Copy vs. Xcopy vs. Robocopy | What Is the Difference Between Them
Transferring files in Windows can be achieved using various command line tools, including XCopy, Robocopy, and others. However, even experienced Windows users may struggle to determine the best tool for their needs and understand how to use them effectively.
Copy, Xcopy, and Robocopy are three commands used for copying files and folders, each with its own unique features and applications. The copy command is the most basic, simply copying files from one location to another. Xcopy is an extension of copy, allowing for the copying of entire directories and files, including subdirectories. Robocopy, on the other hand, is a more advanced command that provides additional features such as file verification, compression, and logging, making it a popular choice for bulk file transfers and backups. A comparison table highlights the differences between the three commands, making it easy to choose the right one for a specific task.
What Is Copy
The copy command is a frequently used command by multiple users daily. Its self-explanatory name indicates that it copies data from one location to another, making it a versatile tool for various tasks.
Definition
The "copy" command is a basic command used to copy files from one location to another. It is available in various operating systems and can also be used to combine multiple files into one file. The destination directory is typically the current working directory.
The copy command can be used in both text and binary modes. In text mode, it stops at the EOF character, whereas in binary mode, it accumulates files completely, ignoring EOF characters.
Copying files to different devices is a straightforward process. For instance, using the "copy file con" command outputs the file to the screen console, while "copy con file" command considers the text typed into the console and saves it in "FILE".
Availability of Copy Command
It is available in text mode and binary mode in the following ways:
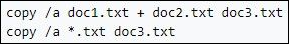
Text mode: The command for copying multiple text files in text mode is `copy /a doc1.txt + doc2.txt doc3.txt` and `copy /a *.txt doc3.txt`.
Binary mode: The command to combine two images into one in binary mode is "copy /b image1.jpg + image2.jpg image3.jpg".
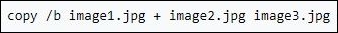
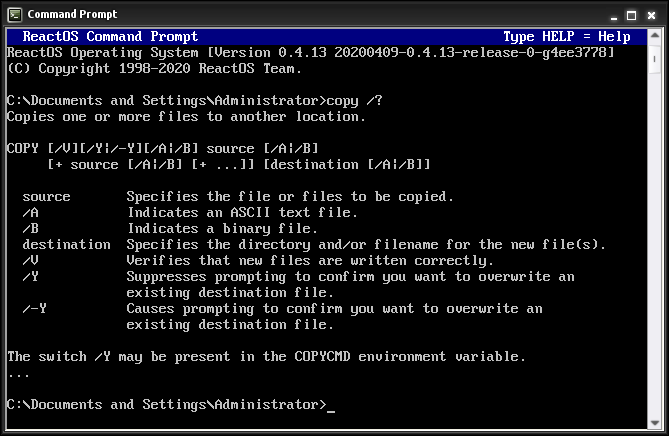
Copy command options
Some of the standard copy command options are:
- 86-DOS is an operating system that was developed by Tim Paterson and his team at Seattle Computer Products (SCP) in 1981. It was a single-user, single-task operating system that ran on 8086 microprocessors.
- The program has been available since version 1 in IBM PC DOS/ MS-DOS.
- It is known as "cp" in the Unix command.
- In CP/M, the copy command is "PIP".
- In Stratus OpenVOS, it is familiar with the "copy_file" command.
What Is Xcopy
The Xcopy command is used to create files with the specific archive attribute set, regardless of their location in the source file. It is commonly used in operating systems such as ReactDOS, FreeDOS, Microsoft Windows, IBM OS/2, MS-DOS, and IBM PC DOS.
Definition
The command "xcopy" is used to copy multiple files or entire directory trees from one directory to another, and is also used for copying files across different networks. It is an extended version of the "copy" command, offering more functionality, and was first introduced in DOS 3.2, with its use extending to various operating systems including IBM PC DOS, MS-DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows, FreeDOS, and ReactDOS.
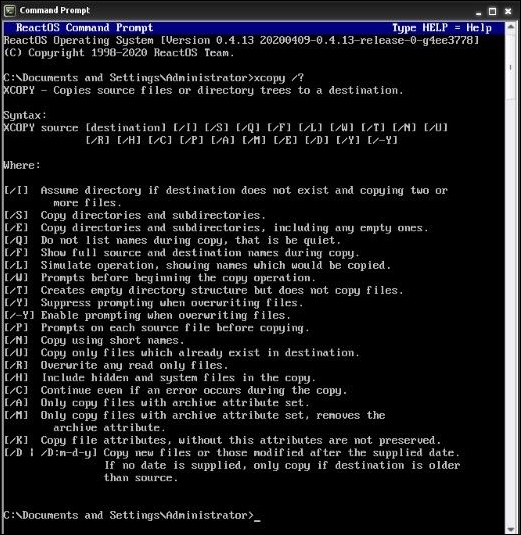
Availability of Xcopy command
Xcopy command is available in:
- Xcopy is a command-line utility in Windows 10, as well as in the Desktop operating system and Microsoft Windows Server.
- The DR DOS 6.0 and Datalight ROM-DOS have the "XCOPY" command, which is also available in the FreeDOS version, licensed under GPL.
- "Xcopy" has a Wine compatible version, licensed under the LGPL.
Xcopy command options
Some of the Xcopy command options are:
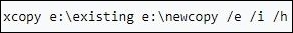
The command creates a new directory by copying the existing directory contents. It includes different subdirectories or files in the hidden attributes and empty directories, and is used as Xcopy e:\existing e:\newcopy /e /i /h.
When using Xcopy to copy files, if the pathnames contain spaces, you can use the following command to copy files from "D:\Documents and Settings\MY.USERNAME\My Documents\" to "E:\MYBACKUP\My Documents\": Xcopy "D:\Documents and Settings\MY.USERNAME\My Documents\*" "E:\MYBACKUP\My Documents\" /D/E/C/Y. This command will copy all files from the specified source to the destination, while also including files that have been modified, created, copied, or are younger than the specified date.

The command `xcopy *.* z:\Netmirror /E /V /C /F /H /Y /Z` can be used to copy entire data in the mapped network drive in a network restartable mode, ignoring possible errors and logging output and errors to `out.txt` and `err.txt` respectively.

The command "cmd /c echo F | Xcopy "c:\directory 1\myfile" "c:\directory 2\myfile"" copies a single file from one directory to another without prompting for confirmation. It uses the Xcopy command to perform the file copy operation. The "cmd /c echo F" part is used to pipe a single character "F" to the Xcopy command, which tells it to overwrite the file if it already exists without prompting.

What Is Robocopy
Robocopy, also known as "Robust File Copy", is a command-line directory and file copy utility for Microsoft Windows. It is a powerful tool that allows users to copy files and directories with a high degree of flexibility and control. Robocopy is particularly useful for large-scale file transfers and for situations where the source and destination file systems have different structures or permissions.
Definition
Robocopy, a command-line utility, replaces the Xcopy command with advanced options. It was first released in the Windows NT 4.0 Resource Kit and is now included in Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista. Robocopy offers capabilities beyond the standard Windows copy and Xcopy commands.
Robocopy can handle network interruptions and resume copying, making it a reliable option. It also allows you to skip NTFS junction points, which can cause infinite loops and copying failures. Additionally, Robocopy preserves original timestamps and copies file data or attributes precisely, making it a valuable tool for file transfers.
Robocopy examples
Some of the Robocopy examples are:
1. The command "Robocopy" copies the contents of directory "A" to directory "B", both located on drive "C", and includes all subdirectories and files with the "/E" option.

2. To copy all files and directories from C:\A to C:\B, use the Robocopy command: `Robocopy C:\A C:\B /COPYALL /E /R:0 /DCOPY:T`. This command copies all file attributes (COPYALL), ensures the destination directory is created if it doesn't exist (/E), retries the copy operation 0 times (/R:0) in case of errors, and copies the directory timestamps (/DCOPY:T).

3. To mirror files from location A to location B, destroying any files in B that are not present in A, the command "Robocopy C:\A \\backupserver\B /MIR /Z" can be used. This command transfers all files from A to B, and then deletes any files in B that are not found in A. The "/MIR" option specifies a mirror copy, and the "/Z" option enables the use of compression to speed up the transfer process.

Copy vs. Xcopy vs. Robocopy| What Are the Differences
The main difference between copy, Xcopy, and Robocopy lies in their features, with copy being the most basic, Xcopy adding compression and error checking, and Robocopy providing advanced features like mirroring, checksum verification, and multi-threading.
| Name | External or Internal | Command type | Data type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copy | It is part of the internal command. | It is the basic command. | It can copy one or more files. |
| Xcopy | It is an external command. | It is the extended copy command. | It can copy groups of files from one directory to another. |
| Robocopy | It is an external command. | It is the advanced Xcopy command. | It can copy multiple files across a network. |
Bonus Tip: Copy/Backup Files with Robocopy Alternative
You can use the `cp` command to copy files, but it occupies large space. A better method is to use backup commands like `tar` or `rsync` to save space.
Backing up files can be more efficient than direct copying because it involves creating an image of the files, which can be compressed to take up less space and transfer faster. This allows users to choose between a "copy" method, which simply duplicates the files, and a "transfer" method, which compresses and images the files for faster and more space-efficient backup.
For a simple and convenient backup method, consider using software like Qiling Backup, which offers flexible backup options, including file backup, disk backup, system backup, and external HDD backup. You can also back up your files to cloud services like Google Drive or Dropbox, or use Windows File History. Additionally, Qiling Backup allows you to back up to NAS, Qiling cloud, and more.
If an important file is accidentally deleted and there is no backup, you can use data recovery software to restore the deleted file.
Final Verdict
The "copy", "Xcopy", and "Robocopy" commands are essential for navigating command line directories. For beginners and professionals alike, these commands are easy to understand. The "copy" command is used for copying files or data, while "Xcopy" is used to copy multiple files or complete directory trees from one directory to another. Robocopy, on the other hand, replaces Xcopy with various options, making it a more versatile and powerful tool.
The fundamental differences between copy, Xcopy, and Robocopy command lines lie in their unique features, making it easy for professionals to choose the best command based on their immediate needs.
Related Articles
- Windows Command Line Cheat Sheet (Online Table and PDF)
- An Overall View of Rosetta 2 Mac [Free Download]
- What Is Transcode and Why Is It Important for Video Streaming [Everything You Need]
- What Is Dynamic Routing and What are the Dynamic Routing Protocols