What Is macOS Base System [Everything You Need to Know]
The macOS Base System is a fundamental component of macOS, but its exact function and potential issues may be unclear. Fortunately, this post aims to provide information and solutions to common problems related to the macOS Base System, helping users understand its role and address any issues that may arise.
The Definition of macOS Base System
The macOS Base System is the recovery partition on a Mac, which plays a crucial role in reinstalling macOS when the system fails or needs an upgrade. It also helps troubleshoot and resolve Mac issues using Disk Utility, and can restore the device to its previous state using Time Machine in case of any issues.
The macOS Base System is a 2 GB read-only disk image that contains essential information for a Mac to function properly. It's hidden from view during a regular boot, but visible when booting into Recovery Mode using Command + R on an Intel-based Mac.
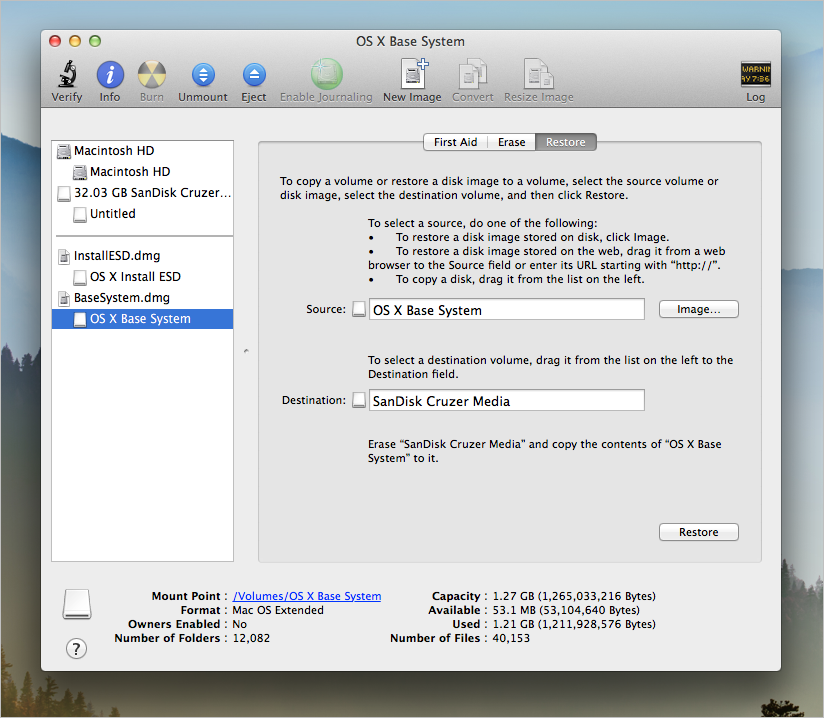
When to Use the Mac Base System
System failures are a common issue when using a Mac, often resulting in crashes, shutdowns, or error messages. In such cases, the device may need to resort to its base Mac system to assist in restoring or reinstalling the macOS.
The Mac base system is used in various situations, including software development, web development, and data analysis, among others. It is often utilized by developers and programmers to create and test software applications, as well as by web developers to build and maintain websites.
- Failed to activate.
- Disk problem.
- Operating system problem.
The macOS base system is only considered when restoring, restoring, or repairing a Mac, and it fixes the Mac's backup when the device is reinstalled with macOS.
macOS Base System Vs. Macintosh HD
The Macintosh HD is the startup volume that users launch when turning on their macOS device. It serves as the base system, allowing users to restore macOS with ease when it fails to function correctly. Additionally, it provides a backup for users to repair their Macs, reinstall macOS, and utilize other low-level utilities.
Possible Issues with macOS Base System - How to Solve Them
Equipment can malfunction due to incorrect operation, but users may also encounter errors when interacting with the macOS base system, such as a locked or out of space drive. This issue can be resolved by following the provided solutions.
- There is Not Enough Free Space in OS X Base System
- macOS Base System Has the Size of Your Mac Hard Drive And Shows That "The disk is locked"
Problem 1: There is Not Enough Free Space in OS X Base System
When installing macOS using a Mac virtual machine tool, you may encounter issues like "Not enough free space on OS X Base System" on your device. To resolve this, you can wipe the container and create a new partition to store the macOS installer, which should fix the problem.
The following are the detailed steps:
Step 1. In the macOS installer window, click on "Utilities" on the menu bar and select "Disk Utility" from the drop-down list.
Step 2. Select the main container under the name and click "Erase."
Step 3. To partition the drive, name the partition, select APFS as the format for Macs running macOS 10.13 High Sierra or later, and choose "GUID Partition Map" as the scheme. For earlier macOS versions, choose "Mac OS Extended (Journaled)" instead.
Step 4. To erase the disk and install the Mac OS to the new partition, click "Erase" on the Disk Utility window, then close the window and proceed with the installation of Mac OS to the new partition.
Problem 2: macOS Base System Has the Size of Your Mac Hard Drive And Shows That "The disk is locked"
If a Macintosh HD is accidentally restored to the macOS base system and becomes locked, try booting from a different startup disk, then run Disk Utility from the Utilities folder in the Applications folder, select the Macintosh HD, and click the "Repair Disk" button. If the disk is still locked, click the "Erase" button and then reformat the disk. This should resolve the issue.
Steps to resolve the "disk is locked" issue:
Step 1. To restart your Mac and immediately press and hold the "Option + Command + R" buttons on your keyboard until you see an animation appear on the screen.
Step 2. In the utility window, click "Disk Utility."
Step 3. Select the macOS base system and click "Erase."
Step 4. If your device is running macOS 10.13 High Sierra or later, name the drive "Macintosh HD" and format it as APFS. If it's an earlier version, name it "Mac OS Extended (Journaled)" and use the GUID partition map.
Step 5. To reinstall macOS, click "Erase" and exit Disk Utility, then reinstall macOS and select Macintosh HD as the drive.
Related Articles
- How to Open Windows Device Manager [Full Guide in 2022]
- Windows 10 Backup Features - All You Need to Know
- What Is WSUS? Windows Server Update Services Explained
- Highlights of SanDisk Extreme | Is it Worth Buying and How to Choose it