Resize Dynamic Disk to Extend or Shrink Dynamic Disk
PAGE CONTENT:
- Why Need to Resize Dynamic Disk?
- Resize Dynamic Disk by Disk Management
- Resize Dynamic Disk by Qiling Partition Master
- Another safe way to resize dynamic disk
- Everything You Want to Know About Dynamic Disk
Why Need to Resize Dynamic Disk?
Resizing a dynamic disk is useful for maximizing computer performance by making efficient use of disk space. For instance, if the system volume is running low on space, resizing a larger dynamic volume to free up unallocated space can help extend the system volume, ensuring the computer runs smoothly. This process allows users to optimize their disk space and improve overall system performance.
2 Ways to Resize (Extend/Shrink) Dynamic Disk
Dynamic disks offer high performance, but come with significant drawbacks. They cannot be converted back to basic disks without data loss, requiring deletion of all dynamic volumes first. Additionally, dynamic volumes often cannot be extended, especially the system volume, which can be a major limitation for those needing to increase their disk space.
Here are the two methods to resize a dynamic disk: the traditional Disk Management method and the use of a third-party tool, Qiling Partition Master, which can resize the dynamic disk directly while protecting all data.
Method 1. Manage and resize dynamic disk by Disk Management
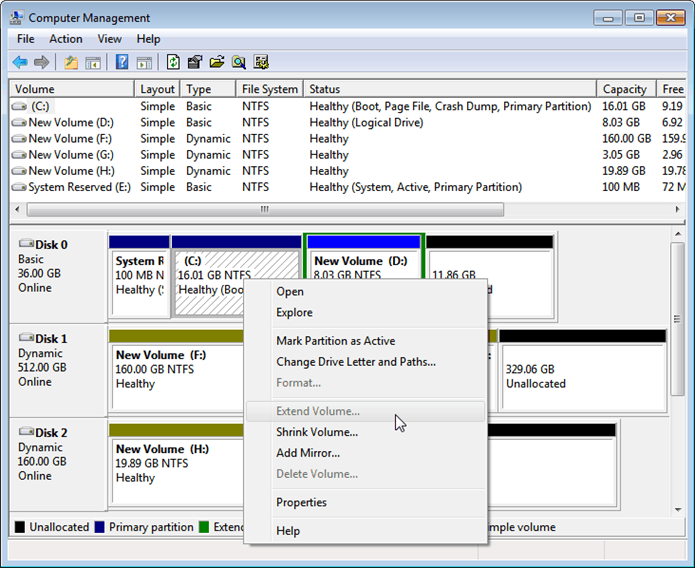
Step 1. Right-click My Computer, select Manage -> Storage -> Disk Management, open Windows built-in Disk Management.
Step 2. Select the volume you want to resize and right-click, choose "Extend Volume" or "Shrink Volume" to resize the dynamic disk.
Step 3. Type the volume size that you want to resize in MB. Then click Next.
Step 4. Click Finish and you will find the dynamic volume has been resized.
The limitations of resizing dynamic volumes in Disk Management before Windows Vista included.
| Features | Windows 2000 | Windows Server 2000 | Windows XP | Windows Server 2003 |
| Extend system volume/boot volume | - | - | - | - |
| Extend/shrink simple volume | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Extend/shrink spanned volume | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Extend/shrink mirrored volume | - | - | - | - |
| Extend/shrink striped volume | - | - | - | - |
| Extend/shrink RAID-5 volume | - | - | - | - |
To extend the simple volume which was converted from the basic disk of Windows XP/2003 that was upgraded from Windows 2000, ensure the disk is not in use, open the Disk Management console, identify the simple volume, and note its current size and free space. Select the unallocated space and right-click to extend the volume, following the on-screen instructions in the Extend Volume Wizard.
In Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, or Windows Server 2008, Disk Management has limitations when resizing dynamic volumes, including resizing.
| Features | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Windows Server 2008 |
| Extend/shrink system volume/boot volume | Y | Y | Y |
| Extend/shrink simple volume | Y | Y | Y |
| Extend/shrink spanned volume | Y | Y | Y |
| Extend/shrink mirrored volume | - | - | - |
| Extend/shrink striped volume | - | - | - |
| Extend/shrink RAID-5 volume | - | - | - |
Method 2. Manage and resize dynamic disk by Qiling Partition Master
Qiling Partition Master is a better replacement for Disk Management when it comes to resizing dynamic disks, which have limitations in Disk Management. This software can perform various dynamic disk management operations, making it a more reliable option.
- Extend dynamic volume, including system/boot/simple/spanned/striped/mirrored/RAID-5 volume, to maximize computer performance.
- To free up disk space, you can shrink a dynamic volume, which includes system, boot, simple, spanned, striped, mirrored, and RAID-5 volumes. This process allows you to reclaim unused space on your disk, making it available for other uses.
- Convert dynamic disk to basic disk without losing data.
- Copy dynamic volume, including system/boot/simple/spanned/striped/mirrored/RAID-5 volume.
- To manage a dynamic volume, you can delete it, explore its contents, check the file system on it, and defragment it. This allows for various maintenance and troubleshooting tasks to be performed on the dynamic volume.
- Convert FAT dynamic volume to NTFS file system
- Repair RAID-5 volume when it failed.
Repair RAID-5 volume when it failed.
Step 1. Locate the Target Partition
To extend a partition, select the drive/partition you want to adjust and choose "Resize/Move" in the Disk Management page.
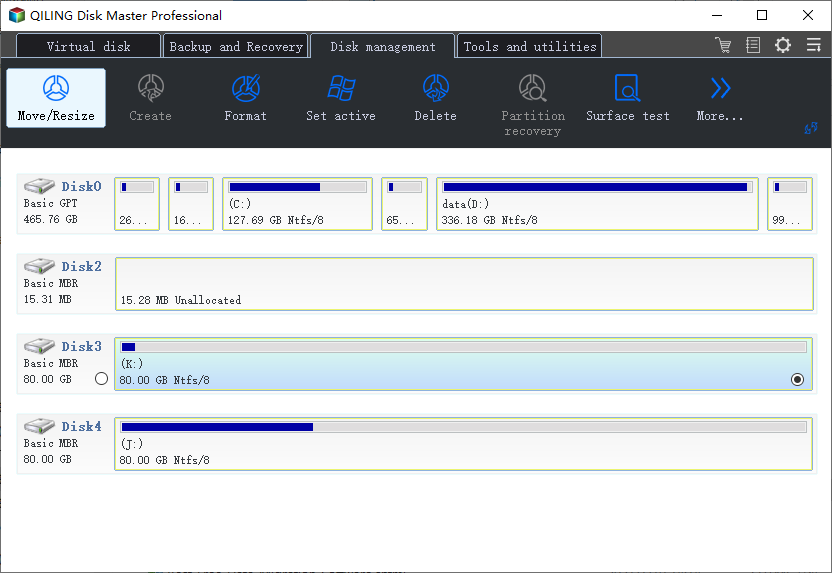
Step 2. Extend the Target Partition
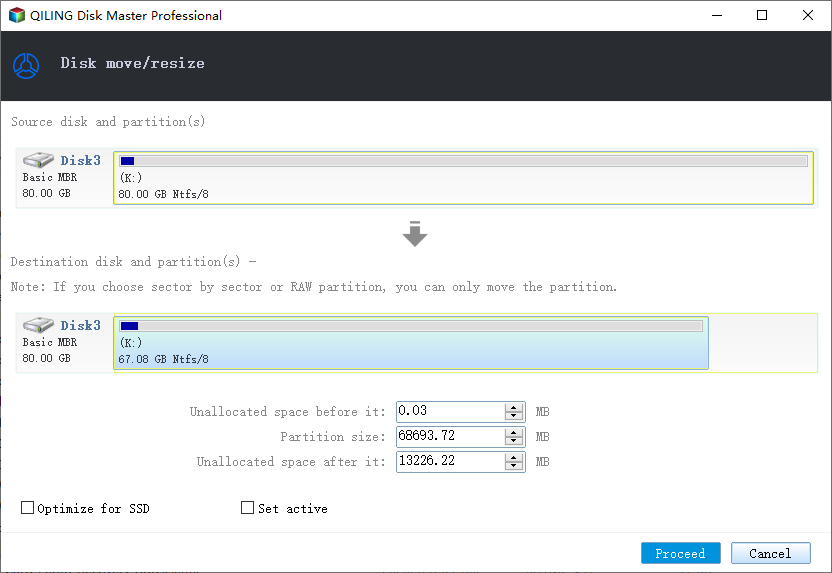
To shrink a partition, you can simply drag one of its ends to free up unallocated space and click "Proceed" to start the resizing process.
To extend a partition, ensure there is unallocated space available. If not, create some. Then, drag the mouse into the unallocated space and click "Proceed" to resize the partition.
To move a partition, you need to have unallocated space next to the target partition. If there isn't any, free up some space first. Then, drag the whole partition left or right to adjust its position and click "Proceed" to start the move.
Another safe way to resize dynamic disk
To resize a dynamic disk partition, you can either resize the dynamic volume or convert the dynamic disk to a basic disk and resize the partition directly. This approach allows for safe and efficient resizing.
Converting a basic disk back to a dynamic disk can have different outcomes depending on the specific dynamic volume configuration. The process is generally straightforward, but the results can vary significantly depending on the initial setup.
After resizing the Simple Volume on a basic disk, you can easily convert the basic partition back to a Simple Volume in Disk Management without any issues.
To convert a Mirrored Volume back after being converted to a basic disk and resized on a basic disk, first convert it to a Simple Volume in Disk Management, then add a mirror with another dynamic disk.
Qiling Partition Master does not support Striped, Spanned, or RAID 5 volumes, but you can copy these volumes to a basic disk, resize the basic disk, and then convert them to a simple or mirrored volume. To do this, refer to the step-by-step instructions on copying dynamic disks.
Everything You Want to Know About Dynamic Disk
A dynamic disk is a physical disk that offers features not available in basic disks, such as support for volumes spanning multiple disks, and uses a hidden database to track dynamic volume information.
Windows 2000 introduced the Logical Disk Manager and diskpart command-line tool for dynamic storage, supporting simple, spanned, and striped volumes.
Dynamic disk applies to the following Operating Systems. Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, and Windows Server 2012 all support dynamic disks. However, Windows 11 does not support dynamic disks.
| Operating System | Simple, Spanned, and Striped Volume | Mirrored Volume | RAID-5 Volume |
| Windows 2000 Professional | | - | - |
| Windows 2000 Server | Y | Y | Y |
| Windows 2000 Advanced Server | Y | Y | Y |
| Windows XP Home | - | - | - |
| Windows XP Professional | Y | - | - |
| Windows Server 2003 Standard | Y | Y | Y |
| Windows Server 2003 Enterprise | Y | Y | Y |
| Windows Vista Home Basic | - | - | - |
| Windows Vista Home Premium | - | - | - |
| Windows Vista Business | Y | - | - |
| Windows Vista Enterprise | Y | - | - |
| Windows Vista Ultimate | Y | - | - |
| Windows Server 2008 | Y | Y | Y |
| Windows 7 Starter | - | - | - |
| Windows 7 Home Basic | - | - | - |
| Windows 7 Home Premium | - | - | - |
| Windows 7 Professional | Y | Y | - |
| Windows 7 Enterprise | Y | Y | - |
| Windows 7 Ultimate | Y | Y | - |
Conclusion
Qiling Partition Master offers advanced features to manage hard disks, including partition management, and additional tools such as a Partition Recovery Wizard for recovering deleted partitions and a Disk & Partition Copy Wizard for upgrading or backing up disks.
Basic knowledge of Dynamic Volume:
A simple volume is a type of volume in a dynamic disk that occupies only one disk space, but can be expanded to a spanned volume, which allows it to use space from multiple disks.
A spanned volume is created from free disk space that is linked together from multiple disks, with a maximum of 32 disks allowed. Unlike other types of volumes, a spanned volume is not fault-tolerant and cannot be mirrored, making it less reliable than other options.
A striped volume, also known as RAID-0, stores data across multiple disks in a striped pattern, balancing disk reads and writes for improved performance. This allows for faster data access and processing, as the load is distributed across several disks.
A mirrored volume, also known as RAID-1, is a replication of logical disk volumes onto separate physical hard disks in real-time, ensuring continuous availability. It's a complete logical representation of separate volume copies, requiring at least two dynamic disks to create. If one disk fails, data can still be accessed from the remaining disk, providing redundancy and minimizing downtime.
RAID-A RAID-5 volume is a type of fault-tolerant storage that spreads data across three or more disks, with parity also distributed across the array. If one disk fails, the lost data can be reconstructed from the remaining data and parity, allowing the RAID-5 volume to be repaired.
Related Articles
- Extend C Drive or Increase Partition Size on Windows Server 2008
- 2021 Qiling Partition Master Crack + Serial Key Free Download [New]
- How Do I Use DiskPart to Delete All Partitions in Windows? Your 2021 Guide Is Here
- Diskpart Delete Server Partition: Get Solutions to Delete Recovery Partition
- Partition Clone Guide | Clone EXT4/EXT3/EXT2 Partitions in Windows 10
- Fix Windows 11 Update Stuck at 0%, 100% on Your Own - Qiling