Which Is the Best NTFS Allocation Unit Size, How to Set?
The "Allocate Unit Size" setting is a default option that can be changed from a drop-down menu, typically found when formatting a USB thumb drive or a hard drive.
The NTFS allocation unit size is the size of the cluster that allocates disk space for directories and files. The best allocation unit size depends on the type of files being stored, with smaller sizes suitable for files with many small pieces and larger sizes suitable for files with fewer, larger pieces. The allocation unit size can be set when formatting the drive, and it can also be changed later using the built-in disk management tools. However, changing the allocation unit size can cause data loss and other issues, so it's generally recommended to leave it at the default size.
What Means NTFS Allocation Unit Size
The allocation unit size, also known as cluster size, is the smallest chunk of data on a hard drive, which can be set during formatting. It's a setting that determines the smallest unit of space that can be allocated to a file. The allocation unit size is typically set to a power of 2, such as 4KB, 8KB, 16KB, 32KB, 64KB, or 128KB, but can be set to any value that is a power of 2. The choice of allocation unit size depends on the operating system and the intended use of the drive. A smaller allocation unit size can result in more efficient use of space, but may also result in slower performance.
To avoid wasting space on your hard drive, it's recommended to set a smaller allocation unit size, ideally equal to the size of an empty file, so that each file takes up only the space it needs, rather than being forced to fit into a larger block size. This will help save space and make your drive more efficient.
On an NTFS system with a 1MB allocation size, storing 10 files of 8KB each would occupy 10MB of space, not 80KB, demonstrating wasted space.
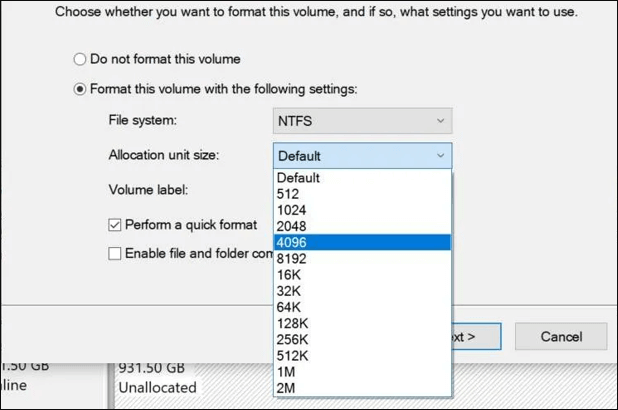
4 Kilobytes is the typical NTFS allocation unit size, but keeping it too small can slow down your PC due to increased allocation time, while keeping it too big can waste disk space.
You may also like:
What Is the Best NTFS Allocation Unit Size
For standard users, it's recommended to stick with the default 4096 bytes allocation unit size, as it aligns with the block size used by NTFS when formatting the hard drive. This default criterion can be adjusted based on specific partition needs, but for most users, using the default allocation unit size is sufficient.
NTFS Allocation Unit Size for Movies:
To optimize storage for a drive or partition used solely for movies, consider using a larger NTFS allocation unit size. This is because movie files can be quite large, often in the hundreds of megabytes or even gigabytes. Choosing a 2MB maximum allocation unit size can be beneficial, but keep in mind that smaller files like subtitles will be allocated the minimum of that space, potentially wasting some storage space.
NTFS Allocation Unit Size for Images:
If you have a strong drive to store images and music, it might change things, as music and image files are smaller than movie files, allowing you to keep allocation units smaller.
While most cases don't require a non-standard NTFS allocation unit size, there are a few instances where keeping it smaller than the default is suggested. However, if you have large files, setting it higher can improve your PC's performance by reducing fragmentation.
How to Set NTFS Allocation Unit Size
To change or reset the NTFS allocation unit size, you can either manually set it based on the partition or drive's characteristics, or simply leave it as the default. This involves scanning the partition or drive to determine the ideal allocation unit size, which can be a bit tricky. If you're unsure, it's perfectly fine to stick with the default value. However, if you're comfortable with making adjustments, you can manually set the allocation unit size to optimize performance and storage efficiency.
Method 1. Change NTFS Allocation Unit Size with Qiling Partition Master
With the help of a professional partition manager, you can change the NTFS allocation unit size, and a top-notch software for this is Qiling Partition Master Professional, an all-in-one free tool designed for every user.
Step 1. Right-click the partition you need to change the cluster size for, select "Advanced" and click "Change Cluster Size".
Step 2. To adjust the cluster size for a disk partition, click the size list below the New size section and select a desired cluster size from the available options.
Step 3. Click "Proceed" to confirm the operation.
Qiling Partition Master helps you imitate or clone partitions from one hard disk to another without risking data loss on your disk partition, making it a useful tool when you're bored of copying and pasting things. The best features of Qiling Partition Master include. (Note: I removed the list as it was not provided in the original text)
- Create or Remove a partition: The drive saves all data after creating or deleting partitions.
- Move or Resize the partition: You can change the used partition space without losing any data by moving or resizing it to adjust the disk space as needed.
- Delete/Format Partition: You can use the free Qiling partition manager to effectively format or reformat a hard drive or eliminate a partition.
- Quick Partition a New Disk: The disc can be installed directly to the computer, and the operating system can be installed to the disc without a partition. This is a suitable option for installing a fresh disc without a partition. The disc can be installed directly to the computer, and the operating system can be installed to the disc without a partition.
- System Partition Extension: To resolve the "C drive full" error, you can expand the system partition to free up space. This involves resizing the partition to occupy the available space on the disk, making room for new files and applications. This process can be done using built-in Windows tools, such as Disk Management, or third-party software like EaseUS Partition Master.
Method 2. Change NTFS Allocation Unit Size with CMD
To change the NTFS allocation unit size for videos and games using the CMD command prompt, follow these steps. You can use diskpart commands in CMD to alter the NTFS allocation unit size. This process involves using the diskpart command to select the disk, then use the "convert" command with the "allocation size" option to change the NTFS allocation unit size.
Step 1: To launch the run, hit window + R.
Step 2: To access the command prompt as the administrator, type "CMD" and hit Ctrl + Shift + Enter.
Step 3: Hit "Enter" to open Diskpart.exe after entering the diskpart.
Step 4: Type the below-mentioned command, and keep pressing enter:
- list disk
- choose disk * The target disc or partition's number is indicated by the * symbol. This symbol is used to specify which disc or partition the command should operate on.
- list division
- choose a partition
- format fs=ntfs unit=64k
Conclusion
The article explains what NTFS allocation unit size is and provides two methods to set one, as well as an alternative using third-party software or a built-in Windows application.
Qiling Partition can modify cluster size without extra cost, repartition hard drives, convert FAT32 to NTFS, and NTFS to FAT32 without formatting or losing data, among other disc partitioning-related tasks.
FAQ About NTFS Allocation Unit Size
The FAQs about NTFS Allocation Unit Size are given below to comprehend the topic better. If you have further problems, continue to read.
1. Does allocation unit size affect speed?
If the allocation unit size is too small, it may slow down your PC and make allocation longer, while making it too large will waste disk space.
2. What allocation unit size should I use for the NTFS flash drive?
If your flash drive is larger than 16GB, the ideal cluster size for NTFS is 16KB, but the default cluster size for NTFS drives is 4KB for drives between 7MB and 2TB in size.
3. What will happen if the allocation unit size is large?
Maintaining a minimum allocation size is beneficial when dealing with small files, keeping disk space manageable. However, when working with larger files, a higher allocation size can improve system performance by reducing the number of blocks to access. But, extremely large allocation sizes can consume maximum disk space, making it essential to strike a balance between these two approaches.
Related Articles
- Full Guide: How to Fix HP Laptop Black Screen
- How to Use the Apple Menu on Mac? [New Information]
- Upgrade Hard Disk to Fix 100% Disk Usage Error in Windows 10 & More Tips
- [Detailed Info] How to Upgrade to macOS Ventura Without Losing Data