Which of the Following Commands Can be Used to Create Partitions on Either a MBR or GPT Hard Disk? - Qiling
When you search questions - The command used to create partitions on either an MBR or GPT hard disk is parted. This command can be used to create, resize, and delete partitions on both MBR and GPT formatted hard disks. The other options, gdisk, cfsck, and fdisk, are also used for partitioning but have specific limitations - gdisk is used for GPT, cfsck is used for checking file system integrity, and fdisk is used for MBR.
1. Fdisk
2. Gdisk
3. Parted
4. cfsck
1. Fdisk
What is fdisk?
fdisk is a command-fdisk is a line utility for managing disk partitions in Linux, allowing users to create, delete, and resize partitions, set attributes, and view existing partition information. It is typically used on new or unused disks but can also modify existing partitions with caution. fdisk can be invoked with the -l argument to display detailed information about a specific disk or partition, such as fdisk -l /dev/sda for the first hard disk. However, it should be used carefully to avoid data loss and its usage should be consulted in the documentation.
How to Create Partition with fdisk Command (On Linux)?
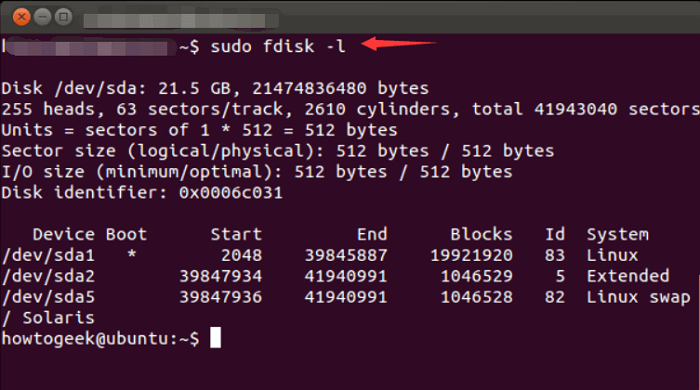
Step 1.Enter the `sudo fdisk -l` command to list the existing partitions on your system.
Step 2. Type sudo fdisk /dev/sda to access command mode.
Step 3.To add a new partition using single-letter commands, you would use the 'n' command. This command is used to create a new partition. For example, you would type 'n' and then enter the partition number to create a new partition.
Type n first - create a new partition
Select partition number
type first sector as 3622912 and last sector as +2GB.

Step 4. To write the changes on disk, you can continue to type the w command. This will save the modifications you've made to the file and update the file on disk.
Step 5. Run sudo fdisk -l to check partition is created.
2. Gdisk
What Is gdisk?
gdisk is a free, open-The gdisk command-line utility is a powerful tool for managing disk partitions, allowing users to create, resize, delete, and format partitions, as well as convert between different partitioning schemes. It also supports dynamic disks and GUID partition tables (GPTs), the newer standard for disk partitioning. With more options and flexibility than fdisk, gdisk is a versatile utility available for Windows, Linux, and macOS, developed by Rod Smith.
Gdisk is used to create partitions on a GPT (GUID Partition Table) hard drive, but not on a traditional MBR (Master Boot Record) hard drive.
How to Use gdisk to Create GPT Partitions in Linux?
Note: The following steps will erase all saved data. Please make a backup if you need it.
Step 1. Enter sudo gdisk /dev/sdb.
Step 2. Type n to create a new partition.
P.S. If you want to manage partitions (not just create partitions), you can type the question mark to get a list of all commands.
Some commonly used command lines:
c - Change partition name
d - Delete partition
p - Print partition table
I - Check partition type
q - Quit utility but not saving changes
t - Change the type code of partitions
w - Write the table to disk and exit
3. Parted
parted is a disk partitioning and partition resizing program used to create, delete, resize, check, and copy partitions, including primary and secondary partitions, and can resize NTFS partitions without data loss. It is available for GNU/Linux, BSD, macOS, and Windows, and is free software licensed under the GNU General Public License (GPL).
How to Create A Partition Using Parted Command?
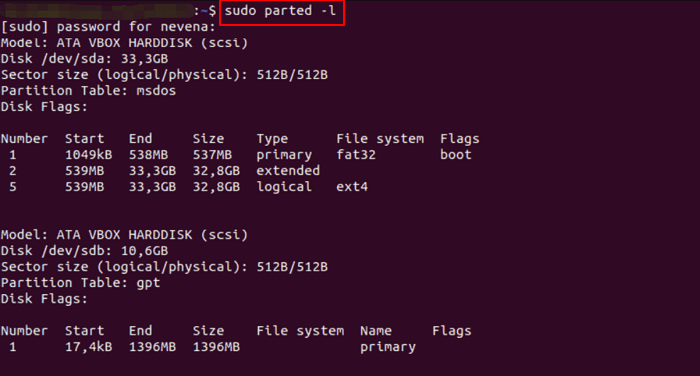
Step 1. To list the existing partitions, run the command `sudo parted -I` in your terminal. This will display a list of all the partitions currently present on your system.
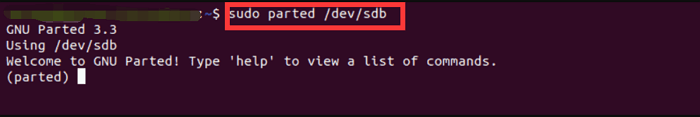
Step 2.Enter `sudo parted /dev/sdb` to open the hard disk that you want to manage partitions.
Step 3. Enter mklabel * to set partition table (* stands for the partition table type, such as mklabel gpt) and type Yes.
Step 4. Run print command to check the partition table.
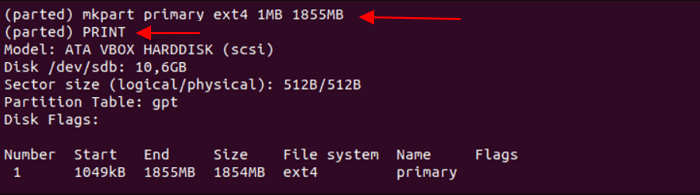
Step 5. The command `mkpart primary ext4 1MB 1855MB` creates a partition on the device, and then you can verify the partition information by typing `print`. This command is used to create a partition with a specific file system type (in this case, ext4), and it specifies the start and end points of the partition (1MB and 1855MB, respectively). The `primary` keyword indicates that this is a primary partition, which is a partition that is directly accessible by the operating system.
Step 6. Enter quit command to save changes.
4. cfsck
cfsck is a utility used to check the consistency of a Unix file system, often employed to repair file systems after an unclean shutdown. It scans the file system to recover lost or damaged data and can also fix common issues like incorrect file permissions. However, cfsck should only be used on unmounted file systems, as it may cause further damage to a mounted file system. It's part of the e2fsprogs package and commonly included in Linux distributions.
The command `fdisk /dev/sdb1` is not related to creating partitions, so you can skip this command.
More Easier Solution: Use Partition Creator Software
If you need to create a partition on your Windows computer, Qiling Partition Master Free is a reliable alternative to the built-in Disk Management or Diskpart. With this software, all operations can be completed in a straightforward and hassle-free manner.
Download free disk manager:
Step 1. Launch Qiling Partition Master. Right-click on the unallocated space on your hard drive or external storage device and select "Create" from the context menu.
Step 2. Adjust the partition size, file system (selecting the file system based on your specific needs), label, and other settings for the new partition, then click "Proceed" to proceed with the process.
Watch the video tutorial to learn how to create a partition in various file systems, including NTFS, FAT, and EXT, and discover the step-by-step process for achieving this.
Related Articles
- BitLocker Partition: How to Partition A BitLocker Drive on Windows 10
- Slow Boot Time! SSD Taking Long Time to Boot in Windows 11/10
- How to Reformat a Hard Drive in Windows 11/10 and Mac [2022 Guide]
- [Fixed] Windows Resource Protection Found Corrupt Files but Was Unable to Fix Some of Them