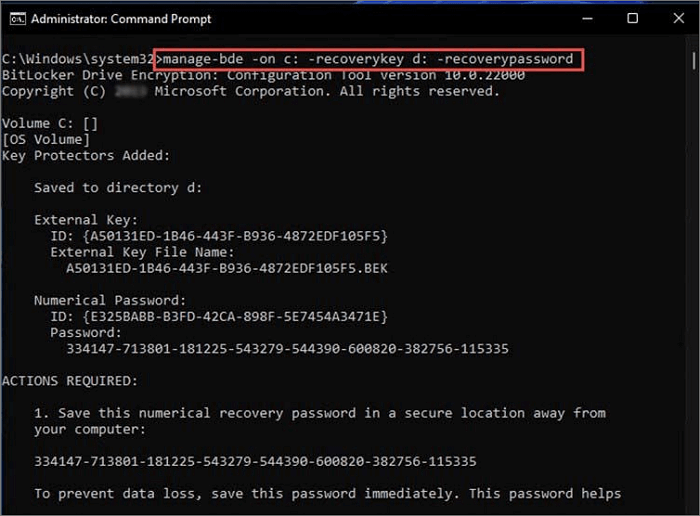
Step 6. The command "manage-bde -status" displays the encryption state of all available disks on Windows 10, 11, and Home, providing information on the encryption status of each disk.
Since some of you may think it is not necessary when you work at home and store data on your personal computer. If you want to disable BitLocker, check this out:
How to Disable BitLocker Encryption in Windows 10
This guide will show you how to disable BitLocker encryption in Windows 10 and how to disable BitLocker altogether.

Conclusion
BitLocker is a Windows feature that encrypts devices, protecting data from unauthorized access. To use it, enable BitLocker on your device, create a recovery key, and back up the key to a secure location. The encryption process may take some time, but it's a worthwhile investment in protecting your data.
Bitlocker Encryption FAQs
Other questions about BitLocker Encryption you may be interested in:
1. Who should be using Bitlocker?
BitLocker should be used by large multinationals, schools, government facilities, and other institutions with sensitive data that require high security.
2. How can I obtain a Bitlocker Encryption?
To access BitLocker, type "Manage BitLocker" in the taskbar search box, then go to Settings > Privacy & security > Device encryption, and click on "Encrypt BitLocker disk". Note: BitLocker is only available on devices that support it.
3. Where can I find my BitLocker recovery key?
Microsoft accounts can save a key (search BitLocker Recovery Keys) and if another user set up or activated BitLocker, the recovery key may be in their Microsoft account.
Related Articles
- What Is Windows Hyper V? [Detailed Description]
- [3 Ways] How to Uninstall Apps on Windows 11
- Backup vs. Replication: Which One to Choose
- How to Boot from USB on Different OSs [Step-by-Step Guide]