SSD Data Recovery – How to Recover Deleted Files from SSDs
Quick Navigation:
- Part #1: The Reasons for SSD Data Recovery
- Part #2: Quickly and Completely Way for SSD File Recovery
- Recover deleted files from SSD
- Formatted SSD recovery
- Restore deleted/lost partition files from SSD drive
- Other reasons need to recover files from SSD
- Step-by-step Guide on Using Best Software to Recover Files from SSD
- How to Use Tool to Recover Files from NVMe SSD
- Step 1: Choosing the file type
- Step 2: Picking the scanning location
- Step 3: Preview and Recovery of SSD Files
- Part #3: The Symptoms of SSD Failure
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a storage device similar to an internal hard drive, but with a key difference: it lacks mechanical components. Instead, SSDs use circuits and assemblies to store data, making them more durable and faster than electromechanical drives, which can withstand physical shock to a certain limit. This results in a silent and quick storage experience. Data is stored in semiconductor cells, with the number of bits per cell affecting the properties, with single-bit cells (SLCs) being expensive but reliable, durable, and fast.
Part #1: The Reasons for SSD Data Recovery
Solid-state drives (SSDs) have a longer lifespan compared to mechanical hard drives, but they can still be vulnerable to misuse and damage. Physical shocks exceeding the specified limit can cause harm, while power fluctuations can also lead to short circuits that damage the cells storing data, making SSD data recovery necessary.
Here are the vital points why one would seek data recovery from an existing SSD:
- Accidental deletion, formatting, or sudden SSD death can result in file loss, making data recovery essential. Users can recover data by using a recovery tool or connecting the SSD to another system to perform the recovery procedure.
- Restoring an SSD becomes essential when only a few files are accessible, and there's a chance the SSD displays a partition as a RAW file format due to bad sectors.
- When creating additional partitions on an SSD, there's a risk of accidentally erasing data. If this happens, you'll need to recover deleted files from the SSD.
- As an SSD ages, its transfer rate slows down, and files may be lost or unable to be opened during transfer. To prevent data loss, it's recommended to perform SSD drive recovery before the drive stops working, ensuring that all files are safely recovered and accessible.
Part #2: Quickly and Completely Way for SSD File Recovery
Even though the market has seen impressive developments in programs for recovering files from SSD, Deep Data Recovery still leads the pack. This software offers a valid path to SSD file recovery that users can perform in a simple and straightforward manner, thanks to its user-friendly design that even a newbie can handle with ease. The program's simple steps and clear instructions make it easy for any user to choose the file type, select the location for recovering the data, and retrieve the same.
There is no output for this. It seems like the input was a prompt for a specific task, but no text was provided to process.
Recover deleted files from SSD
A recovery tool helps in recovering files lost due to accidental deletion, pressing the "Delete" key, "Shift + Delete" keys, copy, cut, and moving data/folder.
Unfortunately, it's not possible to recover data that has been deleted without creating a backup, as the data is no longer stored on the device or system. Once data is deleted, it's typically removed from the storage and can't be retrieved. If you want to recover deleted data, it's essential to create a backup before deleting anything, so you can restore the data from the backup if needed.
c. Emptying "Recycle Bin" without backing up the content.
Formatted SSD recovery
a. Restoring data from unexpectedly formatted SSD
If your SSD prompts "Media/Drive is not formatted" when trying to recover files, it's likely that the drive has been corrupted or has issues with its file system. To recover files from an SSD in this situation, you can try using a data recovery software that can bypass the formatting process and directly access the drive's data. Some popular options include EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, Recuva, and Disk Drill.
c. Retrieving data from drives that are inaccessible
Restore deleted/lost partition files from SSD drive
a. Recovery of data from SSD partition deleted mistakenly
SSD file recovery becomes necessary when a partition is lost due to various reasons such as accidental deletion, cloning, repartitioning, or disk accidents, making it essential to utilize data recovery tools and techniques to salvage valuable files and information.
Other reasons need to recover files from SSD
Recovering lost data due to improper media ejection or factory reset involves using specialized software to scan the device for remaining data. This process can help recover deleted files, restore corrupted files, and even recover data from a factory reset. The software can scan the device's file system, identify remaining data, and recover it.
b. RAW SSD recovery that displays file system as RAW
To recover SSD data lost due to a virus attack, software crash, Windows reinstallation, and other reasons, you can use data recovery software specifically designed for SSDs. These tools can scan the SSD for deleted or corrupted files and attempt to recover them. Some popular options include EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, Recuva, and Disk Drill.
Step-by-step Guide on Using Best Software to Recover Files from SSD
To recover deleted files from an SSD without stress, users can follow these steps. First, they need to download and install a Window or Mac SSD data recovery software on a computer. The trial version of the Deep data recovery program is available from the official website, allowing users to get started.
How to Use Tool to Recover Files from NVMe SSD
The software is designed to be user-friendly, making it easy to recover deleted files from SSD or perform formatted NVMe recovery, even for those without prior experience. You don't need advanced tech skills to use the tool, and the process is straightforward.
Step 1: Choosing the file type
The SSD file recovery application automatically selects all recoverable file formats by default. Users can choose specific file formats they want to recover, such as images, documents, or videos, and proceed with the recovery process by clicking the "Next" button.
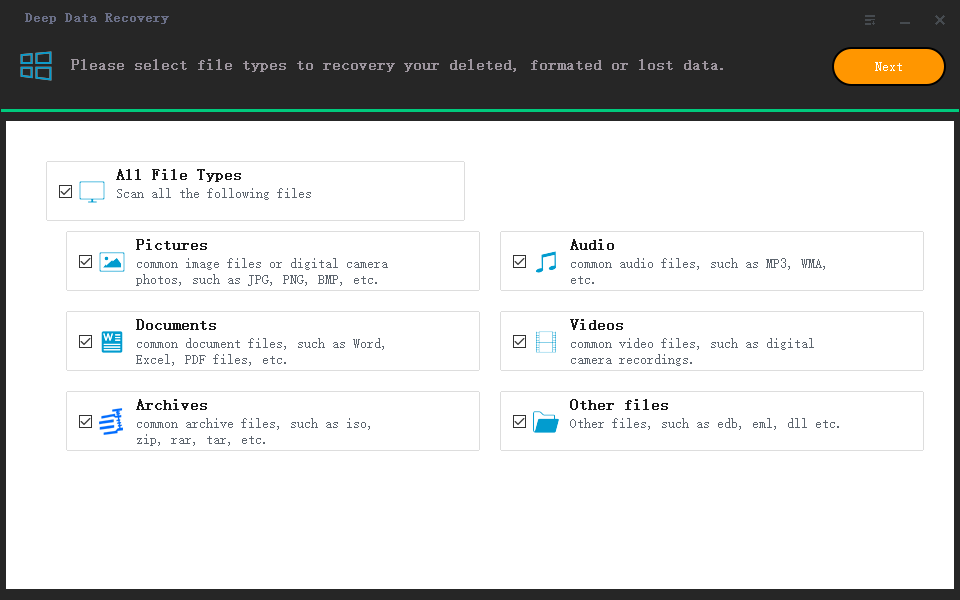
Step 2: Picking the scanning location
After selecting the file format, the SSD recovery tool will prompt you to choose the location for scanning. This is where you need to connect the failed SSD to the computer, as it's essential for the scanning process. Once connected, select the desired SSD and press the "Scan" button to initiate the recovery of deleted files from the SSD.
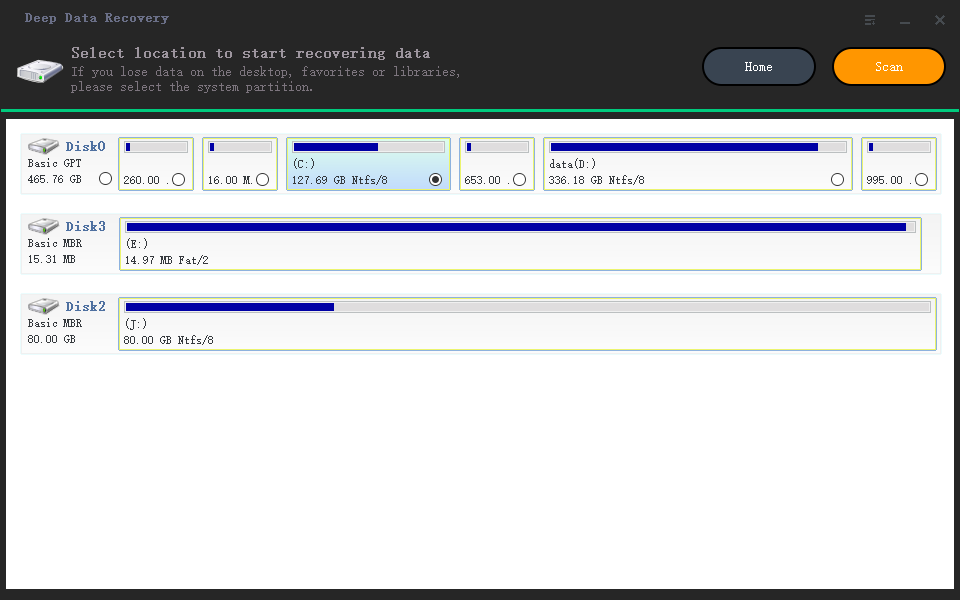
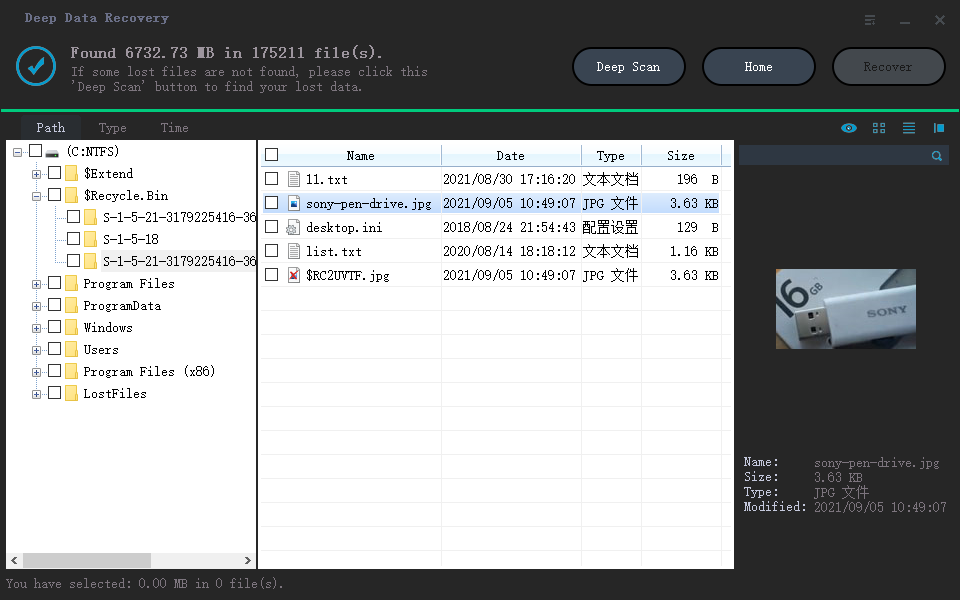
Step 3: Preview and Recovery of SSD Files
SSD drive recovery is a straightforward process for the software, which employs a robust algorithm to scan the selected partition and identify all recoverable files. The deep data recovery feature then displays detailed information about these files in a new window, providing a clear and simple overview of the recoverable data.
Users can browse the information using the tree directory in the left pane of the window, choosing how they want to see the data - path, type, or time. Based on this selection, the software discloses the folders available for recovery, such as the "Pictures" folder, which can be chosen to select the type of files to recover, like jpg, BMP, or others, and the corresponding files will be displayed in the center pane.
To view the content of a file, you must click on it in the center pane, which will then display a thumbnail of the file's content in the right pane, allowing you to select the files you want to recover from the SSD.
After marking the files, users need to save them to an external storage location or a different partition of the SSD. To do this, they press the "Recover" button and specify the saving path, which can be browsed using the available buttons in the pop-up window.
Deep Data Recovery offers a "Deep Scan" mode in its undelete or unformat SSD utility, which employs sector-by-sector scanning technology. This mode is helpful for users who believe there are more files in the selected partition, and is a time-consuming process that scans sector-by-sector. Users can choose the mode that suits their requirement and initiate the scanning process for retrieving additional files.
Part #3: The Symptoms of SSD Failure
Given the advantages of SSDs over electromechanical hard drives, it's likely that they can fail within a short period. The nature of their malfunction varies from one individual to another, but common factors that contribute to an SSD's failure include:
1. Data corruption is a common factor in the failure of SSD drive functionality.
2. Bad sectors on an SSD can arise due to mishandling, such as physical shocks or incorrect storage, which can ultimately lead to the drive's failure. Proper handling and storage, such as placing the SSD in its designated bay, can help prevent damage and reduce the risk of bad sectors.
3. A virus attack can cause damage to data and lead to malfunctioning of the SSD drive. To prevent this, it's recommended to choose a leading anti-virus software that monitors the computer's activity continuously and prevents any malware or virus attack.
4. SSD failure can occur due to reasons other than bad sectors. One such reason is the improper transfer of data, which can corrupt the data and ultimately lead to SSD failure. For instance, removing an external storage device, such as a USB drive, during data transfer can damage both the device and the SSD, and in some cases, even the operating system.
5. A short circuit or fluctuations in power supplied to the computer can cause an SSD to malfunction. Improper power input can lead to severe damage to the components or cells that hold data in memory form, causing the SSD to fail. This can be caused by changing power and voltages, which can disrupt the optimal performance of the SSD.
6. The failure of SSDs can be attributed to its age, with users experiencing a decline in performance and speed over time, ultimately requiring a replacement to prevent data loss and ensure the drive's continued functionality.
Related Articles
- Toshiba SSD Recovery – Recover Files from Toshiba SSD Drive
- Witcher 3 Missing Saves | How to Restore Witcher 3 Game Saves
Witcher 3 missing saves on PC? Don't worry! We are here to help you recover Witcher 3 missing saves; five methods will be mentioned in this passage. You'll know how to recover missing data on different devices.