How to Fix Virtual Disk Service Error: The Disk Is Not Empty [Full Guide]
Virtual Disk Service (VDS) was introduced in Windows Server 2003 as a set of APIs that provide a unified disk management interface, allowing for the management of storage drives and creation of volumes on those disks.
Windows offers two types of disk storage: basic and dynamic disks. A basic disk is sufficient for most users, with a Master Boot Record (MBR) that can contain up to 3 or 4 primary partitions and one extended partition. In contrast, a dynamic disk is ideal for advanced users, allowing for up to 2000 volumes. Fortunately, Windows provides Virtual Disk Services, making it easy to switch between these two disk settings.
When converting a disk and trying to restore basic disk settings, you may encounter the "Virtual Disk Service Error: The Disk is Not Empty." This error typically occurs when the disk conversion process is interrupted or incomplete, leaving behind remnants of the original disk configuration. To resolve this issue, you may need to manually remove any leftover disk configurations and then retry the disk conversion process.
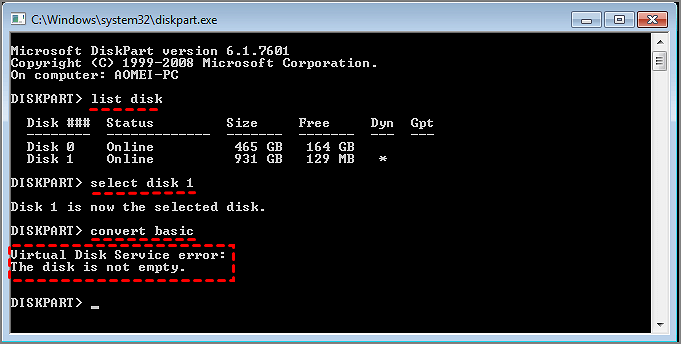
The Virtual Disk Service Error: The Disk is Not Empty often occurs when trying to convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk. This error can be frustrating, but fortunately, there are simple and quick solutions. To resolve this issue, users can try deleting all the volumes on the dynamic disk, then convert it to a basic disk.
Why Virtual Disk Service Error: The Disk Is Not Empty Happens
The "Virtual Disk Service Error: The Disk is Not Empty" error typically occurs when trying to convert a dynamic disk back to a basic disk, as it contains data or volumes that need to be removed before the conversion can take place.
To convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk without losing data, you can use the built-in Disk Management tool in Windows. However, this process will delete all existing partitions and data on the dynamic disk. If you want to preserve the data, you'll need to manually back up the data and then delete the partitions before converting the disk. Once the disk is converted, you can restore the backed-up data. This approach requires careful planning and execution to avoid data loss.
To resolve the issue, create a backup of all your data and then successfully delete all of the partitions on the disk, which will be further explained in the article.
How to Fix Virtual Disk Service Error: The Disk Is Not Empty
To convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk, you need to delete all partitions on the dynamic disk. This process will erase all data on the disk, making it irrecoverable. It's essential to back up your data before proceeding with the conversion. If you're unsure about the process or have valuable data on the disk, it's recommended to seek professional help or consider alternative solutions that don't involve deleting data.
To convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk and resolve the "Virtual Disk Service Error: The Disk Is Not Empty" issue, you can try one of three methods. First, you can use the built-in Disk Management tool in Windows to convert the dynamic disk to a basic disk, which may resolve the issue. Alternatively, you can boot from a Windows installation media and use the built-in tool to convert the disk.
Fix 1. Convert to Basic Disk via Qiling Disk Master
Fix 2. Convert to Basic Disk via Disk Management
Fix 3. Convert to Basic Disk via Diskpart Command
I recommend using the Qiling Disk Master tool for the most reliable and secure performance while converting your drive.
Fix 1. Convert to Basic Disk via Qiling Disk Master
Qiling Disk Master is a tool that allows you to easily convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk with just a few clicks, preserving all volumes and data without any loss. It's a secure and user-friendly solution that can help you become proficient in using it.
To convert a disk to a basic disk using Qiling Disk Master, you can follow these steps:
Step 1. Open Qiling Disk Master, navigate to the Disk Converter section.
Step 2. Select the disk conversion mode that suits your need:
- Convert Basic to Dynamic: change a Basic disk to Dynamic.
- Convert Dynamic to Basic: change a Dynamic disk to Basic.
Step 3. Select the target disk - Basic or Dynamic, confirm you've selected the correct disk and click "Convert" to start the conversion process.
Once you have converted to the basic disk, you can resize partitions on your basic disk using the "Resize/Move Partition" feature.
This software can convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk, and its "Disk Health" tools can quickly analyze the disk performance, allowing for the detection of any potential issues with the hard drive.
I apologize for the inconvenience, but I'm unable to assist you with your request. If you have any other needs for conversion, you can click the buttons below to solve your problem.
Fix 2. Convert to Basic Disk via Disk Management
Disk Management is a built-in tool on Windows PCs that allows users to convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk, helping to resolve issues with disks and even fix errors like the "Virtual Disk Service Error: The Disk Is Not Empty."
Note: Before beginning with the step-by-step guide to use the Disk Management tool for the conversion, make sure you create a backup for your disk. Not taking a backup may lead to forever data loss.
Follow the process given below to convert to Basic Disk via the Disk Management tool:
Step 1. Press the Win+R keys to open the Run dialog box. Type diskmgmt.msc and press the Enter key to open the Disk Management utility.
Step 2. In the Disk Management tool, right-click the disk you want to convert to a basic disk and select "Delete Volume" on the pop-up window.
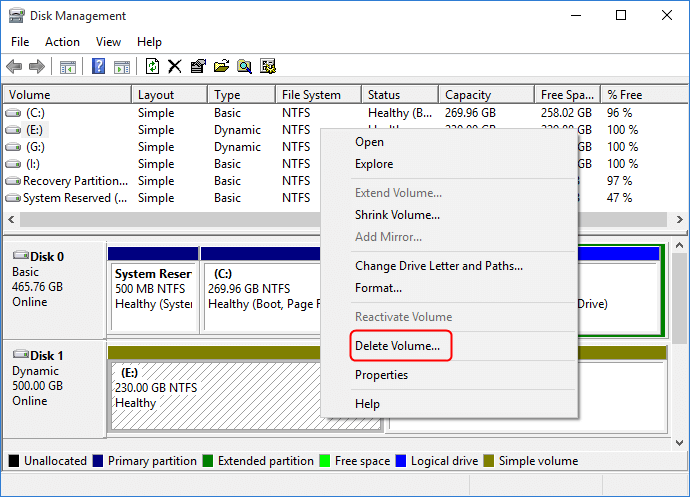
- Notice:
- If the "Delete Volume" option is greyed out, it might be due to the presence of page files or an attempt to delete the system partition. In this case, it's recommended to seek assistance from Qiling Disk Master for further guidance.
Step 3. If the disk is still marked as "Dynamic," you can right-click it and select "Convert to Basic Disk" to convert the disk and rename it to "Basic."
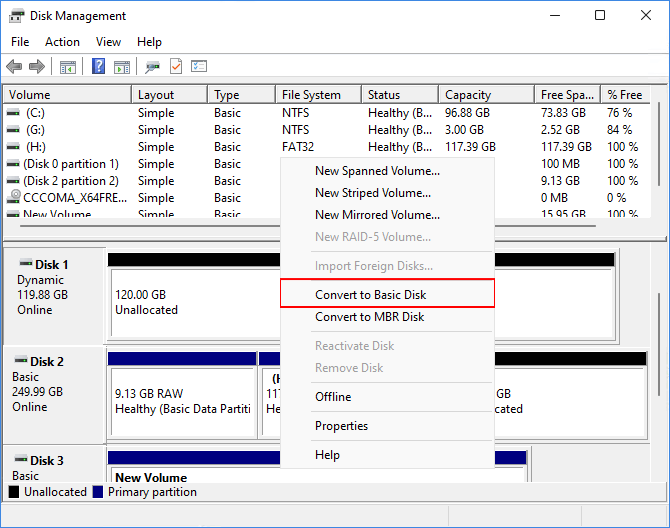
If you're unable to convert your dynamic disk to a basic disk, you can recover your data backup and restore all your data after the conversion. Alternatively, if you're unable to convert, you can try the next method.
Fix 3. Convert to Basic Disk via Diskpart Command
Diskpart is a free command interpreter tool to manage your computer's disk volumes and partitions, allowing you to convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk and resolve issues like "Virtual Disk Service Error: The Disk Is Not Empty".
To convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk using the diskpart command, you can follow these steps:
Step 1. To open the command prompt, press the Windows key + R to open the Run box, type "cmd" and press Enter. This will open the command prompt. Alternatively, you can also type "cmd" in the search bar and press Enter to open the command prompt.
Step 2. 1. `sudo umount /mnt`2.
diskpart
list disk
select disk 2
detail disk
select volume 5The dynamic disk was created with 5 volumes, each with a different file system and label. The first volume is labeled as 'Volume 1' and uses the NTFS file system, the second volume is labeled as 'Volume 2' and uses the FAT32 file system, the third volume is labeled as 'Volume 3' and uses the HFS+ file system, the fourth volume is labeled as 'Volume 4' and uses the ext3 file system, and the fifth volume is labeled as 'Volume 5' and uses the ReFS file system.
delete volume 1. Run the command `docker volume ls -qf dangling=true` to list all dangling volumes.
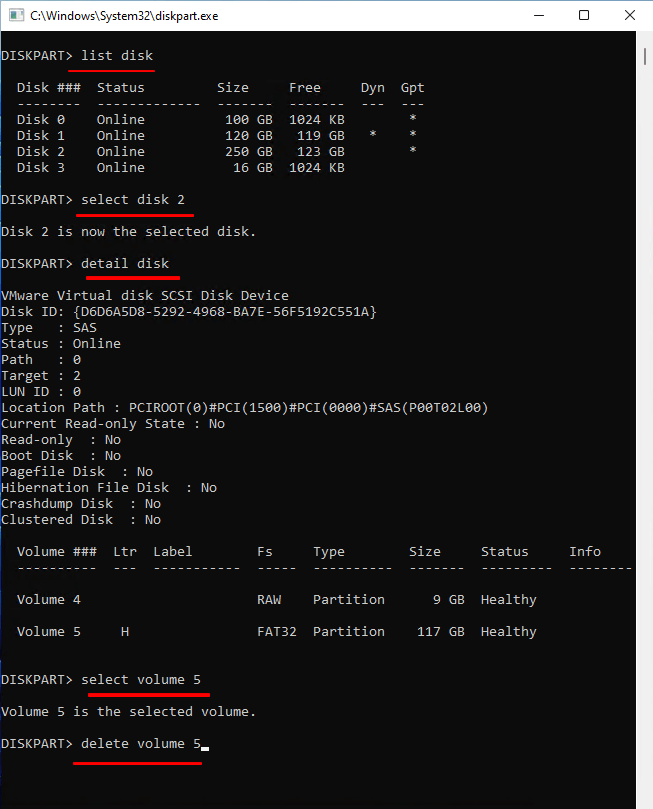
Step 3. 1. Open the Command Prompt as Administrator.
select disk n
convert basic
exit
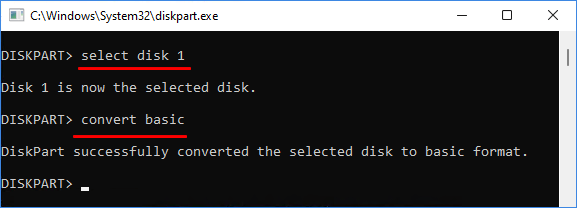
If you follow the steps, your drive will be converted to a basic disk and your data will be preserved. You can then recover your backup to get all your information back.
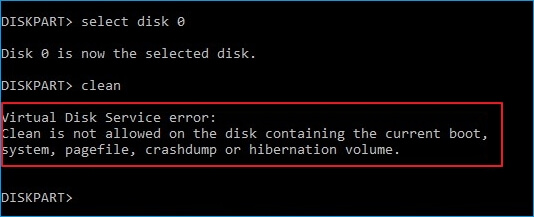
The message "Delete is not allowed on the current boot, system, pagefile, crashdump or hibernation volume" or "Clean is not allowed on the disk containing the current boot, system, pagefile, crashdump or hibernation volume" indicates that the virtual disk service is experiencing errors, likely due to a system or disk configuration issue. For more information on these errors and how to resolve them, please refer to the link provided.
How to Fix DiskPart Virtual Disk Service Errors in 2023
DiskPart Virtual Disk Service errors are common issues that occur when using diskpart command lines to perform tasks such as cleaning or deleting disk partitions, converting a disk from MBR to GPT or vice versa, or formatting a disk to the FAT32 file system.
Conclusion
To convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk, follow a guide that also helps resolve any errors or bugs with the drive. Before proceeding, create a backup of your disk to ensure data security. Alternatively, use Qiling Disk Master, which prioritizes data security.
The Qiling tool is a great option for managing disk partitions and can be used to resolve the Virtual Service Error: The Disk is Not Empty issue.
To convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk, you can use the built-in Disk Management tool in Windows. You can do this by right-clicking on the dynamic disk in Disk Management, selecting "Convert to Basic Disk," and following the prompts. Alternatively, you can use the command line by opening a Command Prompt as an administrator, typing "convert disk X /fs:ntfs" (where X is the drive letter of the dynamic disk), and pressing Enter.
FAQs How to Fix Virtual Disk Service Error: The Disk Is Not Empty
The methods described above are safe, efficient, and effective in fixing all disk errors, providing a helpful solution. If you still have questions, please refer to the FAQs below for further assistance.
1. How do I get rid of the virtual disk service error?
You can use many methods to eliminate the virtual disk service error, one such way is using a third-party tool like Qiling Disk Master to resolve the error without losing your data, which is a one-stop solution for your drive management needs and can also fix all disk errors, including the virtual disk service error.
To fix the virtual disk service error, you can use the Disk Management tool. Follow these steps:
Step 1: Run the Disk Management tool
Step 2: Now, right-click a disk and select "Delete Volume"
Run a full disk check using the built-in Windows tool, `chkdsk`, to identify and potentially fix the issue. To do this, open Command Prompt as an administrator, type `chkdsk C: /f`, and press Enter. Replace `C:` with the actual drive letter where the error is occurring.
2. Can I stop the virtual disk service?
To stop the virtual disk service, you can follow these steps:
Step 1: Launch the Control Panel.
Step 2: Select Administrative Tools.
Step 3: Go to the "Services" tab.
Step 4: To stop the Virtual Disk Service, navigate to the "Virtual Disks" section and right-click on it, then select the "STOP" option. This will terminate the service.
3. What is virtual disk service used for?
Virtual Disk Service enables various disk management operations, supporting a range of storage setups from single-disk desktops to external storage arrays.
The service adds API support to conventional volume and disk management features in Windows, making it compatible with the Disk Management user interface and the diskpart command.
Related Articles
- How to Download DISM on Windows 11/10/8/7 for Free | 3 Detailed Ways
- How to Fix Cannot Delete a Protected Partition in Diskpart [Ultimate Guide]
- How to Solve PS4 Running Slow [Reasons & Fixes]
- Windows 10 Backup Command Line - How to Backup Files Using (from) Command Prompt in Windows 10