Complete Introduction to Searchindexer.exe
Have you ever wondered how your computer can quickly return specific results for your search queries? Thanks to the searchindexer exe Windows service running in the background. This service is responsible for property caching, content indexing, and search results for email, files, and other contents.
Your Windows 7/8/10/11 Start Menu, File Explorer and Cortana Box depend on this powerful technology. In this article, you will learn more about why this service is running, how it affects your system performance and how to disable it when needed.
What Is SearchIndexer.exe, And Why Is It Running?
The searchindexer exe is another pre-installed executable file on your computer, designed by Microsoft and known as the Microsoft Windows Search Indexer. As a built-in service, it is executable by the Microsoft Software Installer (MSI).
Step 1. The searchindexer exe file is located in the C:\Windows\System32 directory
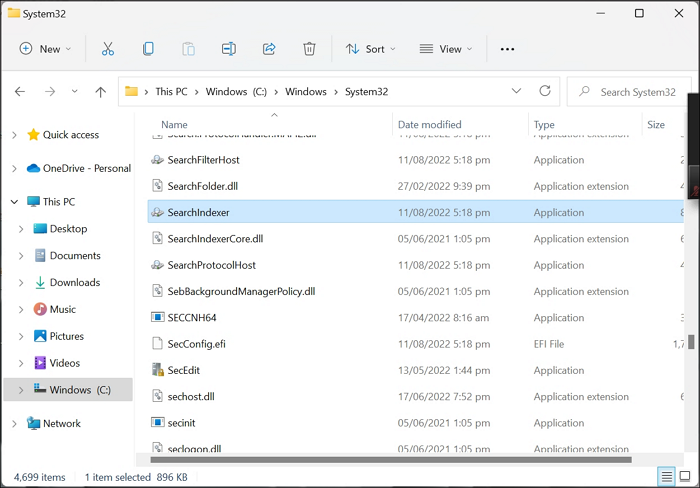
SearchIndexer exe was previously known as WDS (Windows Desktop Search); it prepares folders and files containing the character or phrase typed in the search bar.
Step 2. Alternatively, you can view your searchindexer exe from the Task Manager. Right-click to choose Properties
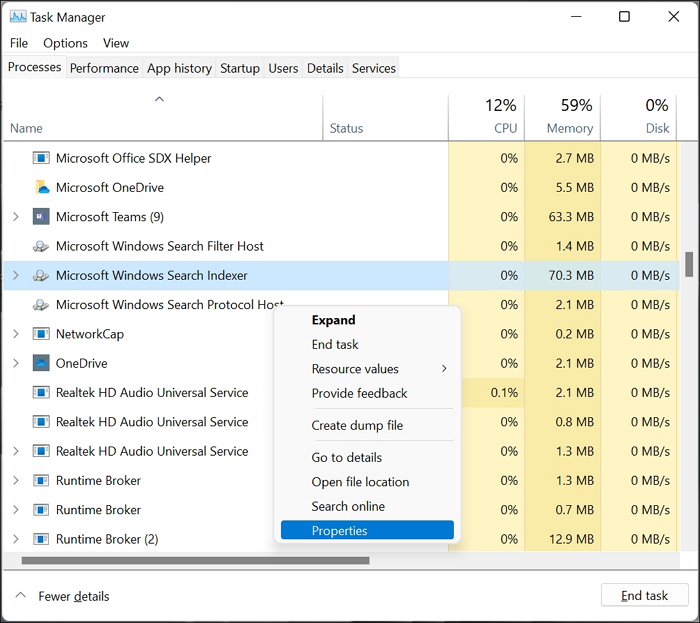
Step 3. After clicking Properties, click the Details tab
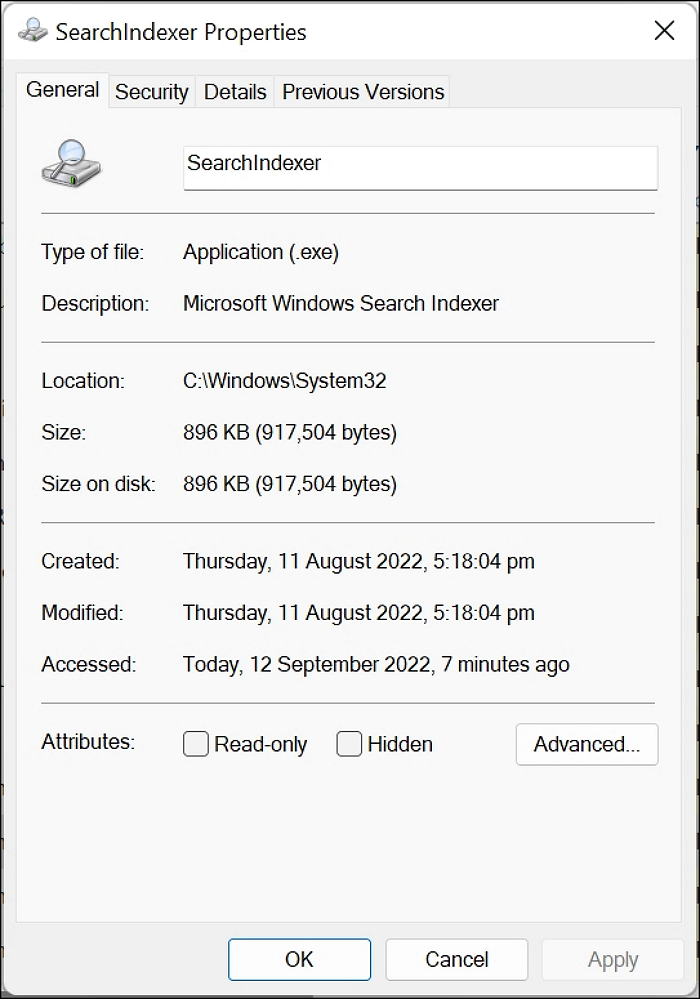
Step 4. Then the Original filename SearchIndexer.exe is displayed
As a Microsoft Windows Service, SearchIndexer indexes user files for Windows searches made in the Start Menu, File Explorer and safe Libraries. In addition, it searches for data in media files, contact lists, and email clients and monitors the additional changes made to them on your computer.
How Does it Affect Your System's Performance?
The version of Windows OS you are running will determine how SearchIndexer affects your system's performance. Starting with Windows XP, it placed an excessive load on the system and affected its performance negatively.
Over time, Microsoft improved the indexing service in Vista and Windows 7 by reducing the load it places on the system. Today, you won't even notice your SearchIndexer running on the newest Windows version, 7/8/10/11, because it is programmed to run when your system is idle.
How Can I Make SearchIndexer Use Less RAM or CPU?
Seeing how robust the operations of the SearchIndexer are, it sometimes consumes more RAM or CPU speed, hence the need to cut down on the local content it indexes. Follow the steps below to reduce its RAM or CPU consumption.
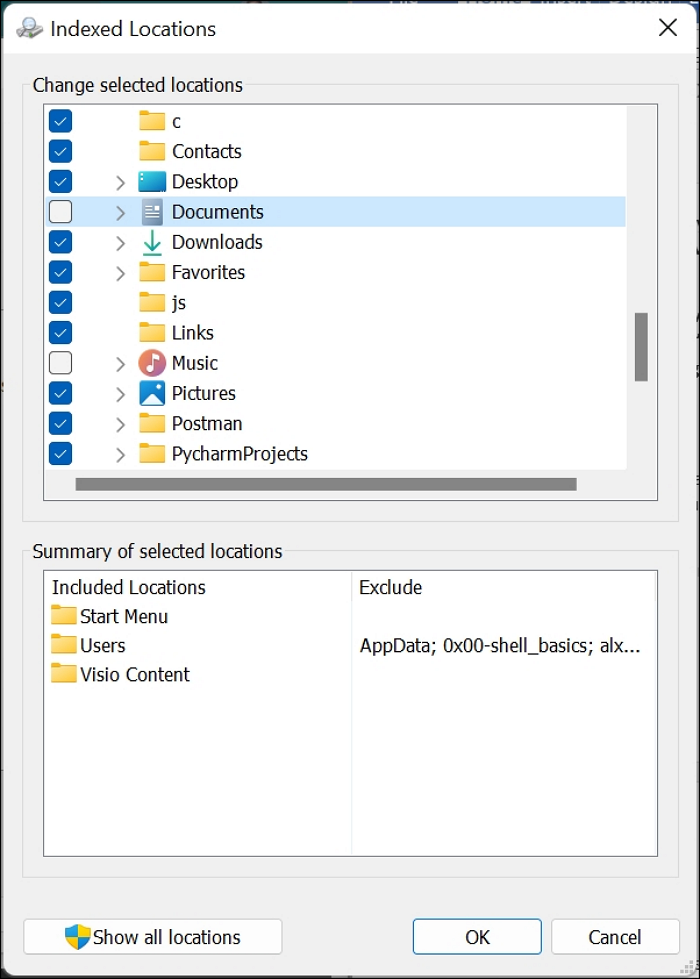
Step 1. Type "Indexing Options" in your Search bar and click on the best match result. A similar screen to the one below pops up.

Step 2. Click on Modify and select the locations you want to leave indexed. After selecting them, click OK to effect changes.
In addition, you can limit the indexing to filenames only by following the steps below:
Step 1. After selecting the Indexing Options from the Search bar, click on Advanced.
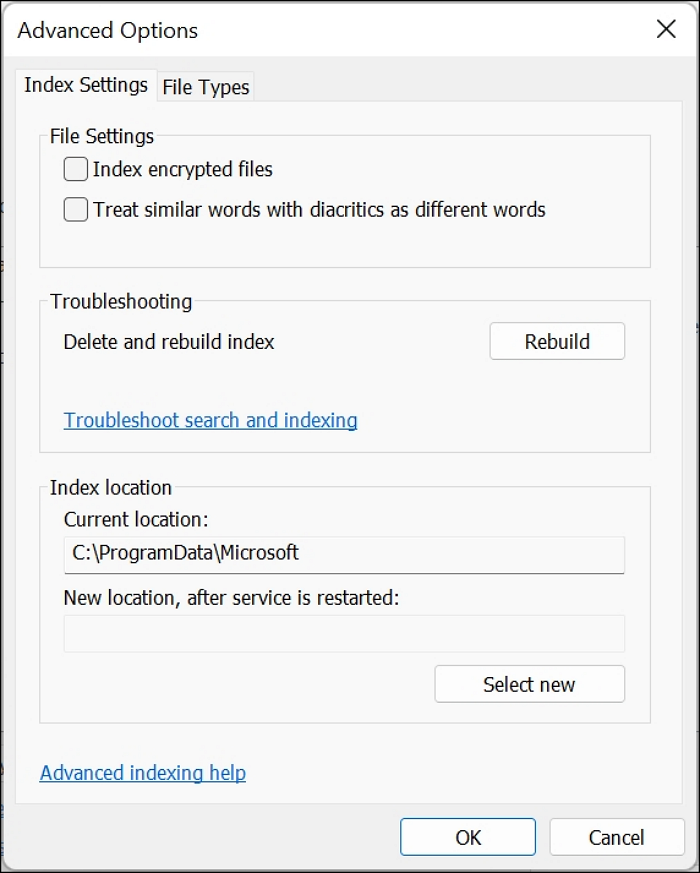
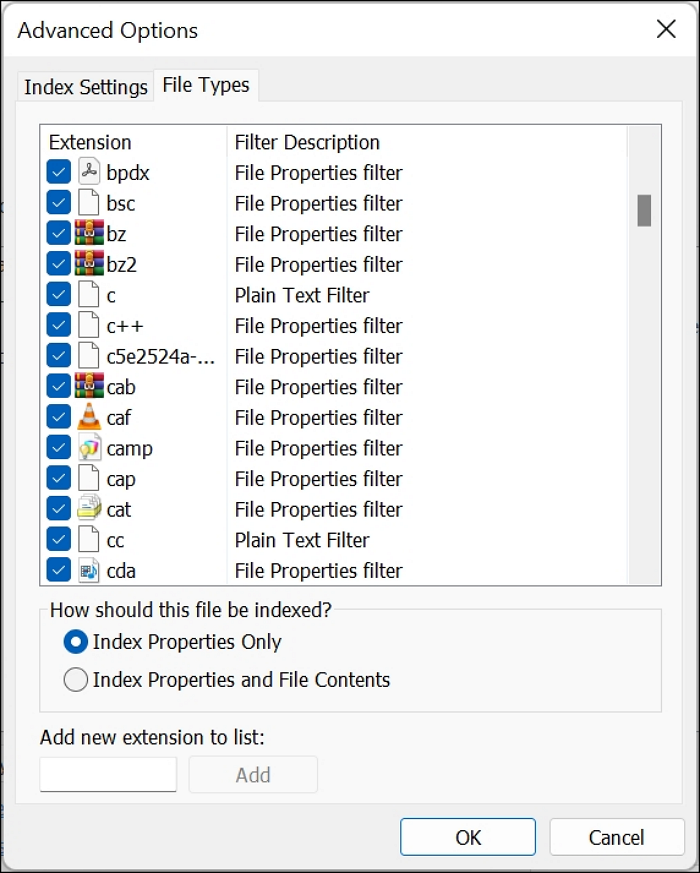
Step 2. Click on the File Types tab
Step 3. Scroll down and see the configuration of some common file types (doc, docx, and so on); it is either Index Properties and File Contents or Index Properties Only.
Step 4. Change the configuration settings of those standard files to Index Properties Only if all you care about is the file name. Then click OK to effect changes.
How to Disable or Uninstall This Service?
As an in-built service, Microsoft Windows SearchIndexer is safe for your system. There is no need to disable or uninstall it. However, in the case of a system hog, you may need to disable it. The steps highlighted below will guide you into that.
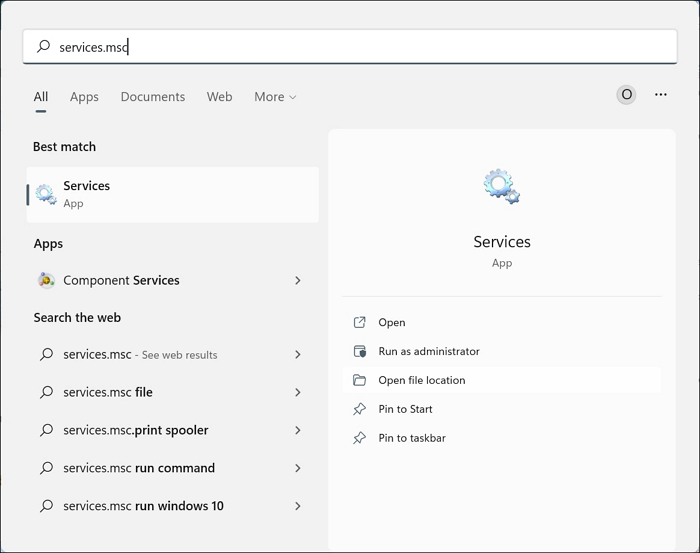
Step 1. Type "services.msc" in your Search bar and open the best match by clicking Enter.
Step 2. Right-click Windows Search to select Properties. Press the key "W" to move instantly to the W-series list. Then, you should have the screenshot below.
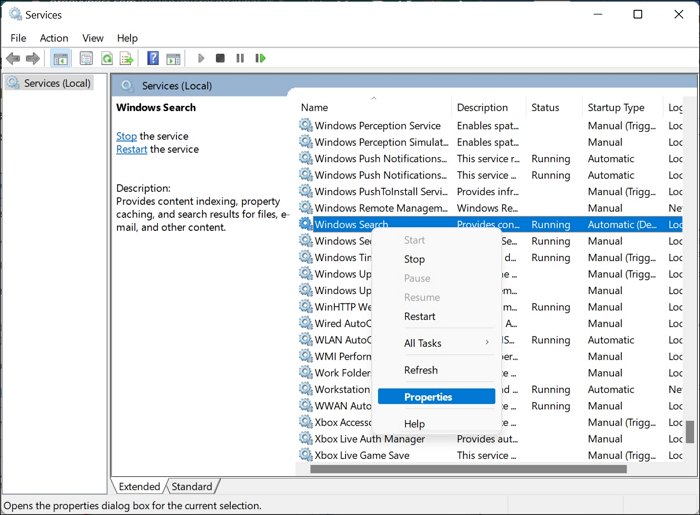
Step 3. A new screen pops up; set the Startup type to Disabled under the General tab.

Step 4. Click Stop to disable the service, then click "OK" to effect changes.

To restart the service, navigate to the previous screen and set the Startup type to Automatic (Delayed Start)
Final Words
In conclusion, you don't have a reason to remove the searchindexer exe on your computer. However, if you must, this post provides all the information you need to know why it is running and how to trim it down to size if it consumes more RAM or CPU.
Related Articles
- What Is SACD? Super Audio Compact Disc Explained
- What Is CD-RW? Compact Disc Re-Writable Explained
- [Beginner Guide] What Is PCIe? What Is It Used for?
- What Is the Mac Terminal? Introduction to the Command Line Interface on macOS