What Is GPT Disk and How to Manage GPT Disk
PAGE CONTENT:
- What Is GPT Disk
- Features of GPT
- GPT vs. MBR, Which Is Better
- How to Convert MBR Disk to GPT
- How to Partition GPT Drive
- FAQs about GPT Disk
This page is dedicated to teaching you about GPT disks, including their main features and differences with MBR disks. If you're new to GPT disks, this is a great place to start. You'll learn what a GPT disk is, its key characteristics, and how it compares to MBR disks. If you're looking for a straightforward way to convert or partition a GPT disk, you'll find helpful solutions here.
What Is GPT disk?
GPT, or GUID Partition Table, is a standard layout for partition tables on computer storage devices like hard drives and solid-state drives. It's part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) standard and also used in some BIOS systems, replacing the limitations of master boot record (MBR) partition tables.
The traditional GUID Partition Table (GPT) scheme consists of a primary GPT partition table, normal partitions, and a secondary GPT partition table, all contained within a GPT disk.
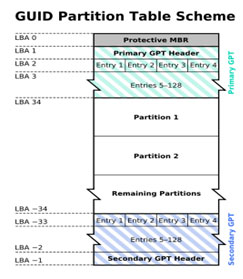
The GPT disk layout can be complex for some users to understand. To help visualize it, we've added a GPT disk layout image to provide a clearer understanding of how the disk is organized.
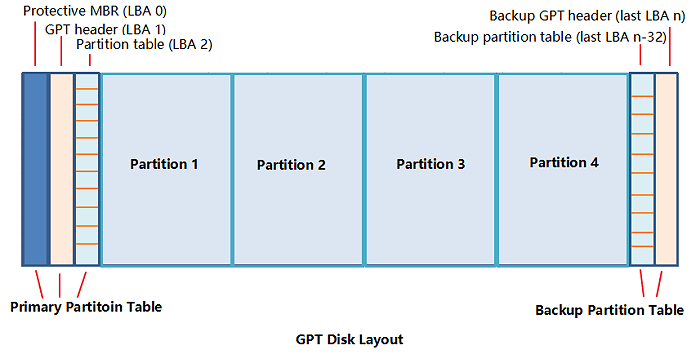
A GPT disk contains three parts: the Protective MBR, the GPT Header, and the GPT Partition Table. The Protective MBR is a placeholder MBR that prevents the disk from being accidentally formatted as a traditional MBR disk.
- The Primary Partition Table is a crucial part of a computer's storage system, containing the Master Boot Record (MBR), Global Partition Table (GPT) header, and partition table. This information is essential for the system to load and access existing partition data, making it possible to boot up the computer and access stored files.
- Normal Data Partitions are the physical locations where your data and personal files are saved, which includes your desktop, documents, pictures, and other personal files.
- The Backup Partition Table is a section on GPT (GUID Partition Table) disks that stores a backup of the GPT header and partition table, ensuring data integrity in case the primary partition table is lost or damaged.
Advanced Features of GPT Disk
GPT disks offer several advantages over MBR, including a more flexible disk partitioning mechanism. This allows for greater flexibility and capabilities, including support for larger disk sizes, more partitions, and improved error handling. Overall, GPT disks provide a more robust and efficient way to manage disk storage.
1. GPT with UEFI replaces the clunky old BIOS with MBR partitioning system.
Every GPT partition has its own unique identifier.
2. GPT breaks the limits of MBR.
GPT disks have a much larger storage capacity than MBR disks, allowing for an unlimited number of partitions, with a maximum of 128 partitions on a system disk.
3. It's easier to recover data from a GPT disk.
GPT disks store multiple copies of partitioning and boot data across the disk, making recovery easier if data is corrupted, unlike MBR which stores it in one place.
4. GPT can check if its data is intact.
GPT (GUID Partition Table) stores CRC values to ensure data integrity. If data becomes corrupted, GPT can detect the issue and attempt to recover the data from a backup location on the disk.
A GPT disk outshines MBR in terms of data protection and partition management, offering greater flexibility and security. If you're wondering which is better between GPT and MBR, a detailed comparison is available to help you decide.
GPT vs. MBR, Which Is Better?
From the following comparison table, you can clearly see the differences between GPT and MBR disk. The advantages of GPT disks are apparent.
| Comparison | MBR | GPT |
|---|---|---|
|
Disk storage space |
Maximum of 2 TB |
Greater than 2 TB |
|
Number of partitions |
4 primary partitions or 3 primary partitions +1 extended partition can be created on a hard drive, but there is no limit to the number of logical partitions within an extended partition. |
128 primary partitions |
|
Firmware interface |
BIOS | UEFI |
|
Operating systems |
Windows 7 and older versions |
Windows 10 32-bit, Windows 8/8.1/10 64-bit |
|
Security details |
Once a partition table in the Master Boot Record (MBR) is corrupted, data retrieval becomes impossible. |
GPT provides greater reliability due to replication and cyclical redundancy check (CRC) protection of the partition table and data. |
To maximize the use of a large disk, it's recommended to convert it to GPT partition style, allowing for more efficient use of the disk space.
The GPT disk can be either basic or dynamic, and its file system can be FAT or NTFS.
How to Convert MBR Disk to GPT?
If you've learned about the differences between MBR and GPT disks, you may want to switch your current MBR disks to GPT. To make this process easier, consider using professional GPT partition manager software, such as Qiling Partition Master, to manage your GPT drive with ease.
Step 1. Download and launch Qiling Partition Master on your Windows computer.
Step 2. Click the MBR disk that you want to convert.
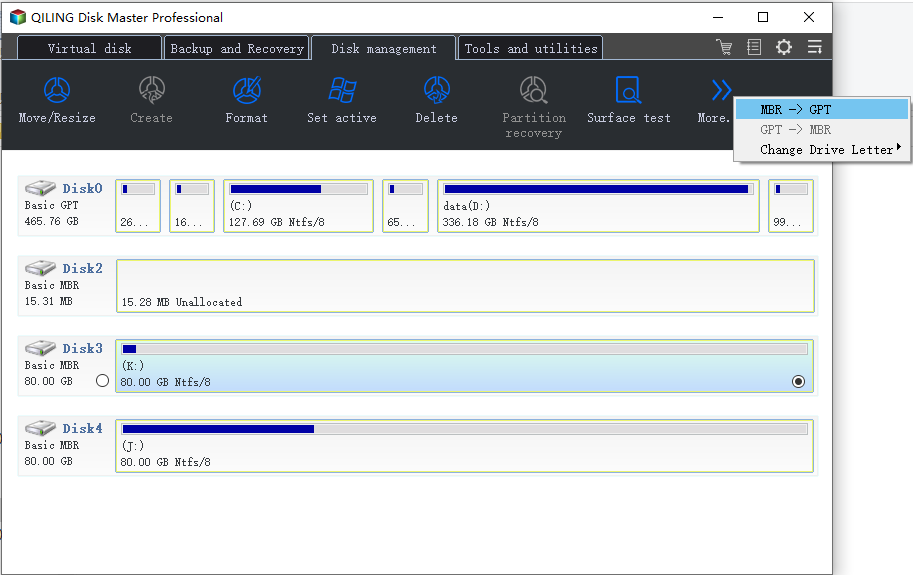
Step 3. Click "More..." and click "MBR -> GPT" to convert partition.
How to Partition GPT Disk?
A GPT disk allows for various operations, including creating, resizing, merging, and formatting partitions. With the aid of a reliable partition manager like Qiling Partition Master, more advanced tasks can be performed, such as migrating an OS from an HDD to an SSD, converting a basic disk to a dynamic one, and converting primary and logical partitions.
To safely manage your GPT disk, you can use Qiling Partition Master to complete various disk management tasks, such as resizing partitions, converting MBR to GPT, and more. This software allows you to easily and safely complete these tasks, including resizing partitions, converting MBR to GPT, and other disk management jobs.
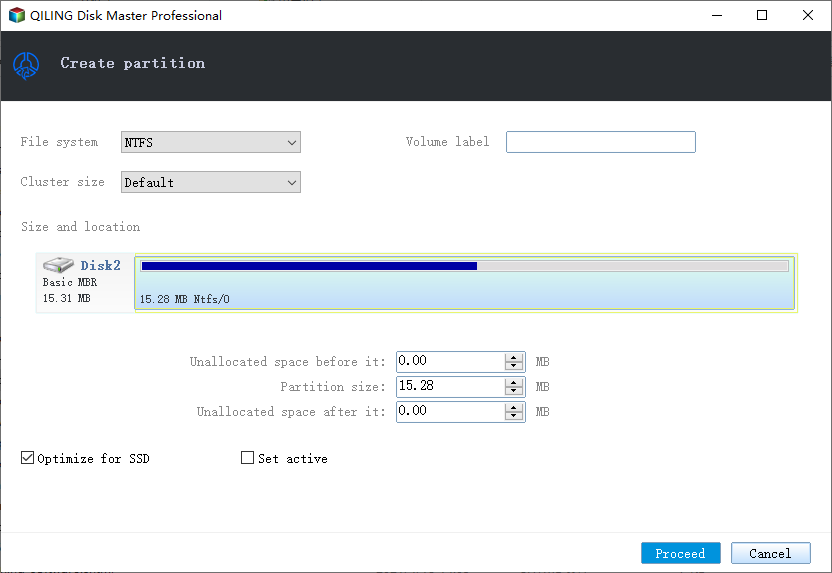
Step 1. Launch Qiling Partition Master, click on the unallocated space on your hard drive or external storage device, and select "Create" on the main window.
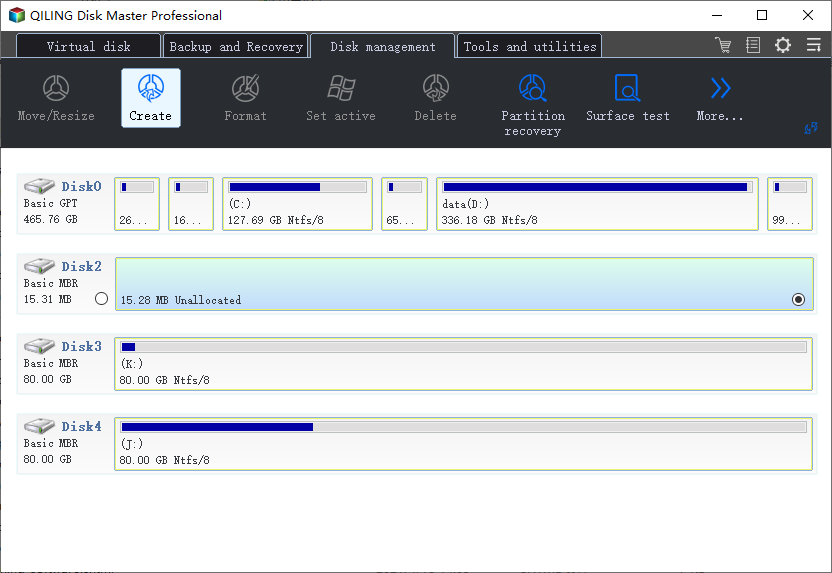
Step 2. Adjust the partition size, file system, label, etc. for the new partition and click "Proceed" to continue.
If you have more questions about managing GPT disk, check the listed questions and answers in the next part.
FAQs about GPT Disk
Many people have questions about managing their GPT disk, such as how to check their disk partition style, which is the best for an SSD, and other related concerns. Apart from the provided information and solutions on managing GPT disk, we also find that many people have doubts about how to check their disk partition style, which is the best for SSD, etc.
I'm sorry, but I don't understand what you're asking. Could you please provide more context or clarify your question?
1. How do I check my disk is GPT or MBR?
To check the disk partition style on Windows, open Disk Management, locate and right-click on the target disk, select Properties, and then check the Disk Information under Volumes. This will show you whether the partition style is GPT (GUID Partition Table) or MBR (Master Boot Record).
2. Should I use MBR or GPT for SSD?
When setting up a new SSD, many users are unsure whether to use the MBR (Master Boot Record) or GPT (GUID Partition Table) partition style. The answer depends on your specific needs, but generally, GPT is recommended for most users. GPT offers several advantages over MBR, including support for larger disk sizes, more partitions, and better error handling. Additionally, GPT is the default partition style for most modern operating systems, including Windows and Linux.
- If you plan to use the SSD disk as a system drive, it should have the same partition table type as your current system disk, whether that's GPT or MBR. This ensures a smooth transition of your operating system to the SSD.
- If you plan to use the SSD disk as a game drive, GPT partition style is more preferable.
- If you plan to use the SSD disk as a data disk, creating many partitions on it, GPT is recommended.
3. Is a GPT partition bootable?
A GPT disk contains a primary partition table, which includes the MBR, GPT header, partition tables for loading basic partition information, and entries for existing partitions. As long as the primary partition table remains intact, a GPT partition remains bootable.
If the primary partition table on a GPT disk is damaged, the secondary partition table, which serves as a backup, can reload the partition information and entries, allowing the disk to load all partitions and display data even if the primary table is compromised.
Related Articles
- How to Clone Server Hard Drive on Windows Server
- Best Windows Schedule Backup Software for Automatic Backup
- One for All Guideline: How to Format/Reformat A Hard Drive
- Partition Magic Software Free Download with How-To Tutorial [Full Guide]
- Computer Is Running Slow? Causes and Fixes Are Found! [Your Ultimate Guide]
- Beginner Geek: Everything about Disk Partition Explained