What Is Tracert/Traceroute Command? How to Run It on Windows, Mac, and Linux?
- What Is Tracert?
- What Is Traceroute?
- How Do I Use Tracert/Traceroute?
- How to Read a Tracert/Traceroute Result?
Tracert or Traceroute is one of the key diagnostics of networking. So, how does it work, and how can you run it?
Tracert or Traceroute is one of the key essentials of networking and data packets over a specific network. This command allows experts to understand the integrity of the network and the speed at which it operates.
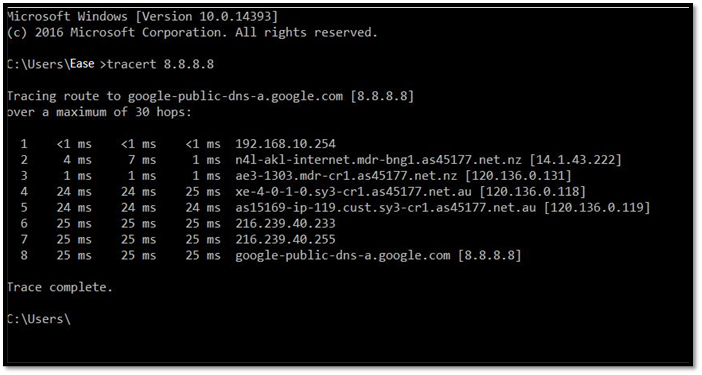
But, understanding Tracert commands requires one to look at their roots and from where exactly they originated. So, let us dive in and talk about the traceroute command, what it is, how it works, and how you can run it.
What Is Tracert?
Tracert is a series of computer commands to help users find network diagnostics and reports. It's used to display the paths of network packets, which transfer data from one end to another. In other words, it's a tracer command that allows you to check the probable display routes of data transitions.
This process requires the computer to send data to another computer and wait for it to receive it in return. Once it does, it measures the speed and abilities of the network to transition such data. Therefore, this is a computer network diagnostic command in Windows.
Etched in the syntax of every Microsoft operating system, this process allows the users to check the ping receiving times from another computer. The focus of the Tracert command on Windows is to trace the route back and forth, which produces much clearer results.
But, in Windows NT-based computers, the same operation is called PathPing, as it allows you to check the specific ping paths and measure their speed through packets sent and received. However, the preferred method is still to use the Tracert command.
What Is Traceroute
Traceroute is the same command as Tracert, except this variant is used in Unix-like operating systems, namely macOS and Linux, i.e., Ubuntu, etc. Compared to Windows, Traceroute is available as a graphical interface in macOS, and you can find it in the Network Utilities Suite.
In Linux, however, it's still a command line tool, requiring you to type out the commands to trace the network route and send data packets down the line. Therefore, it's the Unix operating system's version of Tracert, allowing thorough network diagnostics.
In both Mac and Linux, the working of this command line is vastly different, as it requires you to understand the diagnostics accordingly, which we'll talk about a bit later. However, it's important to understand that the basics of both Traceroute and Tracert are the same.
Therefore, so are their purposes, which allow the user to completely scan their local network for issues and identify problems by solitude a specific data packet or network chain.
How Do I Use Tracert/Traceroute?
- How Do I Run a Tracert Command in Windows?
- How Do I Run a Traceroute on a Mac?
- How Do I Run a Traceroute on Linux Machine?
Using Tracert or Traceroute, or understanding how to use it on each operating system, requires us to understand each aspect thoroughly. Therefore, it's imperative that we break down the Tracert command according to their operating systems, i.e.
- Windows
- Mac
- Linux
Since Linux is the most complicated one, we suggest only well-versed users with the operating system try it. As for Mac, it's perhaps the easiest to run this diagnostic. Whereas for Windows, you need adequate knowledge of command prompt to be able to use Tracert.
So, let's get started:
How Do I Run a Tracert Command in Windows?
The first method we'll explore is to run a Tracert command on Windows operating systems. This is viable for all the operating systems after Windows 7 and should allow you to check the diagnostics accordingly. Therefore, here's what you need to do:
Step 1: Head to the Start Menu or press the Windows button on your keyboard
Step 2: Type CMD and Run as Administrator
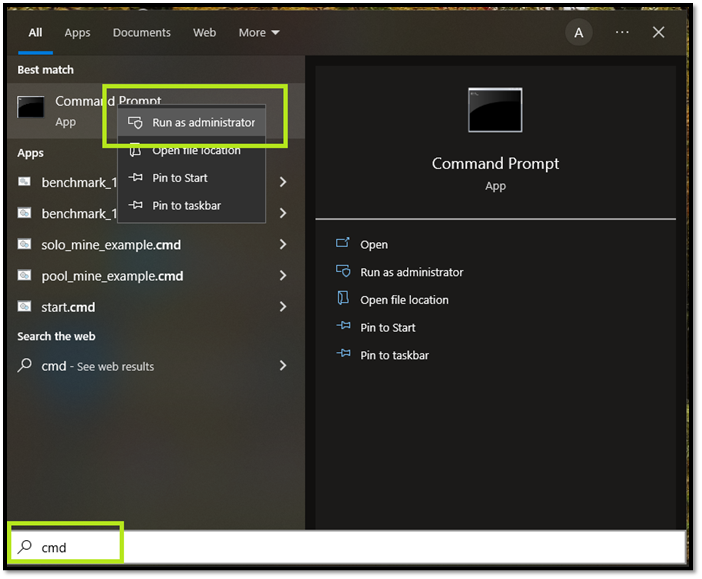
Step3: Let it open the Command Prompt
Step 4: Type Tracert hostname (instead of "hostname," you should type the address of the server you wish to diagnose)
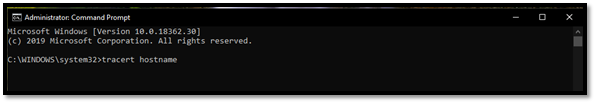
Step 5: Let the test run, which should take about a minute or two
Step 6: Wait for Trace complete to show
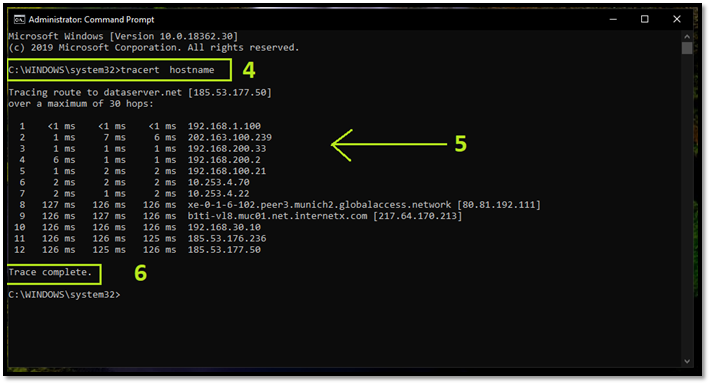
Now that you have the data, you'll have to keep scrolling to be able to read it. However, if you already know how to read it, then you know what each MS indicates.
The test result means milliseconds, i.e., the time it took for the network to send data packets back and forth. Therefore, make sure you follow the reading type of each Tracert command according to its operating system.
How Do I Run a Traceroute on a Mac?
Running a Traceroute on a Mac device is the easiest of them all. That's why all you need to do is have a Mac and know how to use your device's "Utilities" section. While the first one is obvious, here's how to use the second one to run a Traceroute on Mac:
Step 1: Go to Finder on your Mac device
Step 2: Tap on Go in the top bar of Finder
Step 3: Find and Tap Utilities at the near-bottom
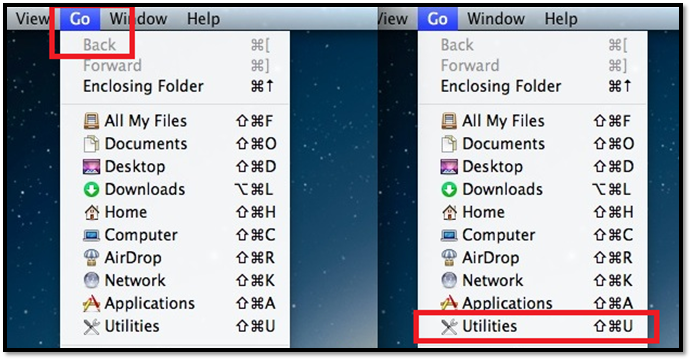
Step 4: Head to Terminal
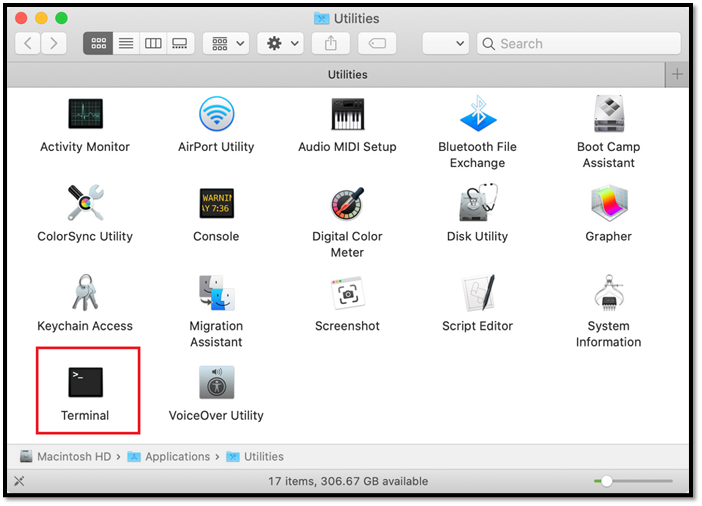
Step 5: Type traceroute in the terminal
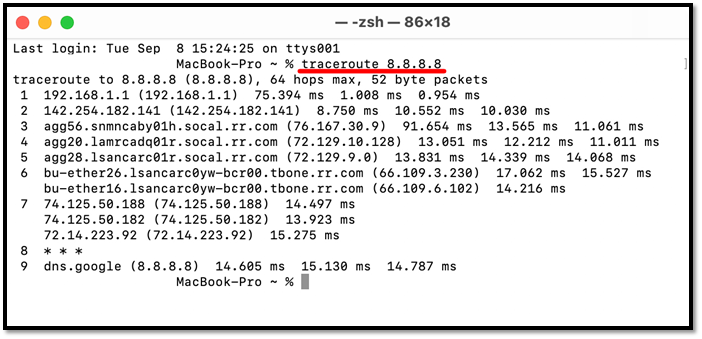
Step 6: Wait for it to finish
As you might already know, you can access Utilities in the Finder app in multiple ways. But, regardless of how you get there, you need to run Terminal, which is the Mac equivalent of Command Prompt. So, make sure you run these commands to do that.
How Do I Run a Traceroute on Linux Machine?
Linux users might already know how to run Traceroute because even running Linux as a common operating system requires them to remember a lot of commands. However, if you're new and are still looking, then here's what you need to do:
Step 1: Open Command Line in your Linux OS
Step 2: Type Traceroute hostname in the command line (replace hostname with actual hostname)
Step 3: Wait for the test to finish
Step 4: Let the final ping detect
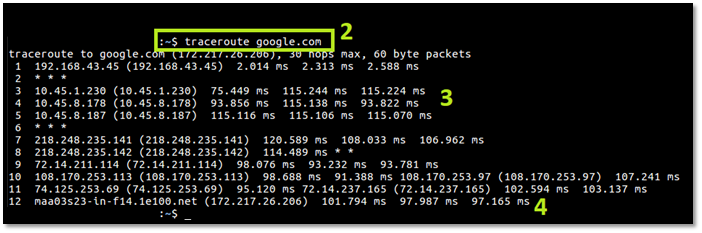
You'll have to determine the hostname by yourself, but to test the local network, you can check any website, just like we checked Google in the aforementioned steps. However, you'll have to be more precise if you wish to check specific IP addresses.
Regardless, you need the command line, Traceroute command, and the server IP/website to be able to trace the route of the network in Linux.
How to Read a Tracert/Traceroute Result?
Reading or understanding Tracert or Traceroute results isn't rocket science. Suppose you've gotten this far in this article. In that case, you know the numbers generated by either the Terminal, Command Prompt, or Command line aren't random.
They're reading of various elements. So, to keep it simple for you, remember this:
- If there is one or more asterisk (*)
- RTT or Round Trip Time shows you the latency, i.e., the delay in one packet. In CMD or Linux Command line, it shows as MS or milliseconds
- Name, i.e., the name of the system and, i.e., the computer that you're using
- The IP address is the one returned by the designated hostname
- RTO or request time out means that the server's pings are broken, and the connection isn't stable
While some connections show MS in response, if it's something like 1000+ms, then the connection is very slow and unstable. However, Request Timed Out means the connection isn't sending back anything and, therefore, is broken.
Bottom Line
We hope this helps you read and understand Tracert and Traceroute commands. Not only did we explore its two types, but also how you can check them on three main operating systems. Therefore, make sure you follow the steps correctly.
Related Articles
- Ultimate Guide on Network and Sharing Center [Updated 2022]
- What Is Cloud Computing? [Everything You Need to Know]
- What is Taskbar in Windows? And How to Use it?
- Network Switch vs. Router: What's the Difference