A Starter Guide to the Windows Disk Management
Main Content of This Guide:
About Disk Management? Who Is This Guide for?
I. What Is Disk Management Windows 10/11?
II. How to Open Disk Management in All Windows PC?
III. How to Use Windows Disk Management to Set Up Hard Drive?
IV. Troubleshooting of Disk Management Windows 10/11 Error
V. Disk Management Software for Windows
People Also Ask about Disk Management
About Disk Management? Who Is This Guide for?
If you decide to manage disks or partitions via Windows Disk Management, this guide is meant for you. You may be a beginner at using the manual way to partition a targeted device or a user who has a half-baked idea for getting everything in the disk management Windows 10/11, this guide is written for you. If you are interested in learning the ultimate overview of the basics of disk manager utility according to our latest practice, you are in the right place. This guide won't provide the obscure terminology that swirls your mind but makes it easier for novices to understand Windows 10/11 disk management and its feature, steps to run it and fix errors without hassle.

I. What Is Disk Management Windows 10/11?
Windows Disk Management is a software utility in Microsoft Windows that provides a graphical interface for disk management. It works to manage disk drives and partitions in a computer system. The main goal of disk management is to optimize disk space use and improve the system's performance.
In older versions of Windows, disk management was accessed through the Disk Administrator tool. Starting with Windows Vista, disk management is integrated into the Computer Management console.
Windows Disk Management Availability: Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and all Windows Server versions.
Disk Management seems like a powerful software available on all Windows versions. Is it strong enough? What features does this software come with?
Essential Feature 1 of Disk Management - Manage Disks
- Initialize a new disk - After getting or replacing a new drive, initialize it before using the disk on the computer.
- Convert an MBR disk to a GPT disk or change a GPT disk into MBR disk - MBR and GPT is a partition style. Read on what is GPT or MBR if you're interested.
- Change or assign a drive letter.
- Change a dynamic disk to a basic disk.
- Manage virtual disk: It enables to create and attach VHD.
- Check disk's properties.
Essential Feature 2 - Manage Basic Volumes with Disk Management
- Create a new simple volume.
- Manage basic volumes, including extending, shrinking, deleting, and formatting an essential volume.
- Set partition as active.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Disk Management Windows 10/11
What we like with Disk Management: It is entirely free and requires basic partition functions. What a big attraction for users tired of downloading a third-party software that claims to be a free feature but requires to upgrade for a fee.
What we don't like with Disk Management: Extending or shrinking volume requires changing disk size in MB. It's hard to count for a novice. Moreover, the functions also have unexpected errors like extend volume greyed out, hard drive not showing up, etc.
II. How to Open Disk Management in All Windows PC?
Where is disk management in windows? To open disk management, you can run it from the disk management command and control panel:
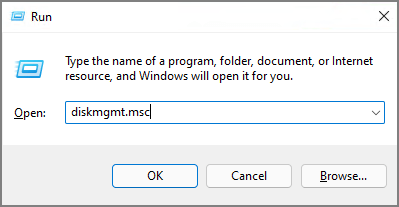
To Access Disk Management with Shortcut (Disk Management Command)
Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box. Then type "diskmgmt.msc" and press Enter. This will open the disk management console. From here, you can view all of your hard drives and partitions and perform various actions on them.
To Get into Windows Disk Management from Control Panel
Search and open Control Panel from the Start menu > Click on the "System and Security"> Type "disk management" on the top-right box > Click on the "Create and format hard disk partitions" under Windows Tools section.

Get More Opening Options
Still curious about other options? Read to open disk management in Windows 11 from the quick access menu, dialog, task manager, and more.
III. How to Use Windows Disk Management to Set Up Hard Drive?
Giving your hard drive a makeover is ordinary as that device is sophisticated but vulnerable to viruses or time. One of the ways to extend the lifespan is to set up your hard drive, manage the disk or partition space, and use unallocated free space. Here are some easy step-by-step tutorials to partition hard drive:
1. Initialize A New Disk
2. Create A New Volume
3. Extend or Shrink Volume
4. Format Partition
5. Convert MBR to GPT or Vice Versa
6. Change A Drive Letter
7. Convert Basic to Dynamic Disk
1. Use Windows 10 Disk Management to Initialize A New Disk
Step 1. Install or connect a new hard drive to the computer.
Step 2. Open Disk Management with the former options. (Forget it? Back to the "how to open disk management" part.)
Step 3. Locate and find the hard drive and click on the "Initialize Disk" from the menu.
Step 4. Select the correct disk to initialize in the Initialize Disk dialog box. Then set the partition style you want.

You May be Concerned about more ways to initiate a hard drive:
2. Create A New Volume by Disk Management
Step 1. Launch Disk Management.
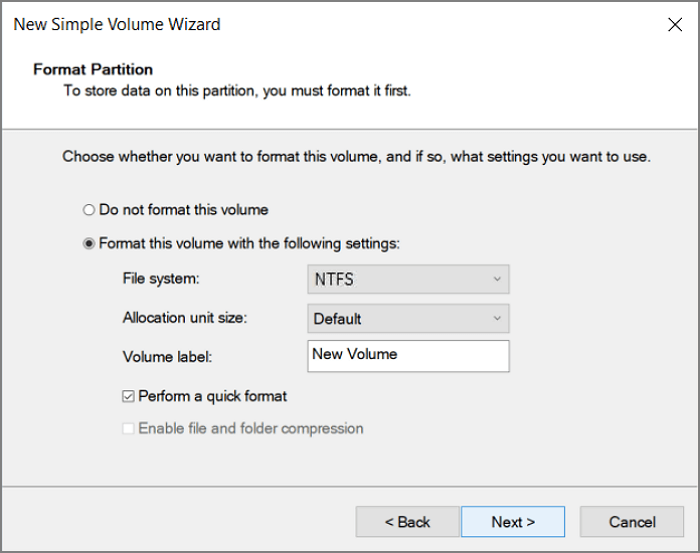
Step 2. You can see the free space marked as "Unallocated". Right-click the unallocated space and click "New Simple Volume..."
Step 3. Set file system, allocation unit size, and volume label and click Next.
Get More Info
Still, want to get more tips? Check to read the complete guide of new simple volume.
3. Extend or Shrink Volume via Windows Disk Management
Step 1. Run Disk Management.
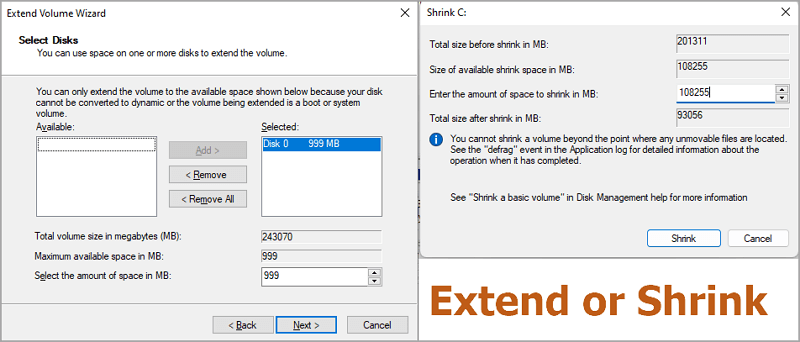
Step 2. Click the volume you want to extend or shrink. Click the "Extend Volume" or "Shrink Volume".
Step 3. Adjust the size in MB.
On the "Extend Volume Wizard", change the space size. And go to Next > Finish.
On the shrink dialog box, enter the amount of space to shrink in MB. Then click "Shrink".
If the extended volume greyed out, move to the troubleshooting section.
4. Format Partition by Disk Management Windows 10
Note: Format function indeed causes data loss. Remember to back up all important data first.
- Open Windows partition utility.
- Right-click a volume you want to format and choose "Format...".
- Change the volume label, file system, and allocation unit size. And select "Perform a quick format".
- Click OK.

5. Convert MBR to GPT or Vice Versa
Notice: Watch out for data loss! Changing partition style (Convert MBR to GPT or convert GPT to MBR) enables to delete partition in Disk Management. Please back up the essential data.
- Delete all volumes: Launch Disk Management > Right-click the volume on the targeted disk > Click "Delete Volume"> Click "Yes".
- Start to convert partition style: Right-click the targeted disk and choose "Convert to GPT Disk" or "Convert to MBR Disk".

6. Change A Drive Letter with Windows 10 Disk Management
Run Disk Management > Right-click the partition and click "Change Drive Letter and Paths..."> Pick the new drive letter > Click "OK".

7. Convert Basic to Dynamic Disk
Launch Disk Management > Right-click the disk for converting > Click "Convert to Dynamic Disk..."

Not enough? Read on to apply other features in Disk Management:
Note that Disk Management is not a one-size-fits-all solution. If you get any greyed-out error or hard drive not showing up issue, get the help of the Troubleshooting part. If that doesn't help, don't worry, keep reading the Disk Management alternative to ignoring the error.
IV. Troubleshooting of Disk Management Windows 10/11 Error
(X )Error 1. Extend Volume Greyed out
Can't extend volume? Extending volume greyed out is a standard error that can happen when trying to expand the partition size on a hard drive. There are a few reasons this error might occur, but the most common cause is that the hard drive is out of space. You can shrink a volume that has enough space in Disk Management to make unallocated space:
- Run Disk Management > Take a peek at a partition next to the targeted volume > Select "Shrink Volume" and click OK.

(X )Error 2. New Simple Volume Out
A new simple volume greyed out is a problem that can occur when trying to create a new volume on a disk that has been partitioned using the Master Boot Record (MBR) scheme. This problem can occur if the disk has more than four primary partitions. To create a new volume on such a disk, you must first delete one of the existing primary partitions. You can then create a new primary partition in its place. Alternatively, you can convert the disk to the GUID Partition Table (GPT) scheme, which supports up to 128 partitions.
Back to change MBR to GPT with Disk Management.
LEARN MORE
Try more solutions to fix New Simple Volume Greyed out
(X )Error 3. Format Volume Greyed Out
Disk Management format greyed out is a common issue when trying to format a storage drive. This usually happens because the drive is corrupted or bad sectors are on the disk. When this happens, the format option will be greyed out, and you won't be able to format the drive. You'll most likely need to use a third-party tool to format the drive. See the software on the next part.
Other Quick Troubleshooting in Disk Management:
V. Disk Management Software for Windows
We know that managing hard drives can be done manually via Disk Management. However, as we see in the former part, you may encounter some errors that count too much time. Why not try another free program and finish tasks in seconds? See one alternative to disk management:
Free Partition Manager - Qiling Partition Master
Qiling Partition Master is a free hard disk partitioning tool that enables you to resize, move, merge, and convert partitions on your hard drive. With Qiling Partition Master, you can easily create, delete, format, and extend partitions. The software also includes a partition recovery wizard that enables you to recover deleted or lost partitions.
Check More Tools
Move to get the other nine free disk manager.
People Also Ask about Disk Management
1. Why does my hard drive not showing up?
- The drive is properly connected to your computer.
- The drive has become corrupted or damaged.
- The drive hasn't been appropriately formatted.
2. How much storage does a dynamic disk require for the disk management database?
When creating a dynamic disk, you must specify how much storage to allocate for the disk management database. This database is used to track changes to the dynamic disk and store information about the disk's layout. The database size will depend on the number of disks and partitions on the dynamic disk, as well as the number of updates made to the disk. You should allocate at least 2MB of storage for the database.
3. Which of the following is not a linux/unix file or disk management command?
A. cfdisk
B. xfsdump
C. tar
D. xterm
The Right answer is "xterm".
Related Articles
- Computer Won't Boot? Causes & Fixes for PC Not Turning On [Full Guide]
- What Is Diskpart? How to Master and Use Diskpart Commands on Windows [Full Guide]
- One for All Guideline: How to Format/Reformat A Hard Drive
- Computer Is Running Slow? Causes and Fixes Are Found! [Your Ultimate Guide]