A Complete Guide to Recover Data from Broken RAID 0, 1, 5, 10 [SOLVED]
What Is RAID 0, 1, 5, 10?
RAID is an acronym for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. With RAID enabled on a storage system, you can connect two or more drives in the system so they act as one large volume fast drive. Or, you can set them up as one system drive used to automatically duplicate (or mirror) your data for real-time backup.
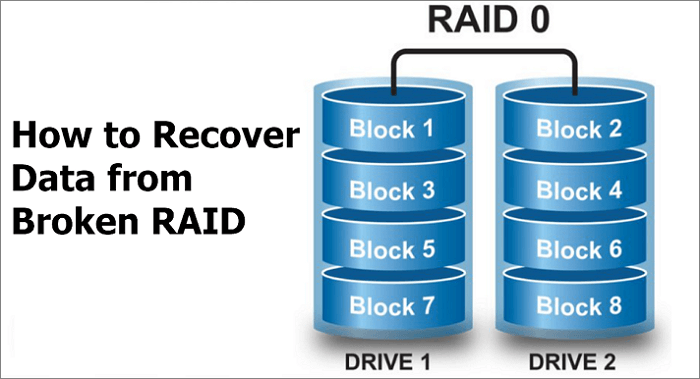
RAID 0
Provides disk striping across all drives in the RAID drive group. RAID 0 can't provide data redundancy but can provide the best performance of any RAID level. It breaks up data into smaller segments and stripes the data segments across each drive in the drive group.
RAID 1
Sets the system to data protection mode and the capacity is divided in half. Half of the capacity is used to store your data and half is used for a duplicate copy. If one drive goes down your data is protected because it's duplicated.
RAID 5
Gives you the best of both advantages: fast performance by striping data across all drives; data protection by dedicating a quarter of each drive in a four-drive system to fault tolerance leaving three-quarters of the system capacity available for data storage.
RAID 10
Delivers very high I/O rates by striping RAID 1 (mirrored) segments. This RAID mode is good for business-critical database management solutions that require maximum performance and high fault tolerance. A system set to RAID 10 yields half the total capacity of all the drives in the array.
Qiling Broken RAID Recovery Software - Outstanding Features
RAID is a complex data storage technology that uses different disks to create one logical volume. Therefore, people think that the RAID data recovery process is complex too. RAID data recovery is indeed difficult if you try the traditional method. You need to pull out the disk, re-build RAID, and then connect to your PC to restore data.
Things become easier when you get Qiling NAS data recovery software. You don't need to pull the disk out and rebuild the RAID. The only thing you need to do is use Qiling data recovery software. Open and run this software. Then, you can let the software scan your NAS server. It has many advantages.
- Designed to recover software and hardware RAID
- Recovers files from RAID like Synology, Western Digital, Dell, etc.
- Recovers files from corrupted RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 4, RAID 5, RAID 10.
- Windows restrictions are bypassed by the recovery process.
How to Recover a Broken/Failed RAID 0, 1, 5, 10
Here are the details to recover data from a broken, damaged, or failed RAID 0, 1, 5, or 10. Follow the steps below to get back data from your broken RAID.
Method 1. Run Qiling NAS DATA Recovery Software
Step 1. Select a NAS server and start recovering.
Download and install Deep Data Recovery on your Windows 11/10 64-bit computer. When you open this software, select "NAS Recovery". All the NAS servers will be automatically listed, choose your target NAS device and click "Scan".

Step 2. Enable SSH service on the NAS server.
Go to "Control Panel > Terminal & SNMP" to check the "Enable SSH service" box. Then view and remember the port for remote access open Deep Data Recovery and click "Next".
Step 3. Connect to the NAS server remotely.
This software will detect your IP and Port automatically. All you need to do is input the user name and password. If the IP address or Port is not right, you can correct it manually. Then, click "Connect Now".

Step 4. Recover lost/deleted NAS data
Then, Qiling data recovery software will connect to your NAS and start a NAS device scanning. After the scan, you will see all the deleted, lost, or existing files on your NAS server.
You can apply the "Filter" feature or click the "Search files or folders" option to find the lost files on the hard drive. Select wanted NAS files that you lost on the server and click "Recover" to save them to another location.
Click the "Recover" button to restore deleted NAS files.

Method 2. Turn to Qiling Manual Data Recovery Service
If you have difficulty restoring NAS/RAID data, you can ask experts to help you. Qiling also provides you with data recovery services. Read on to get more details.
Consult with Qiling data recovery experts for one-on-one manual recovery service. We could offer the following services after FREE diagnosis. Our decades-experienced engineers are knowledgeable and can repair the damaged RAID structure and restore data from all RAID levels.
- Restore data from all RAID levels, including RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, etc.
- Recover data from enterprise RAIDs such as QNAP, Synology, WD, Buffalo, etc.
- Retrieve lost RAID data caused by any issues
- Fix disks that become GPT protected partitions
- Recover data from RAID remotely, no need to ship
Conclusion
Now you have known the basics about broken RAID recovery. You can select the Qiling NAS data recovery software mentioned above to start RAID recovery. It's a powerful data recovery tool for everyone to retrieve lost, formatted, or deleted data.
Related Articles
- Unformat USB | Free Download USB Unformat Tool to Recover Data from Formatted USB
- How to Recover Permanently Deleted Excel File in Windows 10, Mac, iPhone, and Android
- Recover Deleted Files Windows 10 | 6 FREE Ways
- Free PDF Recovery: Recover Deleted, Unsaved, and Corrupted PDF File