What Is A NAS Storage? How Does NAS Work?
PAGE CONTENT:
- 1. What is A NAS Storage?
- 2. Three Common Types of NAS
- 3. How Does NAS Work?
- 4. NAS vs. DAS, Which Is Better?
What Is A NAS Storage?
NAS, the Network-Attached Storage abbreviation, is a dedicated centralized storage server that combines one or more drivers, often arranged into logical, redundant storage containers or RAID, allowing multiple users to access and collaborate data through the Ethernet. NAS makes it faster and easier to access data among multiple computers or devices remotely.
NAS is specially designed to process those unstructured data, like videos, audio, web pages, texts, and Microsoft Office documents.
(information source: https://cloudian.com/guides/data-backup/nas-backup/)

NAS has been around since the 1990s as a convenient way to share files between multiple computers. Many individuals and companies still choose NAS today because of its security and reliability.
According to the different needs of companies or individuals, they will choose different types of NAS. Let's take a look at the specific classifications of NAS.
Three Common Types of NAS
According to the driver capacity, support, and scalability, NAS can be divided into three types. They are enterprise NAS, midmarket NAS and desktop NAS.
Enterprise NAS is a kind of high-end category suitable for companies that need a large quantity of data storage. It can provide fast access to data and NAS clustering capabilities.
Desktop NAS is a low-end device. It is a perfect choice for individuals or home use because its processing speed is slower than the enterprise version but cheaper in price.
Midmarket NAS is a compromise between A and B. It is suitable for small companies that require only a few hundred terabytes (TB) of data.
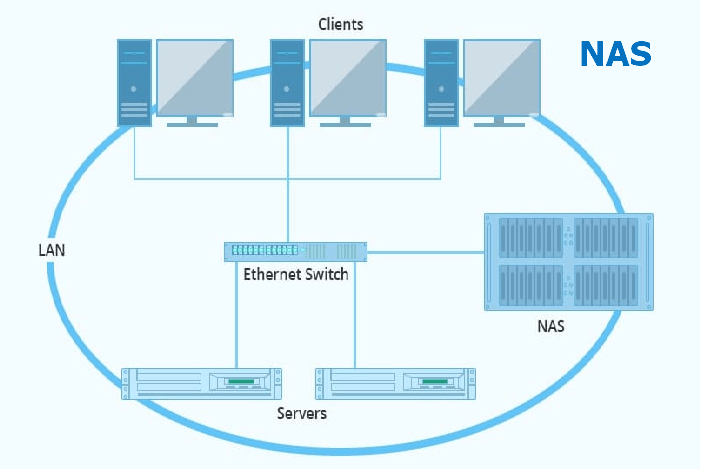
How Does NAS Work?
The NAS works through a network connection. The image below clearly explains how it works.
Multiple devices and NAS are connected to the same network or WIFI. A network switch or server connects the device and NAS so that the data on the NAS can be accessed and shared on multiple computers.
NAS allows us to share the same database across multiple devices faster, making work more accessible.
NAS vs. DAS, Which Is Better?
What is DAS? It is the abbreviation of Direct-attached storage, which refers to a dedicated server or storage device that is not connected to a network, which is precisely the opposite of NAS. One of the typical examples of DAS is PC's internal HDD. If you want to access the data stored in DAS, you are supposed to get the physical storage of DAS.
NAS and DAS are different in many aspects. You can refer to the following chart to find more detailed information.
| NAS | DAS | |
|---|---|---|
| Whether needs network | An easy and self-contained solution for sharing files over the network | An extension to an existing server and is not necessarily networked |
| Performance | NAS is better than DAS for performance because the NAS device can be tuned precisely for file serving | |
| Management | Multi-device share and manage data | Manage every DAS separately |
Apart from the above difference, DAS focuses on data storage, while NAS aims to increase the convenience of data sharing. They are designed for different purposes, and you should choose according to your needs.
Conclusion
You must have found your answer here if you don't know what NAS storage is or how it works. NAS makes it more convenient to use a shared database on different devices and for other users through the network. Three types of NAS are available to store data based on different storage quantity needs. Besides, DAS and NAS are different in focus. A DAS device is a more suitable solution if you want to save data only.
Related Articles
- What Is CD-RW? Compact Disc Re-Writable Explained
- What Is Control Panel? [All You Need to Know]
- Hyper-V vs. VMware: Which Is the Better Choice for You?
- What Is WSUS? Windows Server Update Services Explained