What Is ReFS File System? Everything You Need to Know
What is ReFS File System
Resilient File System (ReFS) ReFS is an advanced file system launched by Microsoft, which was initially introduced with Windows Server 2012 in September 2012, allowing data storage. It has since evolved to support system booting and use on mobile hard disks.
ReFS is built on NTFS code, aiming to create a new generation of file systems that prioritize maximum data availability, meet growing data storage needs, and address NTFS limitations.
Microsoft initially used ReFS only in Windows Server 2012, but later added it to Windows 8.1 in 2013. However, by 2017, the ability to create ReFS volumes was removed from all versions of Windows 10 except for Windows 10 Pro for Workstation. Despite this, Windows 10 can still read ReFS volumes.
How ReFS File System Works
Microsoft uses the NTFS code base to design ReFS, and adds Win32 API support to provide compatibility and more features.
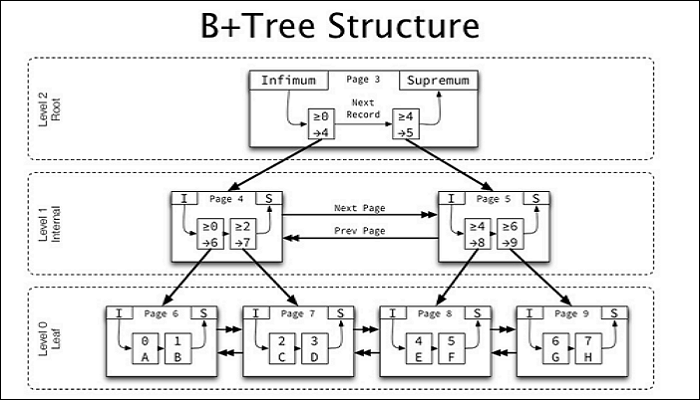
The ReFS file system utilizes a B+tree structure to manage data through metadata indexing, maintaining high compatibility with NTFS. This structure enables ReFS to store more data using the branch mode and reduce disk I/O, thereby improving performance. Building on NTFS, ReFS also ensures higher consistency and data integrity, allowing for data recovery in the event of system errors.
Main Functions of ReFS
As a new-ReFS, a file system after NTFS, has three new functions: Disk Construction Reliability, Build-in Resilience, and Mirror-accelerated Parity.
Disk Construction Reliability
The ReFS file system utilizes a B+tree structure, allowing it to support a large amount of data. As a result, it has a maximum file size of 16 exabytes (EB) and a maximum volume size of 35 petabytes (PB).
Build-in Resilience
ReSF can check files and repair file corruption when users read or write files, and its data integrity scanner regularly checks and repairs all files on the drive, providing higher integrity and availability for the data.
Mirror-accelerated Parity
The mirror accelerated parity function efficiently allocates data to two layers on the drive. It writes data to the disk in the mirror layer and then transfers it to the parity layer to recalculate each written file, making more efficient use of disk space and enabling more efficient data storage.
Pros and Cons
Although highly anticipated by Microsoft, ReFS (Resilient File System) cannot yet be considered a direct substitute for NTFS. While ReFS boasts several unique features not found in other file systems, it still has several shortcomings that need to be addressed to make it a viable alternative.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Conclusion
Microsoft's ReFS is an advanced file system that offers users easy access, writing, modification, and protection of data. Despite its excellent performance, it still falls short of being a perfect substitute for NTFS.
o
The new system uses a more efficient data storage method, which not only makes data retrieval faster but also reduces the overall storage requirements, making more efficient use of disk space.
Related Articles
- What Is M3U8 File? How to Open and Convert M3U8 File?
- What Is Boot Partition? [Specifically Explained]
- What Is SDRAM? Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory Explained
- What Is The Root Directory and What Are The Folders in The Root Directory Used for