ReFS vs NTFS: Which Is a Better File System?
What's File System
The file system is a structure in which the operating system manages the data in groups through logical rules. To put it simply, if you think of the hard disk or server as a library, in which each file is represented by a book, then the file system functions like bookcases and administrators, which can display these books orderly and easily accessible.
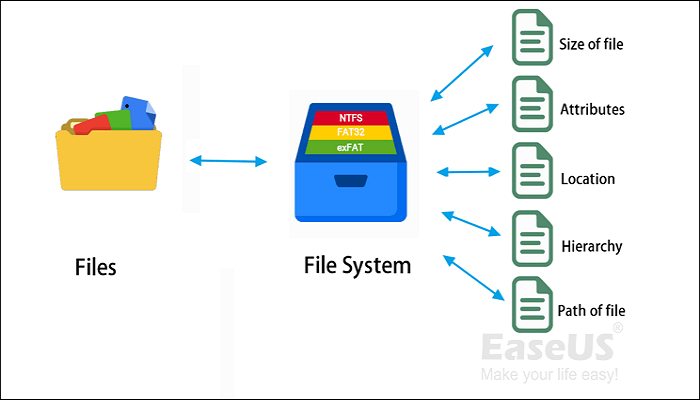
The existence of file system enables the operating system to manage data and files more efficiently and logically. With its help, users can read, access, write, modify and protect the data on the device with great ease.
What's NTFS
NTFS is a file system launched by Microsoft.
In the era of Windows 98, Microsoft used the FAT32 file system and 32-bit file allocation table. Since 2000, the disk capacity began to increase significantly. The FAT32 file management format can greatly enhance the disk management ability, breaking through the limit of 2 GB for each partition of FAT16.
After the Win 98 operating system, Microsoft introduced the New Technology File System (NTFS) file system for Windows NT in 1993, which has been used from Windows 2000 to Windows 8.
The NTFS supports metadata, which is higher in disk utilization than FAT32. Operating systems using FAT32 format can support up to 32 GB partitions, while systems supporting NTFS format can support up to 2 TB disk partitions.
Although NTFS has excellent capabilities, as time goes on, NTFS gradually exposes its disadvantages. For example, limited compatibility, and no maximum data availability to scale to large datasets across different workloads.
What's ReFS
In order to solve the problems of the NTFS file system, Microsoft introduced a new generation of the advanced file system - Resilient File System (ReFS), also known as "Protogon", in September 2012.
ReFS is designed from NTFS code. Microsoft hopes it can have the maximum data availability and meet more data storage needs of users. And Windows is getting ReFS support.
Compared with the NTFS file system, the ReFS file system does improve reliability, especially for aging disks or when the machine is powered off due to movies. The reliability part comes from the underlying changes, such as the storage and update of file metadata. ReFS is compatible with the Storage Spaces spanned volume technology. When the disk fails to read and write, ReFS will perform system verification, detect these errors, and copy the file correctly.
However, although Microsoft has made a lot of efforts to design ReFS, and ReFS also has functions that NTFS does not have, it still has many shortcomings that need to be improved, and it cannot be a perfect substitute for NTFS for the time being.
ReFS vs NTFS: 4 Aspects
Although ReFS and NTFS are file systems launched by Microsoft, and ReFS is composed of NTFS code, they are still very different. The following content will analyze the differences between ReFS and NTFS in 4 aspects: Reliability, Scalability, Performance, and Features.
ReFS vs NTFS: Reliability
Both NTFS and ReFS file systems have data protection tools, but ReFS can automatically verify and repair file corruption without using Check Disk (CHKDSK), while NTFS cannot leave CHKDSK's help.
Because of this, compared with NTFS, ReSF is more flexible and can better protect the integrity and availability of data.
ReFS vs NTFS: Scalability
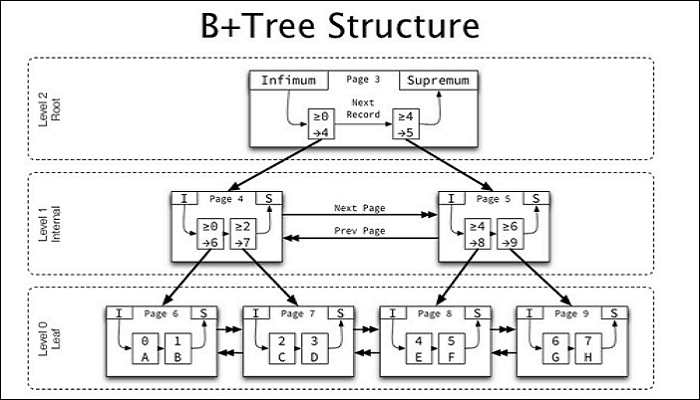
Because of the B+ tree structure, ReFS can store more data by branching, which also leads to better storage performance than NTFS. NTFS can provide a maximum capacity of 16EB, while ReFS can reach an amazing 262,144EB. At the same time, ReFS has a maximum file path of 32,768 characters, while NTFS has a maximum file path of 255 characters.
ReFS vs NTFS: Performance
ReFS has the image accelerated parity function. This function can allocate data to two layers on the drive, enabling ReFS file system to quickly write data to the disk at the mirror layer, and then transfer the data to the parity layer, and then calculate each written file again. Therefore, the mirror accelerated parity feature helps ReFS file systems store data more efficiently and use disk space more effectively.
So, ReFS performs better than NTFS.
ReFS vs NTFS: Features
Because ReFS is designed using NTFS's code, ReFS and NTFS have many similar functions, including:
| Comparison | ReFS | NTFS |
|---|---|---|
| Data Deduplication | √ | √ |
| Cluster Shared Volume (CSV) support | √ | √ |
| BitLocker encryption | √ | √ |
| Access-control lists | √ | √ |
| Soft links | √ | √ |
| Trim/Unmap | √ | √ |
| Changes notifications | √ | √ |
| Thin Provisioning | √ | √ |
| Junction points | √ | √ |
| USN journal | √ | √ |
| File IDs | √ | √ |
| Changes notifications | √ | √ |
| Mount points | √ | √ |
| Volume snapshots | √ | √ |
| Sparse files | √ | √ |
| Named streams | √ | √ |
Of course, they also have different functions, which is the focus of our analysis. Features available only on ReFS include (not available on NTFS):
| Comparison | ReFS | NTFS |
|---|---|---|
| Mirror-accelerated parity | √ | × |
| Block clone | √ | × |
| Sparse VDL | √ | × |
Features available only on NTFS include (not available on ReFS):
| Comparison | ReFS | NTFS |
|---|---|---|
| Transactions | × | √ |
| Short names | × | √ |
| Extended attributes | × | √ |
| Hard links | × | √ |
| Bootable | × | √ |
| Supported on removable media | × | √ |
| Object IDs | × | √ |
| Page file support | × | √ |
| Disk quotas | × | √ |
| File system encryption | × | √ |
| File system compression | × | √ |
Which Is a Better File System
According to the above differences between NTFS and ReFS, we can know that these two file systems must be different in use. NTFS is specially designed for various configurations and common uses in work. Its functions can make it more widely used and more suitable for most situations. Compared with NTFS, ReFS is doomed to be unable to be a substitute for NTFS because of its lack of key functions. It can only be a supplement to NTFS.
However, ReFS is essentially a more efficient file system for advanced users. With its unique advanced functions, ReFS can protect and repair data for PCs that handle a large amount of data and have strong flexibility.
In a word, NTFS is a universal file system with more functions and wider uses. ReFS may be more attractive to users who need to manage data in a large-scale environment and want to maintain data integrity in the event of file corruption.
Conclusion
To sum up, there is no winner in ReFS vs NTFS. These two file systems have their own advantages and disadvantages and are also suitable for users with different needs. Hope you can find your own answers after reading this article.
Related Articles
- What Is macOS Base System [Everything You Need to Know]
- How to Fix Physxloader.dll Is Missing or Not Found Errors
- What is Windows Image Boot (WIMBoot)?
- What Are the Best External Hard Drive for PS5 [Pros & Cons]