What Is A LUN? Logical Unit Number Explained
Logical Unit Number or LUN is a paramount element of storage devices. But what exactly is it?
LUN (Logical Unit Number) is a unique identifier within a storage device that recognizes logical units, used in the SCSI protocol to differentiate between various storage units on a single device.
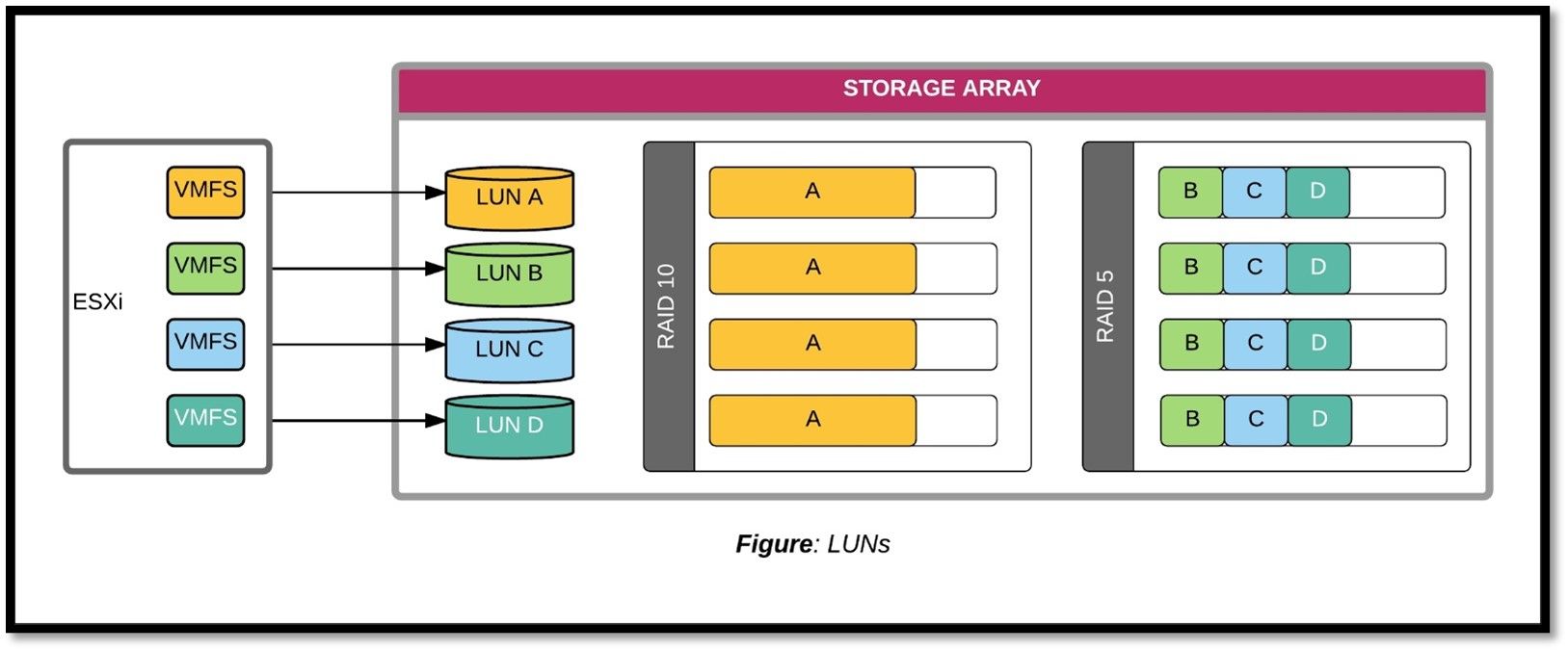
The Logical Unit Number (LUN) is a unique identifier assigned to a storage device, such as a hard drive or solid-state drive, to differentiate it from other devices on the same bus. It works by allowing the operating system to communicate with specific storage devices, enabling tasks like data transfer and management. There are different types of LUNs, including Basic LUN, Composite LUN, and Virtual LUN, each serving distinct purposes in storage management and utilization.
What Is A Logical Unit Number?
The SCSI protocol requires a series of numbers to address each logical unit in a storage device, which determines the area upon which data is written. To facilitate this, storage in use employs SAN protocols to encapsulate the SCSI.
A number is used to address a logical unit in use, and SCSI employs them by their numbers, coining the term LUN or logical unit number. This numbered device can be used in various scenarios, including the obsolete tape drive.
A Logical Unit Number (LUN) is a unique identifier used to refer to a logical disk on a Storage Area Network (SAN). It's a number that allows systems to address and access a specific disk or storage device. In essence, a LUN is a virtual address that points to a physical disk or storage volume, making it possible to manage and organize storage resources in a more efficient and scalable way.
The storage device is a collection of various units, each with a unique address, known as a logical unit number, which is used to identify and access the unit.
How Does Logical Unit Number Works?
In a storage device like a hard disk drive, data is written across multiple physical disks. Each physical disk is given a unique serial number, which is used to identify it as a separate unit. This is similar to how a Logical Unit Number (LUN) works in storage systems, where each physical disk is assigned a unique identifier to distinguish it from others. This allows data to be written and retrieved from specific disks, ensuring data integrity and security.
When a user formats a disk array or creates a partition, SCSI targets a specific serial number and separates the storage into individual volumes. To identify each volume, SCSI configures a logical unit and assigns a unique number, known as a logical unit number (LUN).
When a simple task occurs on a PC, such as opening the drive, the computer sends a Command Descriptor Block (CDB) to a physical storage unit, which is provided by the SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) protocol. This allows the computer to interact with the storage unit and perform operations like opening the drive.
Then, a 3-The bit logical number unit identifies the specific target for writing, allowing the device to start operation and continue writing in that designated storage area.
When one logical storage unit is filled or used up, SCSI sends a command to a new physical storage unit, which then becomes the primary unit until it is also depleted.
Types of Logical Unit Number
Here are the four main types of LUNs:
Mirrored LUN
Mirrored LUN is a fault-The LUN type is tolerant and makes two data copies on separate physical drives, allowing for better control of redundancy and backup. This type is also employed by programs that identify duplicate or redundant files.
Concatenated LUN
Concatenated LUNs condense multiple logical units into a single unit, often used in RAID groups, especially with two LUNs combined together.
Striped LUN
Striped LUN uses a single Logical Unit Number to write data on multiple physical drives, allowing for improved performance and enhanced durability of the drives. This is achieved by distributing the Input/Output operations across different disks, which helps to prevent any single drive from becoming a bottleneck.
Striped LUN with parity
Striped LUN with parity is essentially the same as striped LUN, but with an added layer of protection. It distributes parity information across three or more physical drives, ensuring that if one drive fails or becomes unresponsive, the remaining drives can recover the lost data. This redundancy provides an additional layer of reliability and data integrity.
Logical Unit Number Use Cases
The primary purpose of a Logical Unit Number (LUN) is to identify specific storage devices, and this function can vary depending on the type of LUN. For example, when creating a partition on a drive, a simple LUN is used to identify that particular portion of the physical drive.
LUNs are used to virtualize physical storage sectors, allowing multiple physical LUNs to be mapped to a single virtual one, and are also used to identify and manage logical storage units.
Conclusion
The Logical Unit Number (LUN) is a crucial identification of physical drives that plays a key role in usual computing operations. It's essential to understand LUNs to comprehend the storage process, as they serve as a vital component in identifying physical drives and facilitating storage operations.
Related Articles
- MTS File : What Is It and How To Open It [Updated 2022]
- What is AMD CPU fTPM? Everything You Need to Know
- [2022 HOT] Plist File on Windows: What Is It and How To Open It?
- How to Access Startup Security Utility Mac? [Latest Tips]