Activity Monitor Mac: How to Open and Use It [3 Tips to Optimize Mac]
PAGE CONTENT:
We'll show you how to open Activity Monitor using Spotlight, the Dock, Finder, and keyboard shortcuts. Once open, we'll review its features, tab by tab, to help you get the most out of it.
Learning to use Activity Monitor on your Mac is essential whether you're a beginner or a power user. This tool allows you to monitor and manage the resources your Mac is using, including CPU, memory, and disk usage. By understanding how to utilize Activity Monitor, you can identify and troubleshoot issues, optimize your Mac's performance, and even detect potential security threats.
What Is Activity Monitor on MacBook Pro/Air
Activity Monitor is a useful app pre-installed on all macOS devices, providing in-depth data on system performance, processes, and resources, similar to a Task Manager.
Activity Monitor is a crucial tool for Mac users to diagnose performance issues, identify resource-intensive programs, and optimize their computer's performance.
Mac's Activity Monitor provides a detailed view of running programs and resource usage, offering insights into your computer's performance and helping you manage its various operations.
Activity Monitor allows you to track various system metrics, such as CPU and memory usage, energy consumption, disk reads and writes, and network traffic. With it, you can identify which programs are consuming the most system resources, monitor system performance, and troubleshoot any issues that arise.
How to Open Activity Monitor Mac
Activity Monitor can be accessed through the Applications folder or a Spotlight search, and it provides a detailed view of ongoing processes, resource utilization, and other system information. It allows users to monitor and manage their Mac's performance, making it a valuable tool for optimizing system efficiency.
On a Mac, the robust Activity Monitor may be accessed in various ways, making it more accessible. One way is to search for it in Spotlight, which can be accessed by clicking the magnifying glass icon in the top right corner of the screen. Another way is to use Spotlight search by pressing Command + Space, typing "Activity Monitor," and pressing Enter.
- Press the Mac Spotlight shortcut "Command + Space" and enter Activity Monitor in the search box.

- To open Activity Monitor, click the Spotlight icon in the top-right corner of the menu bar, type "Activity Monitor," and select it from the search results.

- Open Finder, navigate to Applications > Utilities, and double-click Activity Monitor.
By opening Activity Monitor, you can view a comprehensive list of all processes and resources currently used on your Mac, and force quit unresponsive applications, all while keeping tabs on several areas of your system's performance thanks to the tabbed UI.
Activity Monitor is a built-in tool on Macs that allows users to monitor and control their computer's performance. By using Activity Monitor, users can see which processes and applications are consuming system resources, identify potential bottlenecks, and take action to optimize their Mac's performance.
How to Use Activity Monitor Mac
To become proficient with Activity Monitor, we've created a video guide that walks you through its features and capabilities. The video covers opening Activity Monitor, navigating its layout, and closing unneeded programs, providing a visual learning experience for those who learn better by seeing.
Activity Monitor provides detailed information about processes running on your Mac, with various tabs offering different views. The "My Processes" tab shows processes running under your user account, while the "System" tab displays processes running under the root user, and the "Shared" tab shows shared user account processes.
🍏CPU
The "CPU" tab on a Mac shows which apps are using the most CPU power, displaying the CPU utilization percentage for each running process, making it easy to identify resource-hogging apps.
💾Memory
The Memory tab on a Mac displays memory usage details, including RAM usage by process and overall memory consumption. It allows users to track which processes are using the most RAM, helping to identify potential memory hogs.
With the Memory tab in Activity Monitor, you can free up your Mac to get more usable storage for installing new applications.
Delete Files Mac But Still No Space: 4 Fixes
If you're experiencing a lack of space on your Mac after deleting files, don't worry - there are effective solutions to fix this issue. One solution is to empty the Trash, which can free up a significant amount of space. Another option is to check for duplicate files and delete them to reclaim space.
💻Energy
The Energy tab allows you to see how much power each of your Mac's programs is using, enabling you to monitor your device's battery life and identify any power-hungry programs that may be draining your battery.
💽Disk
The Disk tab displays information about disk usage, including data transmission rates for reading and writing activities. It also shows which programs are using the disk the most, allowing you to adjust their access permissions to optimize performance.
🌐Network
The Network tab provides information on how a Mac uses networks, showing network bandwidth used and data delivered and received by each process, allowing users to identify which applications consume the most bandwidth by monitoring network behavior.
📂Cache
The Cache tab provides information on how your Mac's cache operates, displaying the total amount of data cached by each process, allowing you to monitor cache usage by various programs.
Deleting cache files on Mac can be done without affecting the use of the application, but be cautious not to delete important files. If a mistake is made, data recovery software can be used to recover deleted cache files.
To open Activity Monitor on a Mac, click the "Applications" folder on the dock, then click the "Utilities" folder. Alternatively, you can use Spotlight by pressing Command + Space and typing "Activity Monitor".
Bonus Tips: Optimize Your Mac Using Activity Monitor
To optimize your Mac's performance, you can use Activity Monitor to keep tabs on its performance and enhance it using the included features. Two optimization strategies involve terminating inactive processes and stopping apps from opening at startup, which can be achieved using Activity Monitor. By doing so, you can free up system resources and improve overall system speed.
Method 1. Quit Unresponsive/Unused Process
To terminate a stalled Mac program using Activity Monitor, open the app, find the stuck process in the list, click on it to select it, and then click the "Quit" button. This will close the program without affecting other processes running on your Mac. Alternatively, you can click the "Force Quit" button to immediately terminate the program, but be cautious as this may cause data loss or other issues if the program was in the middle of a critical operation.
Step 1. Open "Activity Monitor".
Step 2. To identify the unresponsive or unused process, open Activity Monitor, and look for the "Process Name" column, which will reveal the name of the process that is not responding or is not being used.
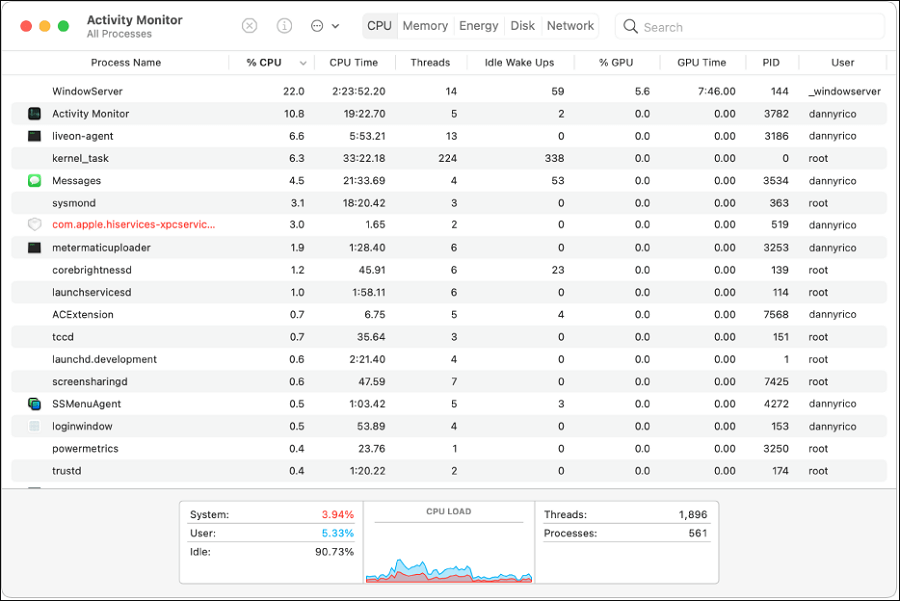
Step 3. Click the unresponsive process.
Step 4. To quit an app, click the "X" button in the Activity Monitor toolbar, select "Quit Process" from the "View" menu, or press the "Command + Q" shortcut.
Step 5. A confirmation dialogue asks whether you wish to exit. If you select "Force Quit", the procedure will be stopped. If you select "OK", the procedure will continue.
Quitting unresponsive programs on a Mac can improve efficiency and startup time, but it may also result in data loss if changes aren't saved before force quitting. In such cases, recovering the lost data on a Mac can be challenging without the use of professional data recovery software, such as Deep Data Recovery for Mac.
The Qiling data recovery Mac software is a reliable and powerful tool that can help recover lost files, including unsaved Word documents, Excel files, and PowerPoint documents, if you accidentally lose vital data when closing programs. This software can rescue files that have been lost or erased from various storage devices, providing a dependable solution for retrieving lost data.
Recover Unsaved Word/Excel Files in Crashed Office 2016 on Mac
If you've lost an unsaved Word or Excel file on your Mac, there are three effective methods to recover it. Firstly, check the AutoRecover feature in Word, which automatically saves a copy of your document at set intervals. You can also try the 'Open Recovered File' option in Word, which may have saved a copy of your file.
Method 2. Disable Unnecessary Login Items
To speed up your Mac's launch, eliminate unnecessary login items that delay the boot process. You can quickly identify and remove extra login items using Activity Monitor. By following these steps, you can spot and eliminate any unnecessary login items, ensuring your Mac launches smoothly and efficiently.
Step 1. Open Activity Monitor and click the "Energy" tab.
Step 2. Find high-energy operations in the "Avg Energy Impact" column. These are energy-intensive applications.
Step 3. Record high-energy apps and launch them manually.
Step 4. To deactivate a login item, go to the Apple menu and select System Preferences.
Step 5. Click "Users & Groups".

Step 6. Click "Login Items" under the Users & Groups options.
Step 7. To deactivate a login item, select it from the list and click the "-" underneath to delete it.
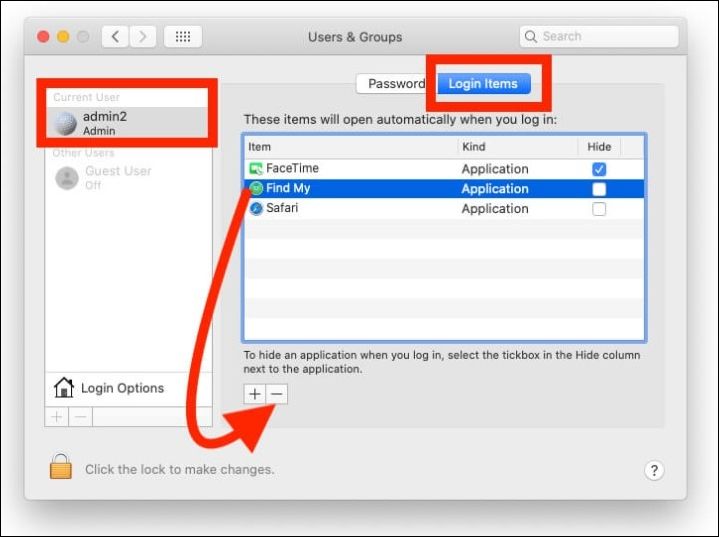
Step 8. Repeat for any superfluous logins.
Method 3. Check Malware with Activity Monitor Mac
Mac Activity Monitor can help identify and monitor suspicious processes and behaviors that may indicate malware, although it doesn't scan for viruses like antivirus software. Instead, it can reveal potentially hazardous actions. To use it for malware detection, you can follow these steps: [insert steps here].
Step 1. Opens "Activity Monitor" from "Applications > Utilities" or Spotlight search.
Step 2. Click "CPU" to see active processes.
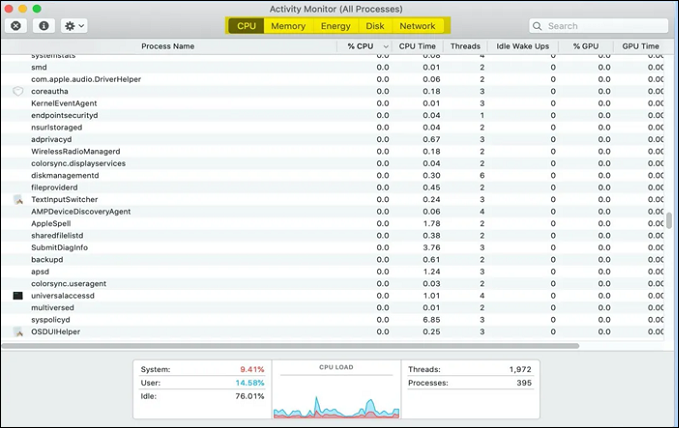
Step 3. Be cautious of unfamiliar or suspicious programs that consume a lot of CPU resources or have unusual names, as they may be malware, especially if their process name matches known malicious software names.
Step 4. To forcibly quit a malicious process, select the process you believe to be malicious and click the "X" button in the toolbar. This will terminate the process immediately, regardless of its current state.
Step 5. Check the "Network" tab in Activity Monitor for unusual network activity that may indicate malware communicating with external servers.
Activity Monitor may provide some information, but it's not a substitute for a dedicated antivirus solution. Instead, rely on trusted macOS antivirus software for comprehensive malware protection.
Conclusion
Activity Monitor on macOS is a tool that helps you manage system resources and diagnose performance problems on your Mac. To optimize your Mac's performance, it recommends quitting slow processes and removing unneeded login items, which can help identify and resolve issues affecting your computer's speed and efficiency.
To optimize Mac performance, use Activity Monitor to identify and close resource-intensive apps, and to monitor system resources. Additionally, use Deep Data Recovery for Mac to recover lost data, ensuring a smooth and efficient Mac experience.
Activity Monitor Mac FAQs
Activity Monitor is a built-in utility on Mac that displays information about the system's CPU, memory, disk, and network usage. It can be opened by searching for it in Spotlight, using the Launchpad, or by navigating to Applications/Utilities.
1. How do I find the Activity Monitor on my Mac?
You can access the Activity Monitor on your Mac by going to "Applications > Utilities" or using Spotlight by hitting "Command + Space".
2. What is Activity Monitor on my computer?
Activity Monitor, a built-in macOS software, displays real-time information on your computer's processes, apps, and system resources, allowing you to monitor CPU use, memory usage, energy impact, disk activity, network activity, and more.
3. What is Activity Monitor Mac memory?
The Memory tab in Activity Monitor on Mac displays various memory-related statistics, including the amount of memory used, cached files, app memory usage, and compressed memory.
4. What is the keyboard shortcut for Activity Monitor?
To open Activity Monitor on a Mac, press "Option + Command + Esc" to access the Force Quit Applications window, then select Activity Monitor and click "Force Quit" to open it.
Related Articles
- What Is System Preferences on Mac | How to Use It
- What Is a TPM, How to Check and Enable TPM 2.0 for Windows 11 [Full Guide]
- What Is the Windows Task Manager? [Everything You Should Know]
- What Is RAW: the Comprehensive Definition and Meaning of RAW Conditions