Quick Format VS Full Format, Which Should I Use? Check The Answer Here
When using a computer, high-level formatting is applied. And partitions are the targets of this formatting. However, in actual operations, high-level formatting is split into two modes: quick Format and full Format (also called general format). Computer users frequently become perplexed by the variations between quick Format and Full Format. Computer users may make the optimum use of discs if they are well-informed about them.
What are Quick Format and Full Format? Does the full or quick Format remove all data? There's a chance that many computer users don't fully understand these. This article will explain the differences between quick Format and full Format and offer suggestions on making a decision.
Quick Format VS Full Format, Everything You Need to Know
In this part, we will discuss the difference between quick Format and full Format in detail, with their features and pros and cons. Keep reading and get an in-depth knowledge of formats.
Quick Format
A Quick Format moves swiftly. The drive is not inspected for damaged sectors before formatting to speed up the procedure. The absence of data would lead anyone who looked at the hard disc or storage device to believe it had been erased. Unfortunately, the files are still present, and accessing them would require rebuilding the volume.
Features
- Deletes all the files, but it does not fully erase the files.
- It doesn't rebuild the filesystem, check for faulty sectors, or remove the already present data.
Pros
- It saves time.
- You can analyze errors without worrying about data loss.
- It removes viruses.
- You can recover files after quick formatting.
Cons
- Quick Format does not resolve the problem if your drive has any.
- It isn't a secure method of erasure.
Full Format
Any files on the drive are erased in a full format, which also updates (or maintains) the file system and scans the disc for damaged sectors. A full format requires much more time than a quick format.
Windows support both the quick and full formats of FAT and NTFS. A full format removes all of the files from the disc. However, extracting data is not a secure way; such a format needs external software.
Features
- Full formatting takes longer than quick formatting since it involves fully deleting all files from the disc.
- It helps in rebuilding the file system, volume label, cluster size, and scanning the partition for bad logical sectors.
Pros
- It increases the PC's performance.
- It solves your drive's issues.
- It will check errors without losing any data.
- Cleans your PC.
Cons
- Time-consuming
- Not recommended for SSD
After all, any formatting tool may damage your data, files, or your system, so you need to be prepared before formatting. This article may help you a lot:

How to Backup Files Before Formatting in Windows 10/8/7 PC and Laptop?
Be ready to backup files before formatting Windows 10/8/7, ensuring a complete backup of hard drive, external hard drive, programs, documents, videos, photos, emails and all data you concerned on a PC and laptop.

Quick Format VS Full Format, Which Should I Choose?
Are you confused about when to use quick Format and when to use full Format?
Since you are still the owner and intend to use the drive again, a quick format is sufficient. A full format is an excellent alternative if you think the drive has issues to ensure there aren't any problems with the drive.
We strongly advise safely erasing any data from the hard disc if you intend to give or sell the drive and it contains sensitive information. Let's discuss some cases.
Cases for Quick Format
In general, computer users can choose a quick format if they don't need to scan their discs for damaged sectors or don't want to wait a long time in case they ever need to retrieve their data.
When installing Windows, clearing out unused files from a partition to make room, the file system corrupts, or quick formatting can do when a notification appears. "Before using the disc, it must be formatted. Do you wish to format it at this time?" happens, and so on.
Cases for Full Format
Computer users typically do a full format because they no longer require the data and don't want it to be recoverable by others. Or, computer users may think about the full Format when they want to check the disc for problematic sectors.
When a brand-new, unformatted disc is acquired, an older disc with numerous faulty sectors is chosen, a device is sold or donated, a computer contracts a virus, etc., and a full format is carried out. Computer users, however, typically do not want the data to be recovered by others if they decide to sell or gift the device.
Quick Format VS Full Format, How Do I Perform Formatting on Windows
Let's use Windows Explorer and Disk Management as our first two instances of formatting. Quick Format is automatically selected when a partition is in Format on a computer, and quick Format will check by default; if they uncheck it, full format mode is chosen.
Method 3. Perform Quick Format or Full Format Using DiskPart
Method 1. Windows Explorer
Step 1. Right-click a local disc under This PC in File Explorer.
Step 2. Next, select "Quick Format."
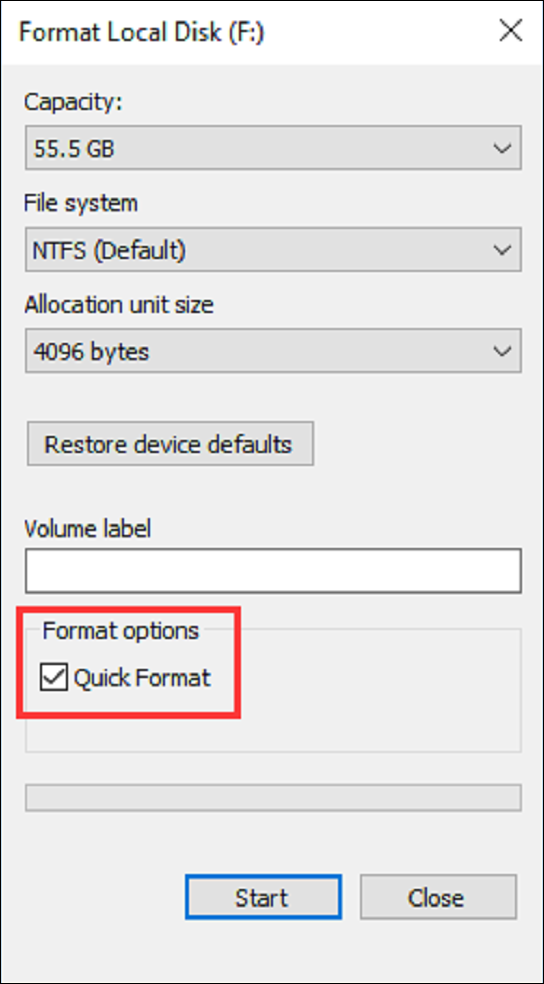
Note: It is executed if Quick Format is selected. In turn, the Full Format is executed
Method 2. Disk Management
Step 1. launch Disk Management, use "Windows + R" and type "diskmgmt.msc."
Step 2. Select "Format" by right-clicking a partition after that.
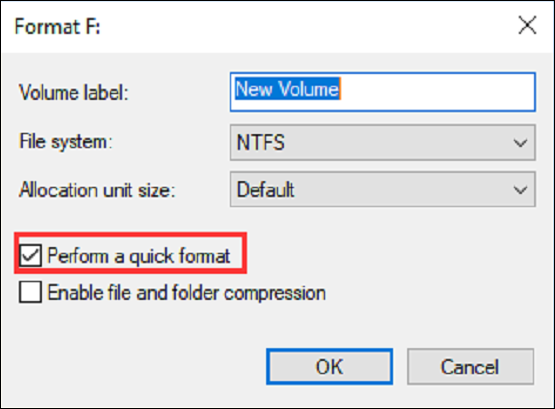
Note: It will conduct Quick Format if you select Perform a quick format. If NOT, it will conduct Full Format.
Method 3. Perform Quick Format or Full Format Using DiskPart
Step 1. Open cmd window by pressing "Windows+R" and type "cmd."
Step 2. Open the diskpart window, and then type "diskpart."
Step 3. Find the partition and use "list disc," "select disc," "list partition," and "select partition."
Step 4. Type "format fs=ntfs quick" to carry out the quick Format.
Step 5. Type "format fs=ntfs" to perform full format.
Recommendation: Turn to Quick/Full Format Tool - Qiling Disk Master
One of the best tools for quick and full Format is Qiling Disk Master. Qiling Disk Master Free is software that enables you to manage your hard drive's partitions. This software is easy to use and has a lot of functions that can help you increase the performance of your computer:
- Check disk and partition
- It supports Windows 7 up to 11
- It's an all-in-one partition management utility
- It offers conversion methods, like MBR to GPT
- It offers file system format conversion, like FAT to exFAT
Download it today and run formatting on your PCs.
Conclusion
In this article, Quick Format vs. full Format has been discussed. A quick format is sufficient if you intend to reuse the drive, and it is functional because you are still the owner. A full format is a wise choice to ensure there are no difficulties with the drive if you suspect it has trouble. To format, there are 3 methods. One of the best methods is to use the tool Qiling Disk Master; it is easy to use and supports users to execute quick formats.
FAQs about Quick Format vs. Full Format
If you are still confused between quick Format and Full Format. Read the answers below and make yourself clear about formatting. Leave your queries in the comment section so that we can answer you!
1. Which is better: Quick Format or Full Format?
A quick format is sufficient as long as you are still the owner and intend to use the drive again. A full format is a smart alternative to ensure that the drive is in perfect working order if you suspect it may have problems.
2. Is a Quick Format good enough?
When you select Quick Format, the partition's files are deleted, but the disc is not checked for damaged sectors. If your hard drive has already been formatted and you are confident it is not damaged, only choose this option.
3. Why is a Full Format more beneficial than a Quick Format?
While a quick format employs the slower NTFS file system, a full format uses the faster FAT32 file system. Explanation: A full format wipes out all the data on a partition and checks the disc for damaged sectors. Files from a partition will be deleted during a rapid format, but a disk's faulty sectors will not be scanned.
Related Articles
- Fix 'Windows Cannot Be Installed to Disk 0 Partition 1' Error
- Kingston Format Utility Fail? Fix with Kingston Format Tool [2024 Guide]
- How Do I Securely Erase Hard Drive/SSD, Wipe Confidential Data? Your Reliable Guide Is Here