Raid 6 vs Raid 10: Which is better in Speed and Security?
RAID (redundant array of independent disks) is a common technique to improve the performance and reliability of data storage devices. RAID is primarily used on HDDs, although previous development has seen its introduction in SSDs. Different levels of RAID processes exist, including RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10.
This article will compare RAID 6 vs. RAID 10 based on speed, security, and disk utilization. We'll also recommend a backup software (Qiling Backup) that you can use to protect your RAID data and uptime.
Brief Overview of RAID 6 vs. RAID 10
Before determining which is better between RAID 6 and RAID 10, it's essential to discuss what both of them stand for.
RAID 6
RAID 6 is considered the safest and most secure of the RAID processes. It uses a block-level basis to perform data stripping. It then spreads the data dual parity blocks on the array disks. The term "dual data parity" in RAID 6 implies that it stores the parity checksum of the data on two disks

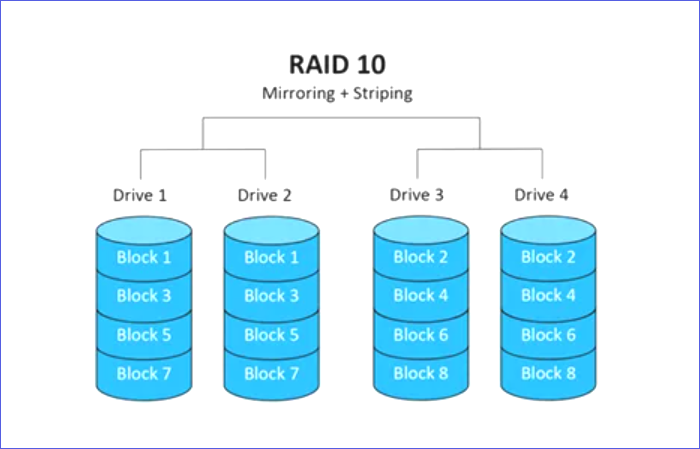
RAID 10
RAID 10 combines RAID 1 (for data mirroring ) and RAID 0 (for data stripping). In RAID 10, data mirroring aims to enhance data security on all secondary drives. The data on one drive is copied (mirrored) on another, so you can still access it even when the first drive fails.
Comparison Between RAID 6 vs. RAID 10 In Terms of Speed, Security, and Disk Utilization
RAID 6 and RAID 10 vary in terms of their performance speeds, data safety, and disk utilization. Therefore, before choosing the best among the two, you must learn how each behaves based on these specific aspects. Below is a detailed comparison of RAID 6 vs. RAID 10.
RAID 6 vs. RAID 10: Speed
Regarding performance, RAID 10 boosts the data transfer rate across drives because of the "data stripping" feature. This feature allows all drives to have improved performance when accessing data in different storage devices. RAID 10, therefore, makes data more accessible.
On the other hand, RAID 6 has less impact on the rate of data transfer across drives. Unlike RAID 10, it doesn't have the "data stripping" feature. However, RAID 6 employs the double parity feature, which guarantees the accessibility of data even when two drives fail.
RAID 6 vs. RAID 10: Security
RAID 6 has an efficient security feature for your data. It can allow you to access data even when the primary drive fails. In addition, the data parity feature guarantees the security of your data and files since RAID 6 can resist up to two disk failures. This implies you'll still have a backup solution for your data even when two disks fail.
RAID 10 also has an improved security feature (data mirroring) for your data provided by RAID 1. This guarantees protection for your data. In addition, it ensures that a copy of your data is kept on a second drive, so you'll still have access to it even when the first drive fails. The only limiting factor with RAID 10 regarding data security is that it consumes a larger disk space than RAID 6 as it tries to keep identical copies of data.
RAID 6 vs. RAID 10: Disk Utilization
In terms of disk utilization, RAID 6 outweighs RAID 10. This implies that RAID 6 uses a smaller disk space than RAID 10. For instance, if you have four drives, RAID 6 will only use half of the total space and leave the other half for other tasks. The more disks in RAID 6, the more usable space.
However, this is not the case for RAID 10 because the data mirroring feature consumes double the amount of disk space as RAID 6. Since RAID 10 needs to create data duplicates, it consumes more disk space than you would have spent on other valuable tasks.
| FEATURE | RAID 6 | RAID 10 |
|---|---|---|
| Reliability | Highly reliable due to the data dual parity feature | Less reliable since it's prone to data corruption |
| Fault Tolerance | Can withstand two simultaneous failures | It can only withstand a single failure |
| Writing Speed | One-sixth when running on a single sector. When running on full stripes, the speed becomes 'n-2' times the original drive speed | 'n' times the original drive speed |
| Reading Speed | 'n' times the original drive speed | 'n' times the original drive speed |
| Redundancy | Maintains dual parity on two distinct backup disks | Stripes the data first before copying it to another disk with no parity |
| Capacity | 32 for SSD, HDD, or Hybrid | 144 for an equal number of SDDs or HDDs |
| Space Efficiency | Up to 93.75% when using a maximum number of drives | Levels up at 50% no matter the number of drives |
| Minimum Number of Drives | 4 | 4 |
RAID 6 vs. RAID 10: Which One Is Better?
Both RAID 6 and RAID 10 have advantages and disadvantages. It's difficult to exclusively pick one as better than the other because this highly changes with user requirements. For instance, if you have an eye for your data's safety while using the least space, you'll quickly pick RAID 6. On the other hand, RAID 6 is efficient for disk failures since it withstands up to two concurrent failures.
Although RAID 10 also offers data protection, it consumes a lot of disk space. If you want a process that boosts the data transfer speed of your system, you should go for RAID 10. Because of the data stripping feature, RAID 10 offers quicker data access than RAID 6.
In conclusion, if you want to experience speed and security, you should pick RAID 10. Although it consumes a lot of space, RAID 10 still offers efficient data safety, just like RAID 6. Our final pick is, therefore, RAID 10 because it stands out in terms of security and speed.
Protect Data and Uptime Using a Backup Software
Although RAID 6 and RAID 10 provide data redundancy, they can't protect your data in all instances. These processes only aim to ensure that your system keeps running after a disk failure. As a result, it's crucial to have software that can help you back up and restore essential files on your storage device.
This software allows you to back up your RAID data regularly and have a place to fall back to in case of a malware or ransomware attack. Qiling Backup Home is easy to use and offers a free cloud storage space of up to 250GB. Other advantages of the software include:
Final Remarks
RAID 6 is better than RAID 10 in terms of security because it can withstand up to two concurrent failures, while RAID 10 can only withstand one. Regarding speed, RAID 10 is considered better than RAID 6 because of the data stripping feature, which allows quicker data access than RAID 6.
Regarding disk utilization, RAID 6 makes better use of space than RAID 10 because it doesn't keep data duplicates like the latter. But, overall, RAID 10 is better than RAID 6 in terms of speed and security because it still offers data protection apart from taking up much disk space.
RAID 6 vs. RAID 10 FAQs
1. How Many Disks Can Fail in RAID 6?
RAID 6 can withstand up to two disk failures. This implies that it has a higher fault tolerance than RAID 10, which only supports one disk failure.
2. What Makes RAID 10 The Best?
RAID 10 is considered the best because it stands out in speed and security. Though it takes up much disk space, RAID 10 offers efficient data protection. In addition, its data stripping feature boosts the overall drive performance.
3. What Is The Total Number of Drives You Can Lose In RAID 10?
You can lose a total of four drives in RAID 10.
4. What Is The Writing Speed of RAID 6?
The writing speed is one-sixth when running on a single sector. When running on full stripes, the rate becomes 'n-2' times the actual drive speed.
Related Articles
- MTS File : What Is It and How To Open It [Updated 2022]
- What Is Verbose Mode Mac and How to Boot into It? [2022 Guide]
- What Is Boot Disk? Get A Boot Disk for Abnormal System Startup
- How to Boot from USB on Different OSs [Step-by-Step Guide]