All You Want to Know about exFAT, FAT32, and NTFS
When a new USB flash drive or external hard drive is plugged into a Windows computer, the system automatically opens a window prompting the user to format the device, offering three file format options: NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT.
Many users are unaware of the details behind three file formats, instead following pop-up window instructions. Windows lacks detailed explanations for these formats, leaving users uninformed. This article aims to provide a detailed explanation for these issues.
What is File System?
The file system is the way a system stores and arranges files, with differences between various file systems related to how data is stored on the hard drive, including file names, permissions, and other attributes.
Windows supports three file systems: NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT. NTFS is the most widely used modern file system, commonly found on built-in hard drives of Windows computers. FAT32, with a longer history, is less compatible with modern file formats but more compatible with other platforms like Linux, Mac, and Android. exFAT is an alternative to FAT32, supported by many devices and operating systems, but currently not widely used.
The Differences Between exFAT, FAT32, and NTFS
The differences between CSV, JSON, and XML file formats can be illustrated through a simple example. CSV files are plain text files that contain a series of values separated by commas, making them easy to read and write.
NTFS: NTFS (New Technology File System) is the default file system for HDD and SSD created by Microsoft, popularized after Windows 2000. It excels in security, ease of use, and stability, making it the most widely used file system. NTFS supports MBR hard drives up to 256TB and GPT hard drives up to 128EB. When partitioning a hard drive on a computer, NTFS is a suggested choice, but it's not recommended for USB flash drives as it can shorten their lifespan.
FAT32: FAT32, short for File Allocation Table 32, is a file system introduced in Windows 95 to replace FAT16. It's commonly found on USB flash drives and offers compatibility with various operating systems. However, its main limitation is that it only supports single file sizes up to 4GB, resulting in an error message when trying to transfer larger files.
exFAT: exFAT (Extended File Allocation Table) is a file system created by Microsoft to replace FAT32. Unlike FAT32, exFAT supports transferring files larger than 4GB, making it more versatile. It is compatible with both Windows and Mac computers, outperforming NTFS in this regard. However, exFAT lacks a file log function, which means it cannot record disk modification records.
How to Convert Between exFAT and FAT32 and NTFS
Users may encounter defects in their file system, prompting the need to convert to a different one. Fortunately, there are tools available to assist with this process, and one recommended option is Qiling Partition Master.
Qiling Partition Master is a tool designed for partition management, allowing users to resize, move, merge, and create partitions. It also provides features to troubleshoot common issues, such as fixing low disk space, checking disk errors, and resolving problems with extending volumes.
To convert between exFAT, FAT32, and NTFS, simply use the clicks within Qiing Partition Master. You can download the tool and follow the guide to convert one file system to another, such as converting FAT32 to NTFS.
Qiling Partition Master Free
- Support creating, shrinking, extending, merging, moving partitions for free.
- Support disk surface test, converting file system, formatting/deleting volumes.
- 1. Clone a hard drive to another drive, either as a full clone or a selective clone. 2.
Convert FAT32 to NTFS
Step 1. Install and launch Qiling Partition Master on your computer.
Step 2. Click the hard drive partition and choose the "Format" option.
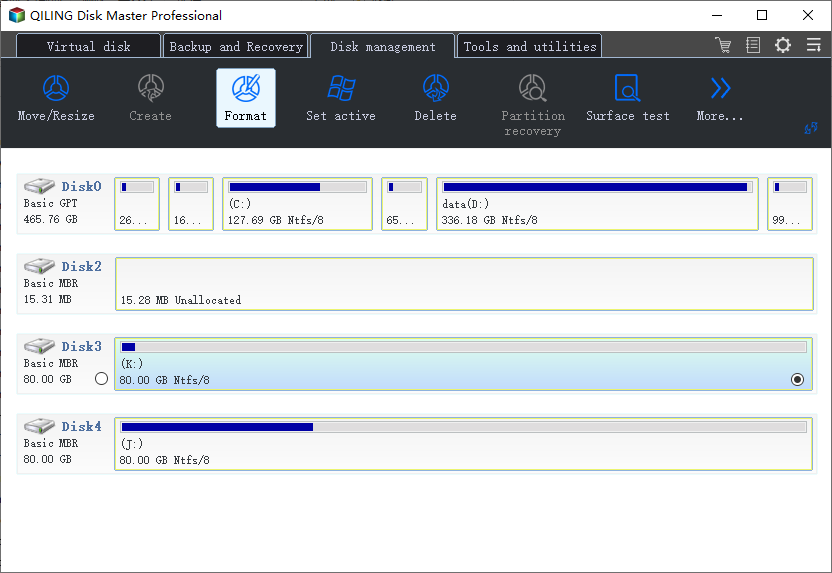
Step 2. In the new window, set the Partition label, File system, and Cluster size for the partition, then click "Proceed".
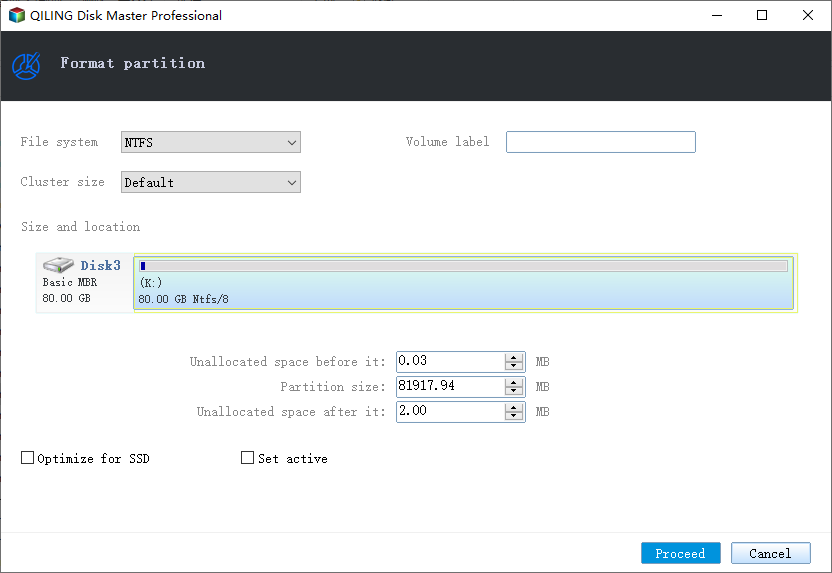
Step 3. Then you will see a warning window, click "OK" in it to start formatting the partition to FAT32/EXT2/EXT3/EXT4.
The Bottom Line
The choice between exFAT, FAT32, and NTFS ultimately depends on the device being formatted. For internal drives like HDDs and SSDs, NTFS is recommended. However, for external devices like USB flash drives, formatting in FAT32 or exFAT is preferable. The main distinction between FAT32 and exFAT lies in their ability to transfer files larger than 4GB, making exFAT a better option for large file transfers. By applying these file systems flexibly, users can effectively manage their partitions and drives.
Related Articles
- 3 Easy Ways on How To View Partitions (2022)
- How to Troubleshoot Critical Process Died Error in Windows 10/8/7 (10 Solutions)
- MBR to GPT: How to Convert MBR to GPT in Windows 11/10/8/7 [2022 New]
- What Is USB Format for PS3 | How to Format PS3 USB
- How to Remove, Delete or Format GPT Disk Partition
- [2021] Three Ways to Convert MBR to GPT Disk on Windows 10