What Is a Snapshot and How Is It Different from a Backup
You must have heard of Snapshot, but do you know what Snapshot is? Don't worry; this post will help you learn more things about Snapshot. Just keep reading.
What Is Snapshot
A storage snapshot is a reference marker for data related to a specific point in time. A snapshot is like a directory that holds copies of data that users can access. Therefore, snapshots can assign snapshot copies of some system or system state. A hard disk snapshot contains the directory structure of the hard disk, including every file and folder on the disk.
How Does Snapshot Work
Storing snapshots is based on the use of differential disks, which are a special kind of virtual hard disk.
When a device administrator creates a storage snapshot, the underlying system creates a different disk bound to the original virtual hard disk. In the future, all writes will be directed to a difference disk, but the original virtual hard disk will remain unchanged. The filesystem continues to behave as if it were on a physical machine, utterly unaware of the existence of the differencing disk. Snapshots have a parent-child relationship and gradually form a tree. Each snapshot taken creates another branch of the tree.
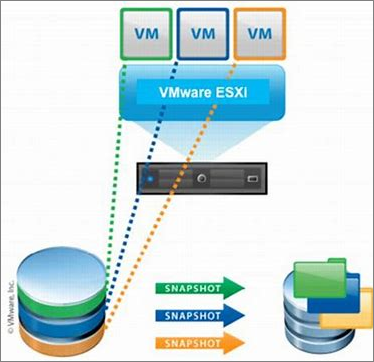
Typically, snapshots are used to protect data, but snapshots can also be used for testing application software and data mining. When information is lost by accident, storage snapshots can be used to restore lost data. Snapshots can also be used to restore the device system if the wrong patch is installed.
Snapshot Type
- Copy-on-write: When an I/O request attempts to change a block of storage, the block will first be copied and retained by the snapshot to which it belongs.
- Redirect-on-write: When creating a new block, only one write to the snapshot is required.
- Continuous data protection: Snapshots will run every second backup.
- Mirror/clone/replication: A clone/mirror is an identical copy of a storage unit, and replication is an efficient form of data protection.
Snapshot Vs. Backup
Creating snapshots manages version control and is a practical way to create lightweight, easily accessible versions of data or systems. They don't take up a lot of storage space and don't take a lot of time to create copies.
A backup is a unique copy of a system or directory stored in a different location. Backup is mainly for data protection against data loss due to server failure or accident. Backups can also be performed on a regular basis.
You may be interested in Top 10 Offline Backup Software Recommended in 2022

Conclusion
Snapshot files save storage space. Because the system can store snapshots alongside existing virtual machine files, administrators don't need to wait to download backup files from elsewhere. However, snapshots consume a lot of disk space, so administrators cannot keep old snapshots for long periods of time.
Additionally, the administrator must rebuild the snapshot to restore the virtual machine. If the previous snapshot file or the original virtual disk is damaged, the system will not be able to fix the snapshot. The system deletes any files from previous snapshots, and if an administrator wants to restore a file, the snapshot must be fully restored.
Related Articles
- How to Build A PC? Follow A Complete Guide to Do It
- What Is ASD File? [Detailed Information]
- What Is Ping in Gaming? Everything You Need to Know
- What Is SFC Scannow Command? How to Fix Corrupted Files Using This System File Checker