What Is RAM? Random Access Memory [Full Explanation]
Introduction
Have you ever heard the word "RAM" pop up before? Although it is a fact that nobody remembers stuff they were taught in middle school, certain words stick in the long run. Random Access Memory, commonly abbreviated as RAM, is a term that almost everyone learned in middle school. Still can't remember much about it?
Following is an in-depth guide containing essential information about the RAM. Keep reading to learn the importance of Random Access Memory, its major types, and the main uses that RAM serves in your devices.
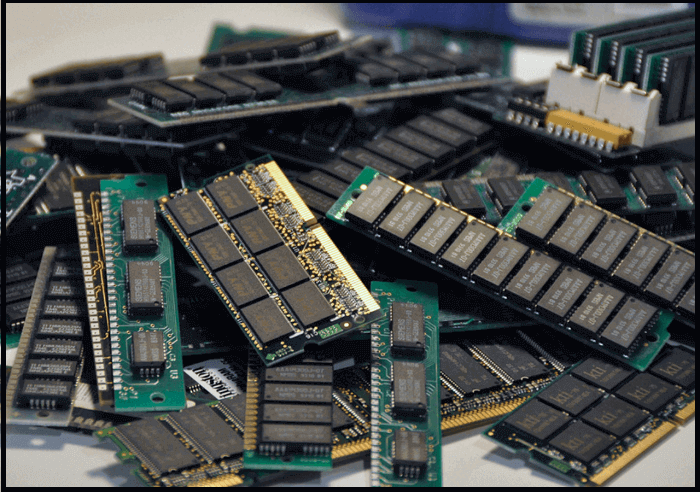
Random Access Memory (RAM): What Is It?
To get things started, let's take a brief overview of Random Access Memory. RAM is a type of internal computer memory that stores information such as application data and transmits it to the system's processor. Because the computer's CPU can directly access RAM, the read and write operations on it are much faster when compared to other types of storage devices.
An important thing to remember when talking about RAM is that it is a type of volatile memory. This means that all the data stored and processed by RAM is lost once the device is powered off. After a reboot, data is reloaded on the RAM from a hard disk or a solid-state drive. RAM is the main type of computer memory that works in correspondence with the system for processing data.
If you want to know more information about RAM, you can read following articles to find the answer:
Types of RAM
After knowing some basic information about RAM, it is time to take a deeper dive into the subject. RAM is generally classified into multiple types. The two main types of RAM are mentioned below:
1. SRAM
Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) is a type of RAM that stores information using static techniques. This form of semiconductor computer memory is extensively used in microprocessors, electronic devices, and other applications.
Data in SRAM is stored in memory chips by using a bistable latching circuitry in a static way. SRAM is also a form of volatile memory, although it does not require dynamic refreshing as long as power is supplied to the system.
Key Features of SRAM
- SRAM offers fast speed in reading and writing operations.
- SRAM requires a moderate amount of energy and can thus operate on low power.
- SRAM storage capacity is limited and usually measured in MBs; therefore, it generally acts as cache storage.
2. DRAM
Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) is another type of RAM that requires periodic and dynamic refreshing of contents. The integrated circuit of DRAM uses a transistor and a capacitor to store data. Because transistors are notorious for leaking small amounts of charge, DRAM needs to be refreshed after short intervals of a few milliseconds.
DRAM is highly volatile and cannot retain data without being refreshed. As opposed to SRAM, storing information on a DRAM is cheaper and requires less space. Due to these reasons, it is one of the most common types of memory normally used.
Key Features of DRAM
- DRAM is a cost-effective solution as it is much cheaper when compared to SRAM.
- DRAM offers a large storage capacity, usually measured in GBs, and can thus be directly connected to the processor bus.
- A single transistor is required by DRAM to form a memory block. Consequently, it can store more memory in less space.
Other Uses of RAM
Like the different types of RAM mentioned above, there are multiple uses of Random Access Memory. As explained above, RAM occurs as a temporary storage site for data. To increase the computer's processing speed, RAM reads data and makes it easily accessible to the CPU. Besides this, RAM also helps in loading software applications on a computer. Some other uses of RAM are mentioned below:
1. Virtual Memory
The operating systems of computers use virtual memory to make up for the shortage of physical memory in the system. Virtual memory works in collaboration with RAM to combine the available space on the hard disk. Data can be moved from the RAM to free up space so the processing functions can proceed uninterrupted.
2. RAM Disk
A RAM disk, also known as a RAM drive, uses RAM resources to form a hard drive or a virtual disk. The system uses the memory blocks on RAM as individual hard disk drives for storage areas. The main function of a RAM disk is to increase the speed and efficiency of the system.
3. Shadow RAM
Shadow RAM uses a RAM stick to store duplicate versions of the system's BIOS data. Shadow RAM can also accelerate the boot speed of the computer. By transferring BIOS information from ROM to RAM, the boot time can be cut up to almost half.
RAM vs. ROM: What Are the Differences Between Them?
In addition to Random Access Memory, another basic type of internal memory is used in computers. RAM and ROM work side-by-side in your computer to ensure the smooth flow and processing of information. Below is a brief overview of ROM and the main differences between RAM and ROM.
What Is ROM?
Read Only Memory (ROM) is a type of non-volatile memory in computer systems. ROM permanently stores data on individual cells with the help of binary codes. Once data is stored on ROM, it cannot be changed or overwritten by users. ROM chips commonly store startup information on computers and have a limited storage capacity.
Comparison Between RAM and ROM
| Features | RAM | ROM |
|---|---|---|
| Access to Data | Data stored on RAM can be easily accessed and modified. | As data is read-only, information stored on ROM cannot be directly accessed or modified. |
| Storage Capacity | The storage capacity of RAM can stretch from 1 to 256 GBs. | ROM chips offer limited storage capacities, typically ranging from 4 to 8 MBs. |
| Speed | RAM chips offer faster access to data and can boost the processing speed. | ROM offers a slower processing speed when compared to RAM. |
| Cost | RAM chips cost much higher than ROM. | The price of ROM chips is relatively low compared to RAM. |
| Volatility | RAM is a type of volatile memory. | ROM is a type of non-volatile memory. |
If you want to know more about the RAM and ROM, you can read the following article to find out more differences:

RAM vs. ROM: 8 Differences between RAM and ROM
In this article, we'll define both of these technologies. Then, we'll also talk about the differences between the two. And finally, we will explore which one is more important—if there is one.
Sum Up
Part of the basic knowledge that is spoon-fed in schools includes information about the significant components of a computer system, including the Random Access Memory. With the help of the information mentioned above, you hopefully have a better and more precise understanding of RAM now and what it does for our devices. So, the next time someone asks you about RAM, you can effortlessly follow the conversation without embarrassment.
Related Articles
- How to Factory Reset from BIOS on a Windows PC [Methods in 2022]
- [3 Ways] How to Uninstall Apps on Windows 11
- What Is Cloud Computing? [Everything You Need to Know]
- Windows 11 Download: How to Download and Install Windows 11 [3 Ways]