What Is Single User Mode Mac? How to Boot Into it? [Everything you need to know]
Apple revenue has only increased from 108 billion USD to 365 billion USD in the past decade. A significant amount of this revenue comes from Mac devices only. A Mac device can be a fantastic user experience due to its diverse functionality and durability. Users often have to start their Mac in single-user mode. It is hence essential to know all about it.
The different modes in the Mac include safe mode, single user mode, etc. Based on the user's needs, it is accessible to login in single user if the Mac operating system has failed or stopped working. Multiple other factors may contribute to the necessity of using this mode. Hence, users may often look to know more about this mode and the detailed process to boot it. It is easy to go through the exact steps followed by the quick questions related to the same. Starting with the brief definition of single-user mode Mac.
What Is Single User Mode Mac
The single-user mode works in the minimal UNIX environment. It has a primary console supporting the command line, minimum system daemons in running state, and no graphical shell. The single-user mode itself indicates a typical UNIX multi-user environment. Hence, only the maintenance tasks are performed to access the generally shared resources by forcing the multi-user system to a single user.
The single-user mode Mac is used to repairing the startup drive, eject stuck media from the drive, etc. The minimalist environment of the single-user method allows the users to follow specific essential commands. These commands can perform the start of different system daemons, reading or writing files, mounting other storage devices, performing basic repairs to the startup drive, etc. All these UNIX demands can be quickly added to the single-user mode.
You may be interested in How to Factory Reset Mac.
How to Boot into Single User Mode Mac
Depending on the type of the Mac, it is easy to boot into single-user mode. There are three common types of Mac based on the T2 chip.
Steps to check if Mac has a T2 Chip:
T2 security chips were introduced by Apple in 2018. The following steps are simple to know about the T2 chip availability in the Mac. These are:
Step 1. Select the Apple menu and select the "About this Mac" option.
Step 2. Select the "system report" menu and "controller."
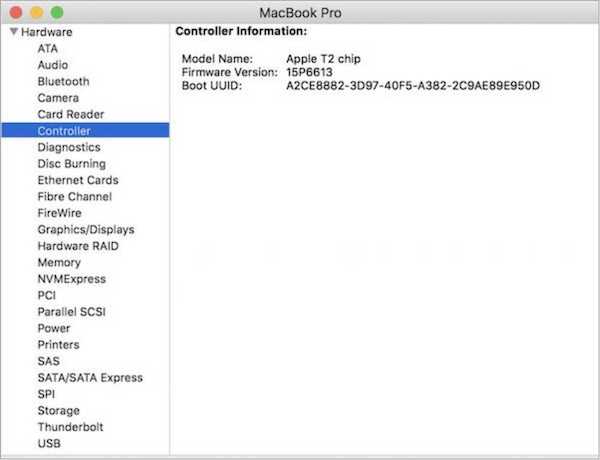
Step 3. Search for any reference to the T2 security.
Top three Mac categories:
Hence, based on the T2 security chip, Mac devices can be categorized into the following three categories:
- 1. Boot Single-user Mode in Apple Silicon Macs
- 2. Boot Single-user Mode in Macs with T2 Security Chips and Intel CPU
- 3. Boot Single-user Mode in Older Macs Without T2 Security Chips
1. Boot Single-user Mode in Apple Silicon Macs
Step 1. Shut down the Mac. Then press and hold the "power" button on the Mac.

Step 2. Release the power button once the spinning globe or Apple logo is reflected.
Step 3. Select the "Disc Utility" menu from the "macOS Utilities" menu.
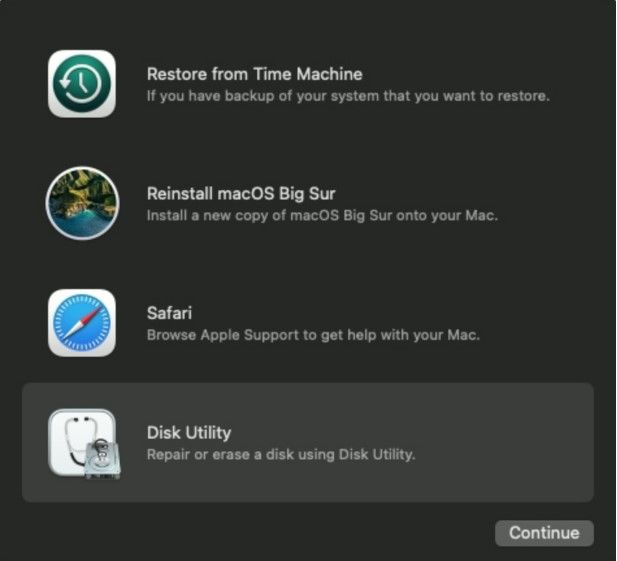
Step 4. Click on the startup volume and press mount. Quit the disk utility and select Terminal in the utility menu.
2. Boot Single-user Mode in Macs with T2 Security Chips and Intel CPU
The Macs with T2 security chips and Intel CPU prevents the working of single-user mode. This mode setting is stored in the "Startup Security Utility" in recovery mode. It is easy to use the Terminal menu to boot this mode in Macs with T2 security chips and Intel CPU in the following way:
Step 1. Turn off the Mac and power up by holding Command-R.
Step 2. Wait for the Apple Release "power" button once the spinning globe or Apple logo is reflected.
Step 3. Select the "Disc Utility" menu from the "macOS Utilities" menu.

Step 4. Click on the startup volume and press mount. Quit the disk utility and select Terminal in the utility menu.
3. Boot Single-user Mode in Older Macs Without T2 Security Chips
Step 1. Shut down the Mac. Power up your system and immediately hold the Command + S button configuration.

Step 2. Enter your password when prompted. Release the command S after going through the black background and white text.
Step 3. You can now enter the commands as per your requirement. Then finally, once you're done, type and enter shutdown -r to restart your computer.
Conclusion
Thus, it is easy to understand all about the single-user mode Mac and how to boot a Mac device into it. The quick definition of this mode, followed by the detailed steps to boot into it, gives details about this useful mode. It is ideal for security purposes or exclusive access to shared resources in special cases like repairs.
It is one of the easiest ways to troubleshoot and fix issues in Mac. The command-line interface makes it easy for the users to solve Mac issues without seeking external help. Not to miss are the related top-rated questions to easily solve the possible queries.
FAQs
It is easy to solve main queries related to the single-user mode Mac when you can go through a detailed list of the probable questions related to it. So, here is a quick check on the top questions faced by users, followed by the best solutions:
1. What are the commands in single-user mode on Mac?
The top commands in single-user mode on Mac are starting different system daemons, performing basic repairs for drive startup, file writing or reading, etc.
2. How do you get into single-user mode on a Mac?
It is easy to get single-user mode on older Macs without a T2 security chip, Apple Silicon Macs, and Macs with Intel CPU and T2 security chip. The quick steps for the same are clicking on the Mac shut down, pressing the power button, and holding "Command- S." Release the "Command-S" after seeing black background and white text. The user may have to enter the password if needed.
3. What is the difference between single-user and multi-user operating systems?
The single-user operating system provides facilities to one user at a time, while the multi-user offers resources and services to different users simultaneously. Examples of single-user operating systems are single-user multi-task OS, single-task OS, etc. Distributed OS, Timesharing OS, etc., are examples of multiple-user operating systems.
4. What can you do in the single-user mode, Mac?
The single-user mode in Mac allows administrative tasks and troubleshooting of different Mac problems. In addition, it allows quick booting of Mac with no drive volumes mounted on startup, minimal text-based environment with no graphics, etc.
5. What is the main purpose of single-user mode in Mac?
The key purpose of the single-user mode in Mac is the dedicated maintenance of multi-user environments like network servers. So it is because the key responsibility of this mode is to boot the multi-user computer operating system into a single superuser.
Related Articles
- Can I Upgrade My Motherboard and CPU Without Reinstalling Windows 10? [New Updated 2022]
- Clean C Drive without Formatting in Windows 10/8/7 [Tested & Worked]
- 5 Best Registry Cleaner for Windows PC [Updated 2022]
- (2 Simple Solutions) How to Re-image a Computer for Windows 11/10/8/7