[Beginner Guide] What Is PCIe? What Is It Used for?
PAGE CONTENT:
What Is PCIe
PCIe stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, often abbreviated as PCI-e, PCIe, or PCI Express; all are the same. PCI Express is a popular high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard that supersedes other legacy standards such as PCI, PCI-X, and AGP.
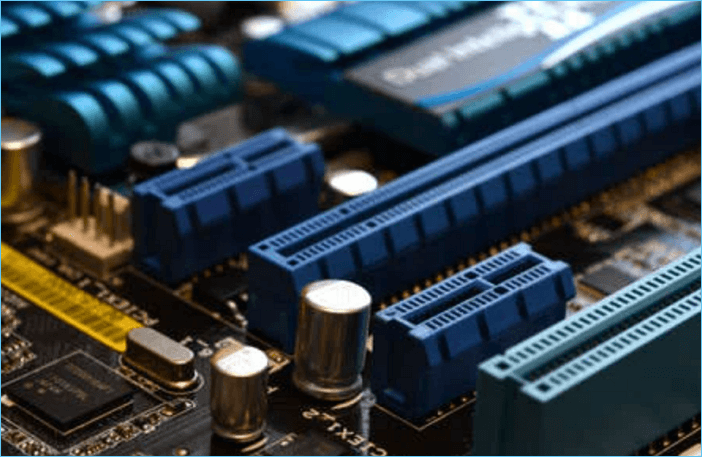
Compared to PCI, which applies parallel communication, PCIe uses a serial link connection architecture that utilizes a point-to-point topology, which makes PCIe more reliable, faster overall, and less expensive to produce than the PCI bus. Therefore, most motherboards and computers today are configured with PCI-e slots for expandability capabilities.
What Is PCIe Used for
The purpose of using PCIe is to achieve significantly improved system throughput, scalability, and flexibility at a lower cost.
Due to its robust scalability, PCIe supports devices including graphics cards, solid-state drives (PCIe interface), wireless network cards, wired network cards, sound cards, video capture cards, PCIe to M.2 interface, PCIe to USB interface, PCIe Transfer Type-C interface, etc.
PCIe not only has a high transfer rate but is also good in compatibility. It is compatible with PCI at the software level, version upgrade, backward compatible with PCI software, and supports hot plug.
Different Types of PCIe
The PCIe standard is future-proof and continues to evolve to provide systems with higher throughput. Currently, the PCIe standard has developed from the first generation to the sixth generation, and connection speeds double with each new generation.
The throughput of the PCIe 1.0is 2.5Gbps, the PCIe 2.0 reaches 5.0Gbps, and the latest PCIe3.0 standard supports a rate of 8.0Gbps. Most current processors, computers, and motherboards support PCIe Gen 3 architecture, while newer applications require PCIe 4.0 performance speeds.
Now the PCI-E slot has become the main expansion slot on the motherboard. And it basically focuses on PCI-E x16/x8/x4/x1 four types.
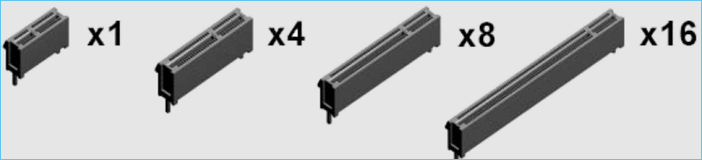
- PCI-E x16: The x16 slot is 89mm in length, has 164 pins, and has a bayonet outside the motherboard. The slot has excellent compatibility and can be backward compatible with x1/x4/x8 level devices, which is the universal slot of PCI-E.
- PCI-E x8: The x8 slot is 56mm long and has 98 pins. For compatibility, some PCI-E x8 slots are processed into the form of PCI-E x16 slots, but only half of the data pins are valid. That is to say; the actual bandwidth is only half that of a real PCI-E x16 slot.
- PCI-E x4: The length of the PCI-E x4 slot is 39mm, which is also realized by reducing the data pins based on the PCI-E x16 slot. However, like the PCI-E x8 slot, most PCI-E x4 slots are now in the form of PCI-E x16 or x8 slots or expanded to M.2 interfaces for compatibility.
- PCI-E x1: The length of the slot is the shortest, only 25mm. The motherboard chip usually provides the bandwidth of the PCI-E x1 slot. It is mainly used for independent network cards, independent sound cards, USB 3.0/3.1 expansion cards, etc. to the PCI-E x1 slot.
Related Articles
- Difference Between Cloud Sync and Backup and Cloud Storage
- RAM vs. ROM: 8 Differences between RAM and ROM
- Windows 11 Is Not Activated: How to Activate Windows 11 OS for Free
- What Is DAS(Direct Attached Storage)?A Beginner Guide for DAS