What Is Cloud Computing? [Everything You Need to Know]
Cloud-Cloud-based storage allows electronic IoT devices to save files remotely in a database, rather than relying on proprietary hard drives or local storage. This enables access to the necessary data and software applications for the device to function.
Cloud computing is a popular choice for individuals and businesses due to its cost savings, increased productivity, speed and efficiency, performance, and security benefits.

Cloud computing is a model of delivering computing services over the internet, where resources such as storage, servers, and applications are provided as a service to users on-demand. Its working principle involves storing and processing data remotely, allowing users to access their applications and files from anywhere, at any time, without the need for local infrastructure. The benefits of cloud computing include scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and increased collaboration, making it a popular choice for individuals, businesses, and organizations. Some examples of cloud computing include online storage services like Google Drive and Dropbox, software as a service (SaaS) like Microsoft Office 365, and infrastructure as a service (Iaas) like Amazon Web Services.
What Is Cloud Computing and How Does it Work?
Cloud computing is a model of delivering computing services over the internet, where resources such as servers, storage, databases, software, and applications are provided to users on-demand. The working principle of cloud computing involves a multi-tenant architecture, where multiple users share the same physical resources, but each user has their own virtualized environment. This allows for scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Definition
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to a wide range of computer services, including servers, storage, databases, and software, over the internet. This allows for faster innovation, more flexible resources, and greater scalability, while only paying for the services that are actually used, reducing operational costs and enhancing infrastructure management.
History
The term "cloud computing" was first used in a 1996 Compaq document, but the concept of distributed computing, associated with the word "cloud", was earlier discussed in the 1960s by J.C.R. Licklider.
In 1969, Bob Taylor and Larry Roberts created ARPANET, a project that revolutionized computing and eventually became the precursor to the modern Internet.
Working Principle
As an executive, it's a significant responsibility to ensure that your staff have the necessary hardware and software to perform their tasks. This involves not only purchasing computers for everyone, but also acquiring software or licensing for the software to provide them with the required capabilities. When hiring new employees, you must either purchase additional software or verify that your current software license permits a different user, which can be a stressful and costly endeavor. This stress can lead to sleepless nights, worrying about the financial burden of keeping up with the company's software needs.
Cloud computing, a revolutionary concept, is on the horizon for CEOs like you. Instead of installing an entire software package on each machine, you can load a single application that grants employees access to a web-based service hosting all necessary programs for their jobs. This includes email, word processing, and advanced data analysis software, all running on remote equipment owned by a different corporation. This game-changing technology has the potential to transform the entire computer industry.
Cloud computing has significantly shifted the workload, allowing applications to run remotely without overloading local PCs. Instead, the cloud's network of computers handles the workload, reducing users' needs for hardware and software. All that's required is the cloud's interface software, which can be as simple as a web browser, and the user's computer can run the applications, with the cloud's network handling the rest.
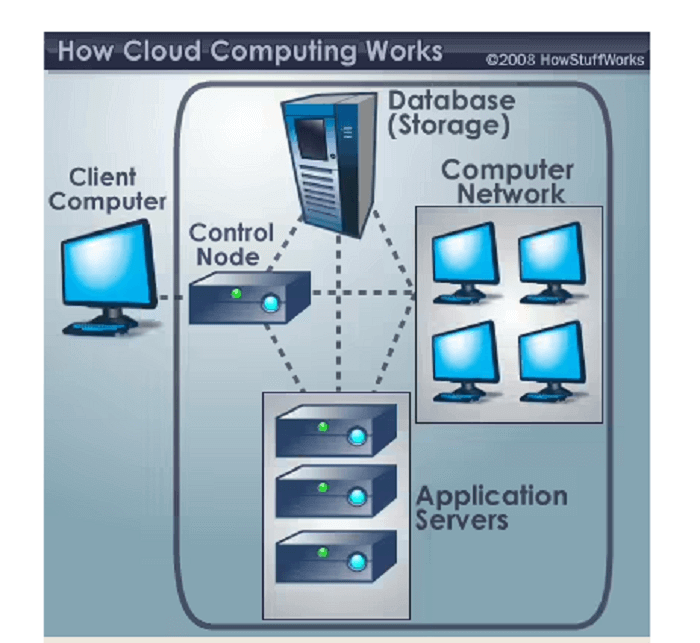
You may have already used cloud computing without realizing it. Services like Hotmail, Yahoo! Mail, and Gmail allow you to access your email remotely through a web browser, rather than running email software on your computer. This means that the software and storage for your email account are located on the service's computer servers, rather than on your own device, which is a fundamental concept of cloud computing.
Characteristics and Benefits of Cloud Computing
Here are the characteristics and benefits of cloud computing in one paragraph:
Provisioning using self-service: End users can now provision computing resources, such as server time and network storage, without needing IT administrators to do so, allowing for instant access to computing resources for any workload.
Elasticity: Companies can now scale up and down as needed, without having to invest heavily in local infrastructure that may become obsolete.
Pay as you go: Users only pay for their actual usage of compute resources, ensuring cost-effectiveness and no unnecessary expenses.
Workload adaptability: Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) implement redundant resources to ensure resilient storage and maintain users' critical workloads, often across multiple global regions.
So let's move on to the benefits of cloud computing.
Benefits with examples:
Companies from all industries can benefit from using cloud-based software, which can be accessed via a browser or native apps on any device, allowing users to easily transfer files and settings between devices.
Cloud computing allows users to access their email and files from any computer, and store files using services like Dropbox and Google Drive.
Users can back up their music, files, and images using cloud computing services, ensuring they always have access to them even if their hard drive crashes.
Large firms can save money by using the cloud, as it replaces the need for costly information management infrastructure, server farms, and IT staff, allowing workers to do jobs online.
Using cloud infrastructure, people can free up storage space on their computers or laptops. This shift also allows software businesses to sell their products online, making it easier for customers to upgrade quickly. For example, Adobe customers can access its Creative Cloud through an online subscription, enabling them to easily download updates and fixes for their programs.
Types of Cloud Computing Services
Cloud computing services are primarily offered through Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Serverless, and Software as a Service (SaaS), which are often referred to as the "stack" of cloud computing, each building on the other. Understanding the differences between these layers can help businesses achieve their goals more effectively.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a type of cloud computing that provides on-demand access to fundamental computing, storage, and networking resources, billed on a pay-as-you-go basis. It is one of the four main cloud service categories, alongside serverless, platform as a service, and software as a service (SaaS).
Moving your organization's infrastructure to an IaaS service can reduce maintenance costs, save money on hardware, and provide real-time business insights. IaaS solutions offer flexibility to adjust IT resource allocation in response to demand, allowing for quick provisioning of new apps and increased underlying infrastructure reliability.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) allows you to use cloud computing without the expense and hassle of owning and managing actual servers and data center equipment. You only pay for what you use, as each resource is provided as a separate service component, and you manage your own software, while the provider handles the infrastructure.
Platform as a service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides a complete cloud development and deployment environment, offering the tools needed to create complex applications. With PaaS, users pay only for the resources they use, accessing them through a secure internet connection from a cloud service provider. This pay-as-you-go model allows for efficient resource allocation and cost savings.
PaaS (Platform as a Service) includes infrastructure, middleware, development tools, business intelligence services, and database management systems, supporting all phases of a web application's lifecycle from development to deployment and updating.
Using a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) can save you money and time by handling the underlying software licenses, middleware, infrastructure, and other resources, while you focus on designing and managing your applications and services. This way, you don't have to worry about purchasing and managing these resources yourself, and can instead let the cloud service provider handle the details.
Serverless computing
Serverless computing allows developers to create apps quickly by automatically provisioning, scaling, and managing the infrastructure needed to run the code.
Serverless computing is a strategy where infrastructure provisioning and management tasks are handled behind the scenes, allowing developers to focus on business logic and add value to the organization. This approach enables teams to work more productively, launch products faster, and utilize resources more efficiently, all while maintaining an innovation-focused mindset.
Software as a service (SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) enables users to access and use cloud-based applications over the Internet, including email, calendaring, and office tools like Microsoft Office 365.
A cloud service provider that offers SaaS (Software as a Service) offers a complete software solution that can be paid for as it's used. Users access the rented app through the internet, typically using a web browser, and the service provider's data center houses all the supporting infrastructure, middleware, app software, and app data. The service provider, who also oversees the hardware and software, guarantees the app's accessibility, security, and privacy under the applicable service agreement.
Cloud Computing Examples and Use Cases
Cloud computing allows access to shared networks, servers, storage, and software via the internet.
The cloud-based system offers data processing on a server held by a third party or a privately owned cloud, resulting in maximum speed and dependability. Its primary advantages are ease of installation, low maintenance costs, and scalability, allowing it to adapt to meet your demands.
The use of cloud computing, specifically IaaS and SaaS, has experienced a significant surge since 2009 and has become widespread. In fact, you're likely reading this on a cloud-based platform right now, and it's likely that many other online services are also cloud-based.
Here are a few real-Cloud computing is crucial to our daily lives, and its importance can be seen in various instances. For example, when you upload a photo to social media, it gets stored on a remote server, which is a cloud computing service. Similarly, when you stream a movie or music online, it's being delivered from a cloud-based infrastructure. Even online banking and shopping rely on cloud computing to process transactions securely.
- Cloud computing applications are widely used by both organizations and individuals. This includes streaming platforms for audio or video, where media files are stored remotely, as well as data storage platforms like Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive, and Box.
- As businesses grow and generate more data, SaaS technology has emerged to store, organize, and maintain this information. Solutions like CRM and marketing automation tools have streamlined operations for lines of business, enabling them to run more effectively. SaaS, or "software on demand," is hosted centrally in the cloud and accessible from anywhere, at any time.
- Building and maintaining infrastructure for data centers can be costly, with expenses including hardware, space, electricity, and overhead costs that can easily total millions of dollars. As a result, many companies are opting to store their data in service provider-run data centers, allowing them to avoid the financial burden of investing in capital projects and instead enjoy the simplicity of cloud access to their data.
- ISPs have taken on the role of cloud carriers, connecting customers with cloud providers and transporting their requests for cloud services, thanks to the bandwidth and tools they provide to link the two.
Role of Cloud Computing:
- Cloud solution architect
- Cloud Developer
- Cloud DevOps Engineer
- Cloud Data Engineer
- Cloud Operations Engineer
Sum Up
Cloud computing is a model that distributes computing services over the Internet, also known as the cloud. This setup provides web-based services that host programs, allowing large organizations to operate smoothly and efficiently.
Related Articles
- 0xC1900101 Error in Windows Update, Cannot Install Windows 11 [FIXED]
- Top 10 Most Basic SQL Commands To Know
- What Is A DLL File and Where Are DLL Files Located in Windows 10
- NetBIOS: What It is, How It Works and How to Use It