What Is VMM? Virtual Machine Manager Explained (All You Need to Know)
Virtual Machine Manager (VMM), a "hypervisor," is a hardware virtualization technique that allows you to run multiple operating systems on a host computer. In other words, it manages a virtual environment through a centralized interface providing the ability to install and configure multiple VMs.
The hypervisor provides a virtual operating platform and manages the execution of the different operating systems primarily on server hardware. Microsoft's VMM also supports ESXi and vCenter, allowing you to manage the entire virtual manager infrastructure with the help of a single console.
What Is VMM?
VMM stands for Virtual Machine Manager. It is part of the System Center suite offered by Microsoft, used to deploy and manage traditional data centers. The VMM helps provide you with an easy-to-use unified management monitoring of your infrastructure/data centers while improving performance across all service providers and the Azure cloud.
How Does VMM Work?
A VMM offers you a console consisting of all the virtual machines in a network to centrally manage them. You can make changes to the underlying network/storage at any time and run various commands.
These commands can help you create new VMs, move VMs from one server to another, modify the underlying network, increase resources, and ensure the VMs run smoothly without errors.
What Is VMM Used for?
VMM can be used for the following:
1. Datacenter: Control, manage and configure your datacenter as a single fabric in VMM. The components in a data center include virtualization servers, networking, and storage arrays. A VMM provides you with the resources to create and deploy virtual machines to local cloud networks. Learn about data centers here.
2. Virtualization hosts: A VMM can also help you create and manage VMware and Hyper-V virtualization hosts and machines. Learn what virtualization is here.
3. Networking: VMM helps you create network virtualization, including support for network gateways. Using gateways on virtual networks can help you connect to physical networks. You can add networking resources defined by IP subnets, virtual LANs (Local Area Network), and static IP addresses.
4. Storage: A VMM can help you assign, classify, and allocate remote and local storage servers. The VMM even supports block storage such as Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) and Storage Area Networks (SANs).
5. Library resources: The VMM fabric also has a library of file-based and non-file-based resources. These resources are used to deploy and manage VMs on virtualization host devices.
How to Install and Uninstall VMM on Windows?
Installing and Uninstalling VMM on Windows can get a bit challenging. However, if you follow our guide, you'll be able to set it up on your PC without any hiccups.
Note: Before you start the installation process, make sure you meet the system requirements. You can learn about system requirements here, and you also need to have local admin permissions on the computer. Moreover, the service account should be an administrator on the VMM server.
1. How to Install VMM?
Here's how you can install VMM on your Windows PC:
Step 1: Kill any tasks running in the background and make sure your computer is updated.
Step 2: Right-click the setup.exe, and then click "Run as administrator" to start the Virtual Machine Manager installation process.
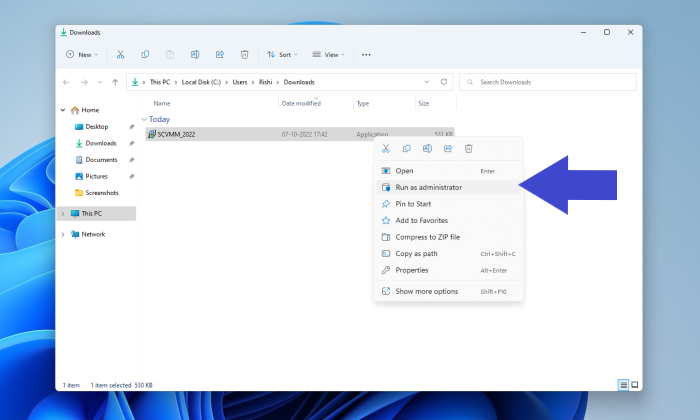
Step 3: Now, click the "Install" button, select the VMM management server check box and click "Next."

Step 4: The VMM console should be installed.
Note: If you're installing the VMM on a cluster node, you'll be presented with an option to make the management server highly available.
Step 5: Go to the product registration information page and provide the required information.
Note: If you don't enter a product key, VMM will expire in 180 days, and you won't be able to use it.
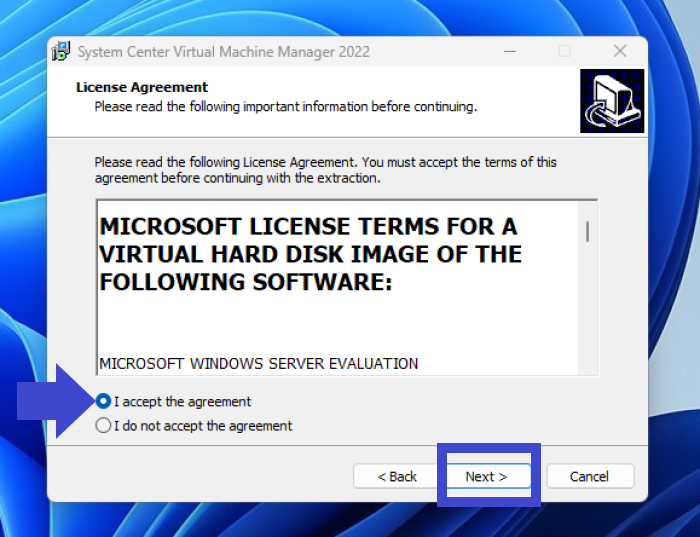
Step 6: Review the license agreement and select all the 3 checkboxes. Also, make sure to review Microsoft's data collection policy.
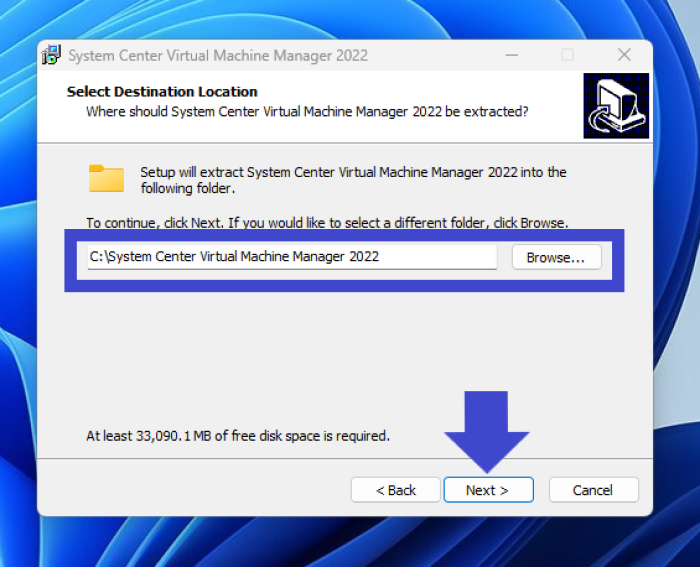
Step 7: Use the default path for the VMM program files, and then click on the Next button.
Note: If your computer does not meet the installation requirements, a window that contains information about the requirements appears.
Step 8: If you are installing the VMM server on a computer with a SQL Server, then type the name of the computer in the Server name box or type localhost. However, if the SQL Server is in a cluster, then type the cluster name.
Note: You don't need to specify a "Port value" if you don't have a SQL Server running on your PC.
Step 9: Specify the account the VMM will use. You can't change the account after installation.
Step 10: Now, select whether you want to store encryption keys in Active Directory.
Step 11: Complete the Port and Library configuration by using the default values.
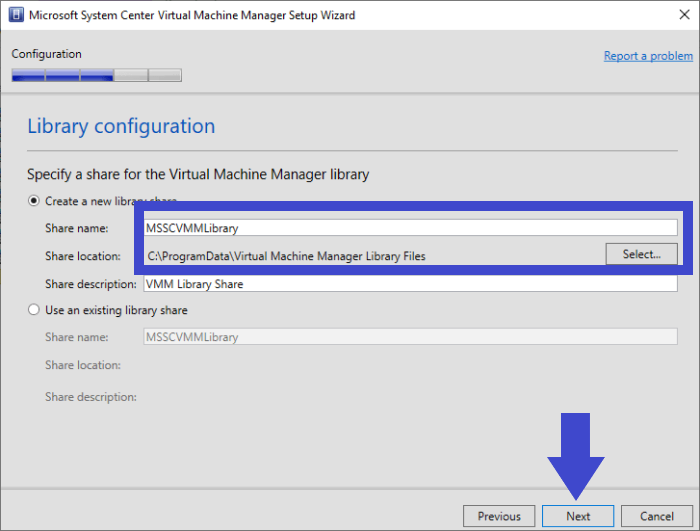
Note: You can also add library shares and servers by using the console or the command shell after the installation completes.
Step 12: Finally, review your selection and then click on the Install button and let the setup complete successfully. Now, click on the "Close" button to finish the installation.

2. How to Uninstall VMM?
If you want to uninstall VMM from your PC, you can do so by following the steps below:
Step 1: Close the VMM console and command shell.
Step 2: Go to the "Control Panel" and select the "Uninstall a program" button.

Step 3: Now, double-click on the "Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager" tab and click on "Remove Features."
Step 4: Select the "VMM management server and console" checkbox, and click on Next.
Step 5: Now, remove the VMM database and the credentials for the database and click Uninstall.
Step 6: Finally, the VMM is uninstalled.
Note: The following will still remain after you uninstall VMM:
- File Server Remote Management
- Windows Standards-Based Storage Management firewall rules
Related Articles
- What Is Core Sync Mac? How To Use It? [Lately Explained in 2022]
- Ways to Delete Windows 7 Backup [Updated 2022]
- CMR vs. SMR Hard Drive: Which One is Better to be Choosen?
- What Is NVMe: One of the Fastest SSD Data Storage [2022 All You Need to Know]