The Beginner's Guide on How to Remove Write Protection
If you want to know how to remove write protection from a USB, micro SD card, or disk drive, this guide provides several options to help you solve the issue on both Windows and Mac.
Main Content:
Understanding the Write-Protection
How to Remove Write Protection on USB Drive?
How to Remove Write Protection from SD Card?
How to Remove Write Protection from SSD?
Unfortunately, yes, you can format a write-protected USB, SD card, or disk drive, but you'll need to remove the write protection first. This can be done by using a USB drive with a built-in write protection switch, or by using a third-party tool to disable the write protection on the device. Once the write protection is removed, you can format the device using the built-in formatting tools on your computer or a third-party formatting software.
Troubleshooting: Specific Write Protection Error
1. Understanding the Write-Protection
Write protection is a feature that prevents data from being written or edited on storage devices, often used on removable media like flash drives and memory cards to prevent accidental deletion or modification. It can also be applied to hard drives and other storage devices through physical switches or software settings.
Pros of Write Protection:
- Can prevent accidentally deleting or modifying data.
Data encryption helps to protect sensitive data from being tampered with.
- Can be a useful security measure
Cons of Write Protection:
This can make it difficult or impossible to edit or delete data, even when you want to, due to the lack of a clear and easy-to-use interface.
The write protection feature can cause issues if it is enabled inadvertently, leading to difficulties in making changes to the system or software.
If you want to write protect an entire drive, you can use the built-in Windows feature called "Write Protect" or use a third-party software to achieve this. This will prevent any changes from being made to the drive, including formatting, deleting, or modifying files. However, keep in mind that this will also prevent you from making any changes to the drive, including adding new files or folders.
Write protection on a storage device, such as a USB drive or external hard drive, is a feature that prevents data from being written to the device, making it read-only. This can be useful for preserving data or preventing accidental overwrites, but it does not provide security against malicious software infections or physical theft. For data security, it's recommended to use a drive with built-in encryption or password protection.
LEARN MORE
Click here to figure out the disk is write protected.
How to Remove Write Protection
While write protection is a great way to safeguard sensitive data, it can sometimes be a hassle when unexpected errors occur, causing devices to show up as encrypted or locked by default, making it impossible to make any changes.
Here are some write protection removal tools to disable write protection on USB, SD cards, and SSD drives, including physical switches, Diskpart, Registry, and Disk Utility, regardless of the operating system being used.
| Workable Solutions | Step-by-step Troubleshooting |
|---|---|
| Remove Write Protection on Windows |
Option 1. Using Lock Switch...Full steps Option 4. Use Windows Registry...Full steps
|
| Remove Write Protection on Mac |
Method 1. Use Disk Utility to format...Full steps |
How to Remove Write Protection on USB Drive
To resolve the issue of a flash drive being write-protected, you have three options. For Windows users, you can remove write protection by changing the lock switch, running Diskpart, or disabling write protection through the Registry. Alternatively, Mac users can use Disk Utility to fix the USB write-protected error. This should resolve the issue and allow you to save data to the flash drive again.
Option 1. Using Lock Switch to Remove Write Protection
Some USB storage drives have a lock switch that allows you to toggle write protection on or off. This switch can be used to change the USB write protected status. If your drive has this feature, you can use it to enable or disable write protection.
Locate the physical switch on the side of the USB drive, usually decorated with a lock icon. It's a small switch that you can move up or down. 2. If you can't find the physical switch, try method 2.
![]()
Step 1. Find the physical light switch and flip it to the other side.
Step 2. Try to drop data on the USB stick again after reconnecting it to the PC. If it still doesn't work, you might want to try checking the USB stick for any errors or formatting issues.
If you can write data on the USB, that's a good sign, and the error may be resolved. Be careful not to accidentally move the switch to the wrong side, which can cause issues. If you're using a standard USB with a smooth surface, you may want to try alternative options to resolve the problem.
Option 2. Remove Write Protection with Diskpart
To remove write protection from a USB drive in Windows 10/11, use the Diskpart command line. First, type "diskpart" in the Command Prompt, then "list disk" to identify the USB drive, and finally "clean" to remove the write protection. Make sure to type the correct command lines to avoid data loss.
Step 1.To open Command Prompt on Windows, type "Command Prompt" in the search box and click on the result to launch it.
Step 2. Type command lines and press Enter each time.
- diskpart
- To identify your devices, use the command "list disk" which displays a list of disks named as Disk 0, Disk 1, Disk 2, etc.
- select disk 0 (You can replace disk 0 with the write-protected USB number.)
- attributes disk clear readonly (Ensure to type "s" and don't separate "readonly".)

Step 3. Wait until progress is complete and type "exit".
Step 4.1. Restart your PC.
Option 3. Turn BitLocker Off to Disable Write Protection on USB
To remove BitLocker encryption from USB drive:
Step 1. Press "Windows + E" to open File Explorer.
Step 2.To access a locked USB drive, go to "This PC" on the left side, locate the drive under "Devices and drives", right-click it, and click "Manage BitLocker".
Step 3.In the BitLocker Drive Encryption window, you'll see a list of all drives, along with their status. To access your write-protected USB, select the drive and click "Turn off BitLocker".

To fix the "write protection" issue on a flash drive with BitLocker enabled, first, turn off BitLocker by entering the password or recovery key and waiting for the decrypting process to complete. Once BitLocker is disabled, you can attempt to add files to the flash drive to see if the write protection issue is resolved.
Tips: If you've forgotten your BitLocker recovery key, there are several methods to recover it. First, check if you've stored the key in a safe place, such as a secure note-taking app or a password manager.
Option 4. Use Windows Registry to Disable USB Write Protection
For experienced users familiar with the Windows Registry, disabling write protection can be achieved through the Registry.
Note:Editor Registry will disable write protection on all devices, allowing for modifications.
Step 1. To access the Registry Editor on your PC, insert a USB drive and press the "Windows + R" keys simultaneously. This will open the Run dialog box. Type "Regedit" into the box and click Enter or OK to open the Registry Editor.
Step 2. Follow the path: Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\StorageDevicePolicies
Note: If your "StorageDevicePolices" is missing, it's recommended to use alternative methods instead of creating them manually to avoid potential system issues.
Step 3. To disable write protection on a Windows device, double-click the "WriteProtect" value in the registry, modify the "Value data" to 0, and ensure the "Base" is set to "Hexadecimal". Then, click "OK" to save the changes.
Step 4. Restart your PC and check if the drive is writable.

LEARN MORE
Here also provides a one-You can remove write protection by clicking on third-party software such as Qiling CleanGenius, which is free and easy to use, featuring a simple toggle button to quickly take write protection off.remove write protection from USB. 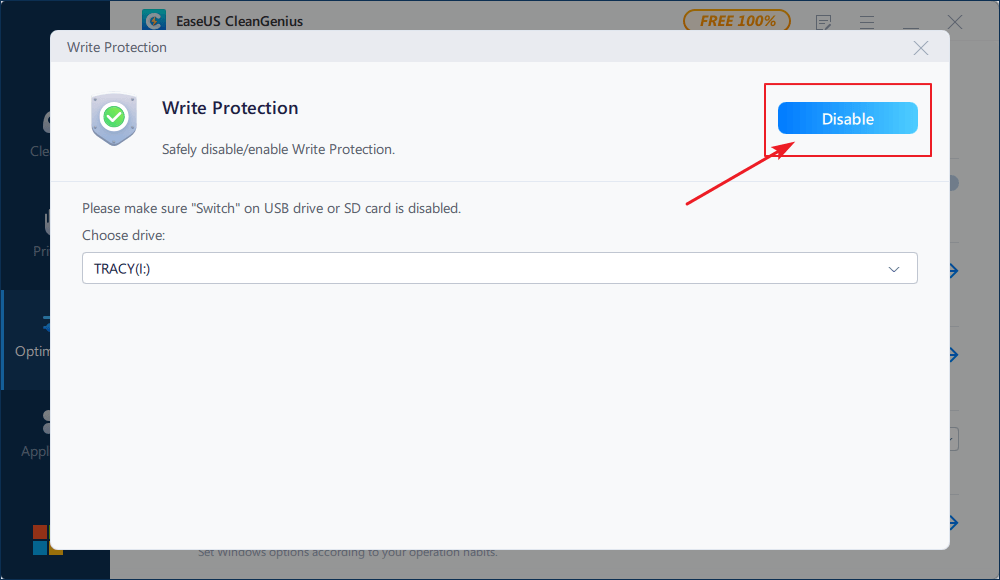
Method 5. Format write-protected USB via Disk Utility
To remove write protection from a USB drive, connect it to a Mac and wake up Disk Utility. This format is a good option to remove the write protection.
Step 1. To open Disk Utility, go to Finder, select "Go" from the top menu bar, choose "Utilities", and then double-click on the Disk Utility app. This will open the Disk Utility window, allowing you to manage and maintain your computer's storage devices.
Step 2. Select the read-only flash drive from the left panel.
Step 3. Click the Erase button.
Step 4. Enter the USB name, select the format and scheme, and click the Erase option.

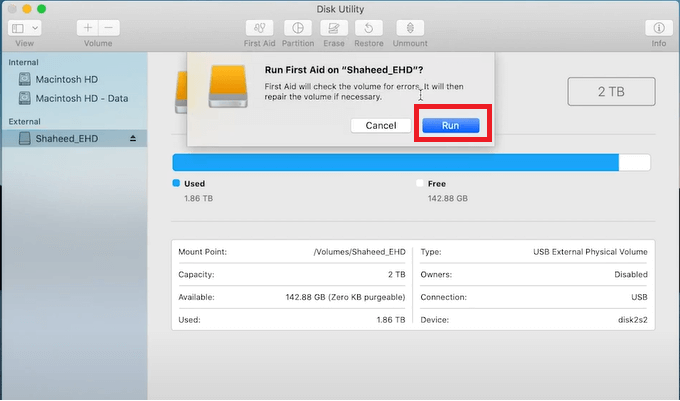
Method 6. Run First Aid to Repair Read-Only Device
To fix a read-only drive, open Disk Utility, locate the drive, and select First Aid. Then, click the "Run" option to initiate the repair process.
How to Remove Write Protection from SD Card
If you've ever tried to copy files to an SD card and got an error message saying it's write-protected, you know how frustrating it can be. Write protection is designed to prevent accidental deletion of important files, but it can also lock you out of your own SD card if not handled carefully. Fortunately, there are ways to remove write protection from an SD card, such as changing a physical switch, and if those methods don't work, you can use command lines on Windows 10/11 or change "Get Info" settings on Mac to regain access to your files.
Option 1. Change the Physical Switch
Some SD cards, like USB drives, have a physical lock that can be enabled or disabled to protect against writing.
- You can remove the SD card from the computer and find the physical lock to access the SD card.
- If it is "On", toggle it to the off side.

Option 2. Use Diskpart to Take Write Protection Off on Windows
- 1. Insert the SD card into the SD card reader.
- To rewrite the command lines, open Run CMD and enter the command lines. The steps are the same as the command line mentioned above. Go back.
Option 3. Modify Read-Write Status on Mac
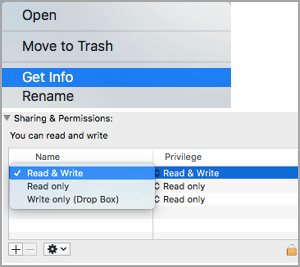
How to change a write-To remove write protection from a SD card on a Mac, take a look at the Sharing & Permissions settings, which allows you to decide who can add or modify files in the Finder app. This should enable you to remove the write protection and use the SD card as needed.
Step 1. Connect SD card to Mac with SD card reader.
Step 2. To access the file, go to the SD card, right-click on the file, and select "Get Into" from the context menu.
Step 3. To change the permissions on a Google Doc, go to the Sharing & Permissions section and click on the "Read & Write" option under Privilege. This will allow the selected user to edit the document.
LEARN MORE
If the toggle is missing or you find diskpart too complex, don't worry. There are other methods to remove write protection on a Micro SD card, and you can explore those instead.
How to Remove Write Protection from SSD
When trying to transfer files from a computer to an SSD, you may encounter an error message stating that the disk is write-protected. To resolve this issue, check the SSD's properties to see if there's a hardware switch that's preventing writing. If not, the write protection might be enabled in the firmware, which can be disabled by connecting the SSD to a computer and running specific commands in the Command Prompt. Once the write protection is removed, you should be able to transfer files to your SSD without any issues.
Remove SSD Write Protection
Want to see more solutions? Click here to learn about how to fix an SSD that's write-protected.
How to Remove Write Protection from A File
When a single file is write-To remove file write protection on a Windows computer, you can follow these steps:
Step 1. To open Windows File Explorer, press the "Windows+E" shortcut key on the keyboard.
Step 2. You can use a search function to locate the write-protected file, which can save you time and effort compared to scrolling through a list of files one by one. This allows you to quickly identify the specific file you're looking for, especially in large collections or folders.
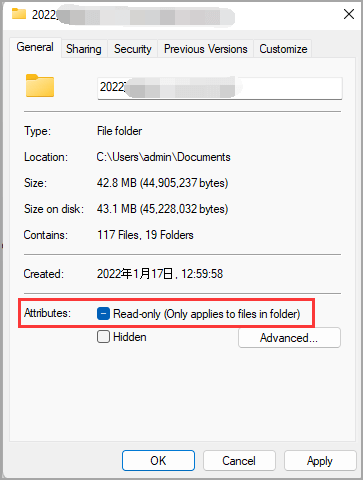
Step 3. Right-click the file and select the "Properties" button.
Step 4. To make an attribute editable, go to the Attributes tab, uncheck the Read-only option and click OK to save the changes.
Can I Format Write Protected USB, SD Card and Disk Drive?
Formatting a write-protected USB drive, memory card, or hard drive can be frustrating, as you may encounter a message stating that the device is write-protected or that formatting is not supported. This is often due to the write protection switch on the device being turned on, and it needs to be locked before formatting can be performed.
Formatting a USB drive with write protection can't be done through formatting. You can use Qiling Partition Master Free to format the device instead.
Step 1. Select the USB drive to format.
To format a USB drive, connect it to your computer, download and launch Qiling partition software, then right-click the drive and select "Format".
Step 2. Set the drive letter and file system on USB.
Assign a new partition label, file system (NTFS, FAT32, EXT2, EXT3, EXT4, exFAT), and cluster size to the selected partition, then click "Proceed".
Step 3. Check "OK" to format the USB drive.
Click "OK" if you see the Warning window. If you have important data on it, back up the data in advance.
Troubleshooting: Specific Write Protection Error
1. Windows is unable to run disk checking on the volume because it is write-protected. This means that the operating system cannot write any data to the volume, which is necessary for the disk checking process.
Windows is unable to run disk checking on a write-protected hard drive, which means the operating system cannot modify files on the drive. To resolve this, you'll need to remove the write protection using the Command Prompt (CMD), Diskpart, and Registry Editor.
2. SD Card Read Only
If you're experiencing an "SD card read-only" error when trying to save a file, it's likely due to a corrupted SD card. Fortunately, you can resolve this issue by formatting the card using a third-party software designed for read-only removal. This should restore the card's functionality and allow you to save files again.
Related fixes - SD Card Read Only
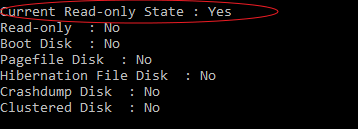
3. USB Current Read-only State Yes
Current Read-If you encounter a "State Yes" error on a USB or SD card, it means the disk is in a read-only state, often due to corruption or a virus. This prevents you from writing to the disk. To resolve the issue, you'll need to clear the read-only state using diskpart.
4. The Media Is Write-Protected
The Media is write protected error in Windows can be caused by a corrupt or damaged file system, which prevents the computer from reading files correctly. This issue can be resolved by checking for system file corruption.

To fix the issue, open the Command Prompt and type "SFC /scannow" to check for system file corruption. This will initiate a scan that will identify and replace any corrupted files, resolving the problem. Simply wait for the scan to complete.

Wrap Things Up
When an SD card or USB disk is write-protected, there's no need to panic as there are several options to remove the protection. One method is to use a physical switch on the drive itself, while another is to use software to unlock the disk. This can be done by changing the drive's permissions or using tools like Diskpart and Registry Editor to modify the drive's settings. Once the write protection is removed, the disk can be reformatted using a disk formatter.
Related Articles
- What Is HDD? See The Ultimate Guide of Hard Disk Drive
- A Starter Guide to the Windows Disk Management
- An Ultimate Guide to the Master Boot Record (MBR)
- Computer Is Running Slow? Causes and Fixes Are Found! [Your Ultimate Guide]